The price of food in 2023 increased due to the influence of the El Nino weather phenomenon and is expected to continue into the first half of 2024. Photo: N.K |
Food prices continue to drive inflation in the first two months of 2024
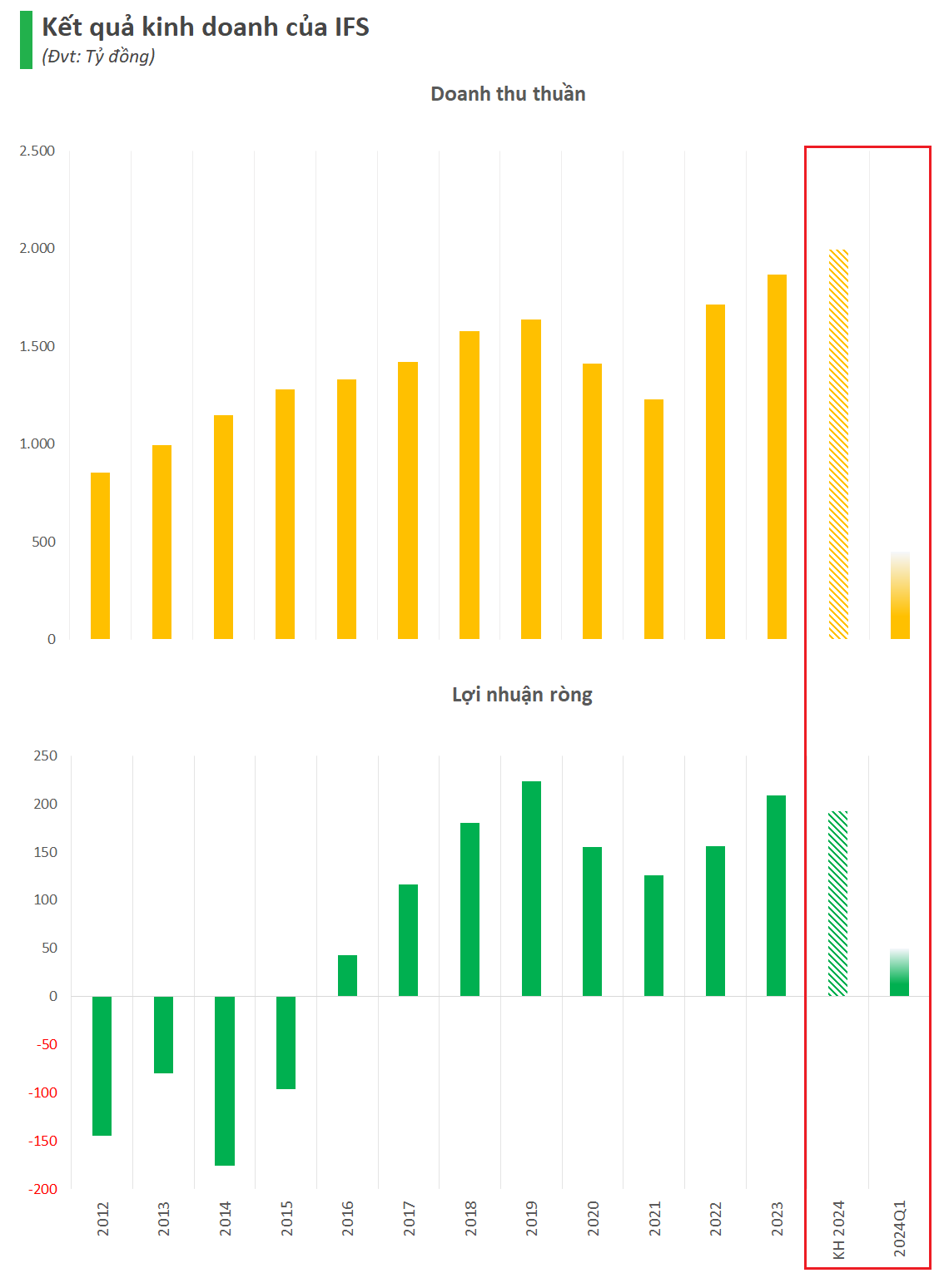
By the end of February 2024, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) increased by 3.67% compared to the same period in 2023; meanwhile, core inflation increased by 2.72%. Looking back at the data from the first two months of 2023, CPI increased by a high rate of 4.6%; while core inflation increased by 5.08% – exceeding overall inflation. Thus, overall core inflation in early 2024 was significantly lower than the previous year and the impact from the monetary factor to the CPI index also cooled significantly.
However, despite the recently published CPI index showing a lower increase than the same period last year and also being affected by seasonal factors, such as the Lunar New Year period, when carefully examining the components in the CPI basket, there are still concerns about the risk of high inflation this year. Specifically, in the CPI composition, the price of food items in February 2024 increased by 17.36% compared to February 2023 and continued to increase by 3.52% compared to December 2023. The average for the first two months of 2024 increased by 16.49% compared to the same period in 2023, which is also the item with the most significant increase in the CPI basket.
Domestic food prices have been trending strongly upward since August 2023. By December 2023, food prices increased significantly by 14.66% compared to December 2022; continued to increase by 1.75% compared to November 2023, and the 12-month average in 2023, this item increased by 6.85% compared to the previous year.
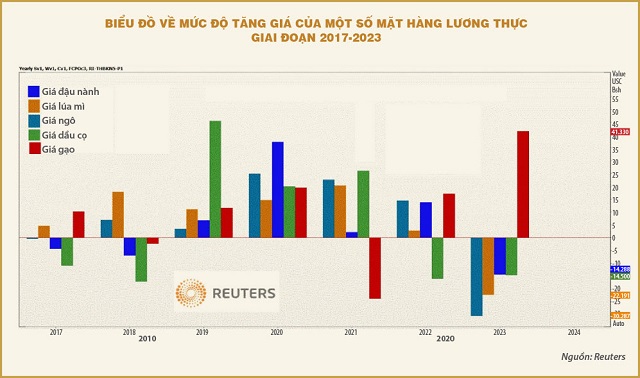
The annual average increase in 2023 was 6.85%; lower than the December increase (compared to the same period last year), as overall food prices only increased slightly in the first half of 2023. Global rice prices, as recorded by Reuters (see chart), hit record highs throughout 2023. The increasing trend of global rice prices has also negatively affected domestic rice prices during this period.
The leading cause of the increase in food prices is believed to be the impact of the El Nino weather phenomenon. The El Nino phenomenon caused drought in most of Asia in 2023, affecting crop production and significantly impacting the supply of food items, especially rice.
This phenomenon is predicted to continue in the first half of 2024, posing a risk to the supply of rice, wheat, palm oil, and other major agricultural commodities in leading global export and import markets. Rice production in Asia in the first half of 2024 is expected to decrease due to the impact of drought on planting and the shrinking of water reservoirs. The global rice supply has already been tightened in 2023 after the El Nino phenomenon reduced production in many places, causing India, the world’s largest rice exporter, to restrict exports.
In 2024, prices of food in the domestic market continue to increase by 1.74% compared to December 2023, maintaining a similar growth rate in the past February. The average for the first two months of 2024, food prices increased by 16.49% compared to the same period in 2023, continued to contribute significantly to the CPI increase of 3.76% in February; higher than the 3.37% increase in January.
Be cautious of inflation in 2024
Therefore, food prices are still on a strong upward trend since the second half of Q3 2023, exerting considerable pressure on inflation. It is highly likely that in the first six to seven months of this year, the figure reflecting the average food prices this year compared to the average of the same period last year will increase significantly, as food prices were relatively low in the first half of 2023. Although the weight of the food group in the CPI basket accounts for only 3.67%, the sharp increase in prices combined with the increase in prices of other goods may make the CPI a difficult-to-predict index this year.
If inflation is at risk of increasing in the coming time, it will put pressure on the State Bank of Vietnam in the effort to maintain a loose monetary policy to stimulate growth, especially in the context where the US Federal Reserve is maintaining high US dollar interest rates and there is no clear signal of rate cuts as previously expected by the market. High and prolonged inflation, if it occurs, can put pressure on the deposit interest rates of banks. Capital can be withdrawn from the system when the difference between deposit interest rates and inflation is low, or in other words, interest rates increase to reflect expected inflation.
In general, at the current period, Vietnam’s macro foundation remains relatively stable. Inflation tends to increase in the first two months, but is lower than the inflation control target for this year at 4-4.5% set by the National Assembly. Exchange rates and interest rates show signs of increase but only in the short term. The interest rate level in the economy is still maintained at a low level, and liquidity in the banking system is relatively abundant. Therefore, monetary policy managers still have time to observe and evaluate the impact of macro variables, especially inflation and exchange rates.
Pham Long