The scale of primary CW issuance is increasing
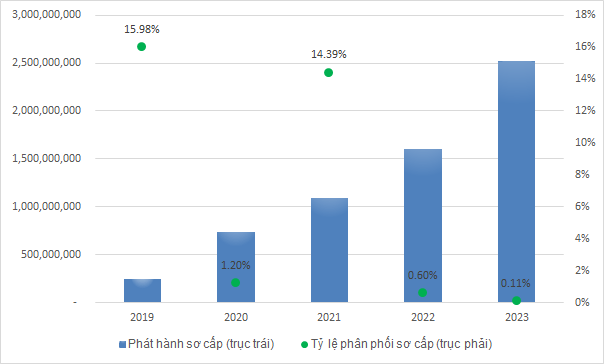
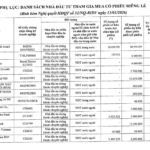
In 2023, the amount of primary CW issuance reached over 2.5 billion CW (by 10 issuing companies), an increase of nearly 60% compared to the previous year. Compared to 2019, the scale of issuance has increased by more than 1,000%, equivalent to 11 times.
Although the primary issuance activity is becoming stronger, the proportion of CW distribution in primary issuances is not high. Out of more than 2.5 billion CW offered in 2023, only over 2.6 million CW were distributed, equivalent to only 0.1%.
Since the market started, the highest distribution rate was in 2019, nearly 16%.
|
The scale of issuance and the rate of buying primary CW in the period from 2019 – 2023
Unit: CW
Source: VietstockFinance
|
Even though investors are not very interested in buying primary CW, why do securities companies continue to issue CW and the scale of issuance is increasing?
We have to consider the method of making profit from CW. Investors who are interested in CW can profit in 2 ways: Holding until maturity and trading.
|
The ceiling/floor prices of warrants are calculated as follows: Warrant ceiling/floor price = Reference price of warrant +/- (Fluctuation range of underlying securities (USF)/Execution rate) Example: Closing price of underlying securities in current trading session: 100,000 VND. Fluctuation range: 7%. Closing price of warrant in current trading session: 5,000 VND. Execution rate: 2:1. Thus, the ceiling price of warrant in the next trading session: 5,000 + (100,000 * 7%/2) = 8,500 VND The floor price of warrant in the next trading session: 5,000 – (100,000 * 7%/2) = 1,500 VND The fluctuation range of the next warrant session is: +/- 70% With such a fluctuation range, investors in trading CW can achieve huge profits. |
With the hold until maturity method, if the payment price of CW is higher than the predetermined execution price, investors will receive a payment in cash for the difference between these two prices.
Regarding trading, it is similar to stocks, but the fluctuation range of warrants is much larger. This makes CW more attractive.
In order for investors to be able to trade CW, the role of securities companies is crucial. According to CW trading regulations, securities companies must create a market so that investors can buy and sell as needed. How can securities companies profit from creating a market for CW?
Earning money from market making business
Speaking of market making, in addition to earning money from issuing CW, securities companies can increase their revenue from market making when buying and selling CW according to investors’ trading needs.
By being proactive in regulating the supply and demand of CW, securities companies can easily choose the most beneficial time and price to buy/sell CW, while also choosing the optimal time to buy/sell underlying securities to gain an advantage in cost, thereby increasing revenue from warrants.
|
Regulations on CW market making by securities companies According to the regulations, the issuing organization, which is the securities company, must create a market to set the buy and sell prices closest to the fair price. Specifically, if the price difference in the market exceeds 5% (the price difference ratio is the percentage ratio of (lowest ask price – highest bid price)/highest bid price), the issuing organization must participate in creating a market within 5 minutes, with a minimum order volume of 100 units, and a minimum order time on the system of 1 minute. In the market making and risk prevention regulations, market makers have cases that are exempt from market making obligations, such as when the price is at the ceiling, floor, the warrant has a profit of 30% or more or 14 days before the expiration date… This means that securities companies can buy if the price is low or sell if the price is high compared to the actual value. |
Therefore, the larger the scale of issuance and market making, the greater the opportunities to increase profit and market share for securities companies. For example, if a securities company issues 1 million CW, assuming daily liquidity is equivalent to 20% of the issuance volume, then in a 3-month period (about 66 trading sessions), the total CW liquidity can reach more than 13 million CW. If securities companies do a good job in market making, they can buy and sell a large amount of CW that is more than 13 times the amount they issued.
Usually, when CW is approaching the expiration date, when the opportunity for underlying securities price fluctuations is narrowing, the demand for investors to sell CW is higher when they want to take profit and withdraw the money instead of waiting until the expiration date. Therefore, the supply of CW in the secondary market will be higher than the demand, leading to lower option prices compared to the calculated theoretical prices.
Securities companies buying CW at this time will have more advantages and more opportunities to make a profit. In addition, securities companies can gradually sell underlying securities which will put pressure on the prices of underlying securities and warrants, creating an opportunity to increase profits from CW products.
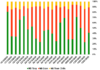
If we delve into the financial statements, the figures from market making with CW are not small.
|
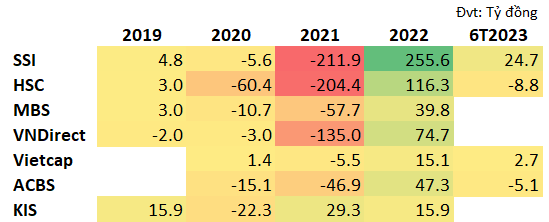
Net profit from self-issued CW buying/selling of securities companies
Source: VietstockFinance
|
In 2022, SSI Securities, HSC Securities recorded hundreds of billions of VND in profit from this activity. Specifically, SSI earned over 255 billion VND, HSC earned over 116 billion VND. VNDIRECT Securities, ACB Securities (ACBS) also recorded high profits, with nearly 75 billion VND and over 47 billion VND respectively.
However, the results of market making activities also depend on market conditions. In 2021, most securities companies suffered large losses from market making with CW.
KIS Securities is a company that has achieved relatively stable profits from buying and selling CW. From 2019 – 2022, the company made a profit for 3 out of 4 years.
In conclusion, securities companies continue to issue CW and increase the scale to provide products for customers; on the other hand, they create conditions to carry out market-making activities and increase revenue.