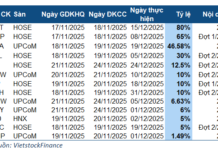
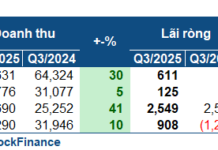
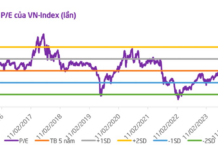
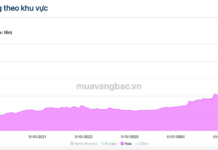
Recently, a Toyota sedan has been listed for sale on social media and has attracted the attention of many people. According to the seller’s information, this is a 2017 Toyota Vios with automatic transmission.
The seller also mentioned that the engine has not been replaced with any external components, ensuring its originality. The seller also suggested that the car is suitable for both family use and as a service vehicle.
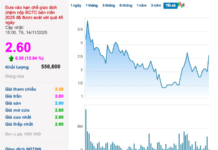
In terms of price, the car is listed for sale in Laos for 135 million VND, and when brought to Vietnam, it will cost around 200 million VND.

The car is listed for sale on social media.
In Vietnam, Toyota Vios is a popular model, known for its durability, spaciousness, fuel efficiency, and ease of use. Upon a quick search on the market, 2017 Toyota Vios cars are being listed for around 350 million VND, depending on the condition of the car. Some special cars are listed for nearly 400 million VND. It’s quite difficult to find listings for cars of the same year below 300 million VND, and there are almost none within the price range of 200 million VND.
The officially distributed Vios models in Vietnam are assembled domestically, with 3 versions available: E MT (manual transmission), E CVT, and G, all using CVT automatic transmission. In 2017, these 3 versions were listed at prices of 564 million VND, 588 million VND, and 622 million VND, respectively.
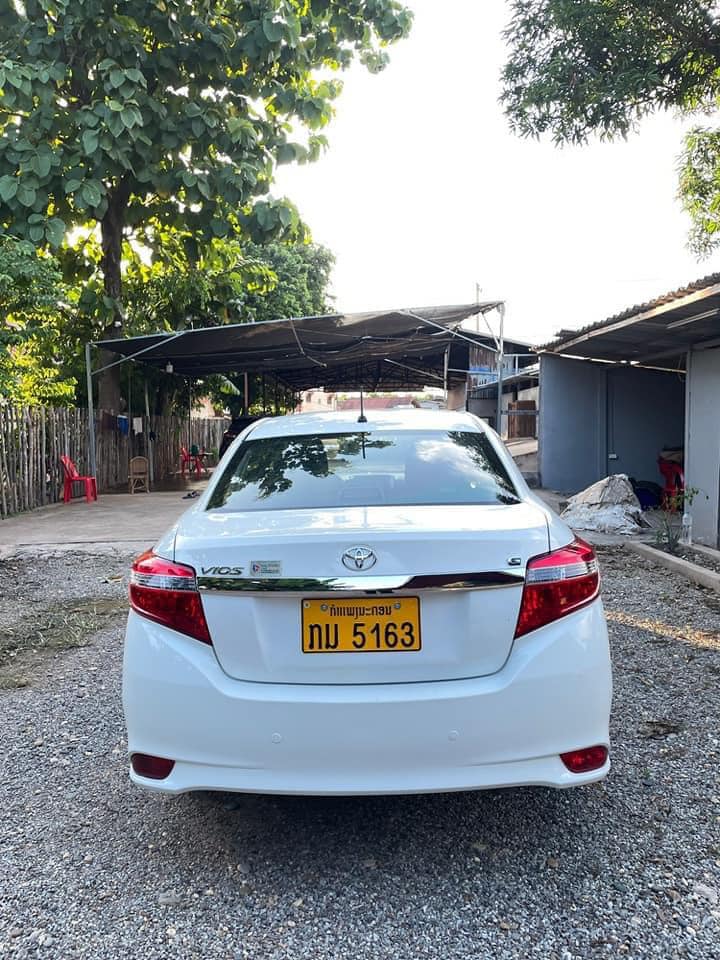




The car is listed for sale at only 200 million VND when brought to Vietnam.
The car listed in the article on social media is the G version and has a Laotian license plate. This license plate has also sparked many debates in the comments section. Many people have recognized that buying the car and changing to a Vietnamese license plate requires a lot of procedures and additional costs. Some suggest a simpler way is to keep the Laotian license plate but regularly complete customs paperwork and inspections in your own country.
Alongside the controversies regarding the inconveniences of buying a car with a foreign license plate, many internet users have also pointed out that the anonymous seller raises doubts.


The post has generated many comments.
The regulations in Vietnam state that foreign vehicles can only participate in traffic in Vietnam for a maximum period of 30 days, with an additional maximum of 10 days in case of force majeure situations such as natural disasters, traffic accidents, or unrepairable damages in Vietnam.
In addition, the car must have sufficient documents such as inspection certificates and valid registration papers issued by the authorized agency in the country of registration. The driver must be a foreign citizen with a passport valid for at least 6 months. When found to stay in Vietnam beyond the prescribed period, the authorities may impose fines ranging from 3 million VND to 5 million VND.