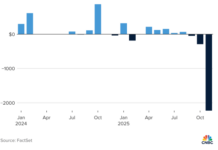
The real GDP growth rate of the world economy in 2023 is estimated to be around 2.9-3.2%. Although many economies have released their third quarter 2023 data, a more accurate figure will have to wait until the end of February 2024, when the fourth quarter 2023 data is published. Thus, compared to the previous forecast, the global economy has shown some improvement, largely due to better-than-expected results in the US and India.
GLOBAL ECONOMIC OUTLOOK: MORE SHADES OF GRAY
However, 2024 will be a challenging year for the US, the EU, and China. The biggest risk still revolves around the impact of high and persistent inflation. While inflation has shown signs of peaking and is gradually decreasing, the core inflation remains high and is still far from the target inflation.
Major central banks such as the US Federal Reserve (Fed) and the European Central Bank (ECB) will face difficult decisions on interest rate cuts: when and by how much. As the Fed acknowledged in its December 2023 meeting minutes, raising interest rates quickly and aggressively could be somewhat excessive.
Meanwhile, geopolitical risks are not only decreasing but also increasing. New instabilities in the Gaza Strip, the Red Sea, tensions between the US and China over the Taiwan issue, and the Russia-Ukraine war could create new instabilities, affecting the global economy. The results of the November 2024 election in the US will also have a major impact on the global economic and political situation in case the Republican Party wins this time.
Global trade decreased by 8% in 2023 due to polarization and protectionism. The fragmentation of the global economy could cause losses ranging from 2.5-7% of global GDP. Ongoing industrial policies in the US and Europe will lead to far-reaching consequences for global trade and foreign direct investment.
CHINA’S ECONOMY LOSING MOMENTUM
Weak domestic demand due to weak purchasing power from Covid-19, de-risking trends between China and the West, real estate crisis, large debt in the economy, and ineffective policies (common prosperity policy) have slowed down the Chinese economy and showed clear signs of losing momentum.
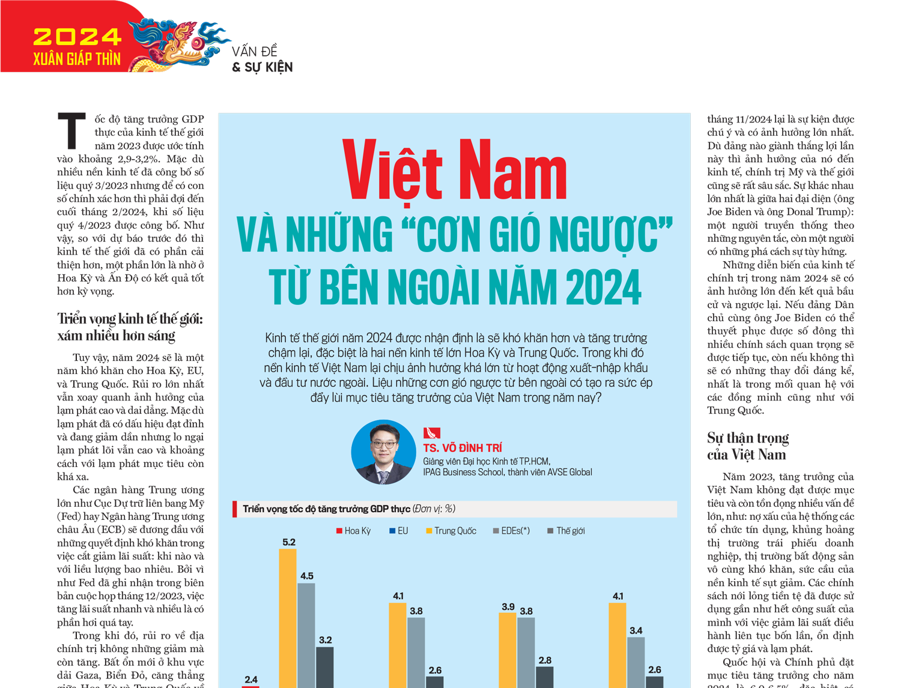
According to The Conference Board, China can only grow by about 4.1% in 2024 and decrease to 3.9% in 2025. Meanwhile, OECD is more optimistic, projecting China’s growth rates at 4.7% and 4.2% respectively.
However, China’s growth is trended downwards regardless. In the long run, China’s potential growth in the 2025-2030 period is 4.1% and the 2031-2036 period is 3.7%. The factors contributing to growth such as capital, labor, and TFP are all slowing down. Notably, the most significant slowdown comes from labor.
China used to be very optimistic about its growth forecasts compared to Germany, Japan, and South Korea, but China’s demographic structure is much less favorable than those countries, as when it started, the average age of its labor force was already high.

Despite significant improvements in the quality of Chinese labor, it is still challenging to compensate for the aging population. In addition, population control policies have also left consequences to this day, such as the “sandwich generation” issue and gender imbalance in the workforce.
The employment situation of Chinese youth and a significant portion of young workers seeking opportunities abroad is a headache for policymakers. Unemployment or unstable jobs among young workers hinder domestic spending, which in turn has an impact on the domestic real estate market. The issue of young workers going abroad to work will have consequences in the future when they return with the burden of social security due to old age and frailty.
IS US FALLING INTO RECESSION?
The US economy will experience a significant decline in 2024, but there is hope for a soft landing or mild recession in the first half of the year. The impact of tightening monetary policy to combat inflation has shown effectiveness as workers’ incomes have slowed, savings have decreased, and the labor market has become more relaxed.
With a growth rate of only 0.9% in 2024 compared to 2.4% the previous year, this is a serious decline. The hope for a soft landing is that inflation has been controlled, and the Fed will proceed to lower interest rates. However, the unpredictable factor is when and by how many percentage points the interest rate will be lowered since there are many other important factors besides monetary policy, such as the labor market, consumer sentiment, and market confidence index.
Many countries will hold leadership elections in 2024, but the US presidential election in November 2024 will be the most important and influential event. Regardless of which party wins, its impact on the US and global economy and politics will be profound. The biggest difference lies between the two representatives (Joe Biden and Donald Trump): one is traditional and principled, the other is unorthodox and capricious.
The economic and political developments in 2024 will have a significant impact on election results, and vice versa. If the Democratic Party, along with Joe Biden, can convince the majority, many important policies will continue, whereas if not, there will be significant changes, especially in relations with allies and China.
VIETNAM’S CAUTION
In 2023, Vietnam’s growth did not achieve the target and encountered many major issues, such as bad debts in the credit system, the corporate bond market crisis, extremely challenging real estate market, and declining economic demand. Loose monetary policies have been almost exhausted, with continuous interest rate cuts four times, stable exchange rates, and inflation.
The National Assembly and the Government set a growth target of 6.0-6.5% for 2024, with a particular emphasis on prioritizing growth over macroeconomic stability. However, given recent negative developments in the international economic and political situation, targets and policies need to be flexible and adaptive, with an approach based on Objectives and Key Results (OKR) instead of Key Performance Indicators (KPI).
Growth is necessary, but the quality of growth and quality of people’s lives are equally important. The driving forces behind growth are capital, the quality of capital, labor, the quality of labor, and total factor productivity (TFP). Therefore, in the short-term, if growth is desired, important contributions from fiscal policies and attracting quality foreign investment should be considered.
Compared to many other economies, Vietnam still maintains high growth momentum, being among the group of emerging and developing economies, a significant driving force of the world economy. Resource allocation through policies, therefore, needs to be carefully calculated to capture the rebound of the global economy in the second half of 2024. In a challenging context, where everyone faces difficulties, it is still an encouraging result to have fewer difficulties.
(*) The author is currently a lecturer at the University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City, IPAG Business School, member of AVSE Global
The full content of the article is published in the Vietnam Economic Review Vol.7+8-2024, released on February 12-25, 2024. Please find it here
https://postenp.phaha.vn/chi-tiet-toa-soan/tap-chi-kinh-te-viet-nam