Binh Duong Province, a vibrant region in Southeast Vietnam, is located north of Ho Chi Minh City. With a rich history and a strategic location, Binh Duong has emerged as one of the eight key economic zones in the country’s southern region.
The province is administratively divided into nine units, consisting of four districts and five cities, with a total of 91 communal-level units, including 39 communes, 47 wards, and five towns. Binh Duong is also the first province in Vietnam to have five directly governed cities: Thu Dau Mot, Di An, Thuan An, Tan Uyen, and Ben Cat.
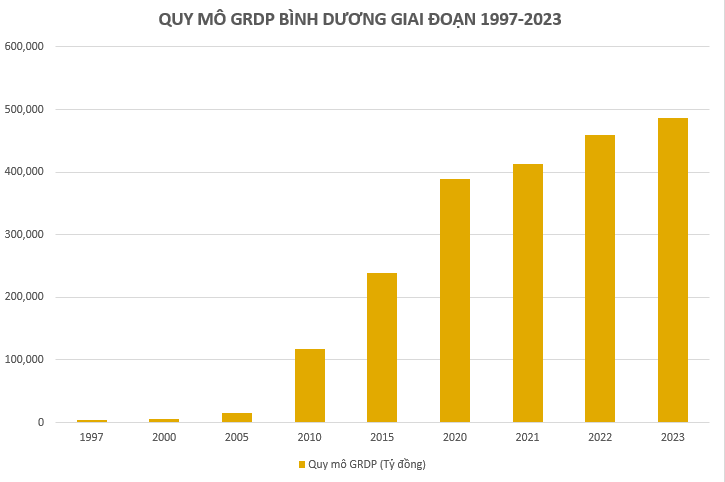
Since its re-establishment in 1997, Binh Duong has undergone a remarkable economic transformation. With a initial modest economic scale of approximately VND 3,919 billion, the province embraced a forward-thinking strategy of prioritizing industrialization and attracting investments into industrial parks (IPs). This visionary approach has paid off, as by the end of 2023, Binh Duong’s economic scale reached VND 486,400 billion, a staggering 124-fold increase since 1997, with a per capita GRDP of USD 7,665.
Additionally, the province’s GDP growth rate for the period 1997-2021 averaged an impressive 10.86%/year. Maintaining this momentum, from 2010 to 2020, Binh Duong’s economy grew at a rate of 8.7%/year, ranking it among the top three provinces with the highest growth rates, alongside Ho Chi Minh City and Dong Nai, and outpacing the national average of 5.6%.
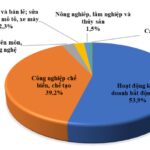
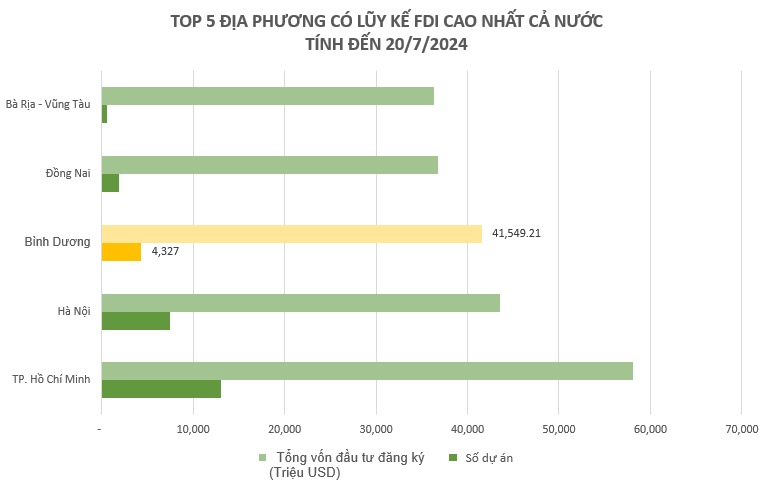
Binh Duong has earned a reputation as Vietnam’s foremost “Industrial Capital.” With a long history of industrial development, the province’s industrial sector reached a scale of VND 276,000 billion in 2021, making it the largest in the country. Binh Duong also boasts being one of the top three destinations for foreign investment in Vietnam. As of July 2024, the province ranks third nationwide in attracting foreign investment, with 4,327 projects and a total investment capital of USD 41.5 billion.
Source: Ministry of Planning and Investment
One of the standout features of Binh Duong’s industrial sector is its ability to attract major corporations as key tenants. Many multinational corporations have chosen Binh Duong as their production base or have primary contractors within their global production chains located in the province. This has facilitated a deeper integration of Binh Duong’s industries into the production chains of these multinational corporations, including well-known names such as Nike, Adidas, P&G, Unilever, and Suntory Pepsico.
In terms of trade, the Provincial People’s Committee reports that the province’s export situation during 2019-2021 was generally positive, although the growth rate was slightly more modest than the national average. Specifically, the total export value of goods from Binh Duong increased at an average annual rate of 12%, rising from USD 25.3 billion in 2019 to USD 31.5 billion in 2021, compared to the national growth rate of 13% during the same period.
In 2023, Binh Duong’s merchandise trade balance is estimated to have a surplus of USD 8,782.1 million. This surplus is comprised of a surplus of USD 2,454.8 million in the domestic economic sector and a surplus of USD 6,327.4 million in the foreign-invested economic sector.
Aiming for a Per Capita GRDP of Approximately USD 15,800 by 2030
The provincial planning clearly outlines that by 2030, Binh Duong aspires to become a centrally governed city and one of the most dynamic and comprehensive development centers in Southeast Asia. It aims to be a leader in science, technology, and innovation, with a modern industrial and service-based economy, and a smart, sustainable, and green-growth-oriented infrastructure.
By 2030, Binh Duong is projected to have three cities meeting the criteria for a first-tier city (Thu Dau Mot, Di An, and Thuan An), two second-tier cities (Tan Uyen and Ben Cat), one fourth-tier town (Bau Bang), and three towns meeting the criteria for a fourth-tier city (Tan Thanh in Bac Tan Uyen, Phuoc Vinh in Phu Giao, and Dau Tieng in Dau Tieng). The province also aims to establish new towns in Bac Tan Uyen, Phu Giao, and Dau Tieng, with an urbanization rate of approximately 88-90%.
In terms of economic indicators, the planning sets forth specific targets. From 2021 to 2030, the province aims for an average economic growth rate of about 10%/year, with a per capita GRDP target of approximately USD 15,800 by 2030.
Regarding economic structure, the province envisions that the industry and construction sector will account for 64%, the service sector will contribute 28%, the agriculture, forestry, and fisheries sector will make up 2%, and taxes on products minus subsidies on products will represent 6%. The digital economy is targeted to contribute 30% of the GRDP.
Furthermore, by 2030, Binh Duong aims to have 42 industrial parks (IPs) spanning an area of approximately 18,600-21,000 hectares. This includes the continuation of 33 already planned IPs (comprising 29 established IPs and 4 IPs under preparation for investment), the establishment of 10 new IPs, and the conversion of one IP (Binh Duong IP) in accordance with legal regulations.
Positive Signs in Exports and Imports: Early 2024
Vietnam’s total import-export turnover in January 2024 reached nearly $64.22 billion, representing an increase of 37.7% compared to the same period last year. This positive signal in the trade of goods shows a promising start to the year 2024.