Illustrative Image
Vietnam boasts of a commodity that accounts for 60% of the world’s export volume – pepper. Specifically, the country has been the world’s leading producer and exporter of pepper for over 20 years, accounting for 40% of the harvested volume and 60% of the global export market share. Vietnamese pepper and spices are currently exported to over 120 countries and territories, dominating many important markets.
According to preliminary statistics from the General Department of Customs, Vietnam’s pepper exports in July reached 21,803 tons, valued at over $129 million, a decrease of 22.4% in volume and 8.6% in value compared to the previous month.
As of the end of the first seven months of the year, the country’s pepper export volume exceeded 163,000 tons, with a value of over $760 million, a slight decrease of 2.7% in volume but a significant increase of 40.7% in value compared to the same period last year.
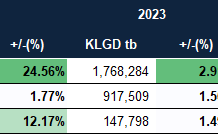
In terms of market destinations, the United States remains Vietnam’s largest importer, with 43,168 tons and a turnover of over $205 million, an increase of 48% in volume and 75% in value compared to the same period last year. Prices also recorded an increase of nearly 20%, averaging $4,755/ton.
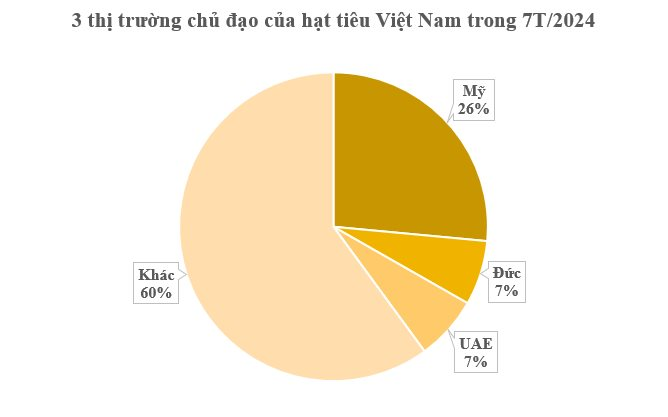
Notably, Germany is aggressively sourcing this commodity from Vietnam, registering the highest increase among the leading markets. In the first seven months, Vietnam exported 11,028 tons of pepper to Germany, valued at over $57 million, a surge of 100% in volume and 152% in value compared to the previous year. The average price reached $5,280/ton, an increase of 26%.
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has emerged as Vietnam’s third-largest customer, importing 10,922 tons of pepper with a turnover of over $55 million, an increase of 40% in volume and a significant surge of 113% in value compared to the same period in 2023. The average price reached $5,085/ton, doubling that of the previous year.
The global pepper market is valued at $5.43 billion per year and is projected to grow at an average rate of over 20% during the period 2024-2032. In addition to domestic cultivation, Vietnam is increasing imports of this commodity from various markets to solidify its leading position in exports.
According to the Vietnam Pepper Association (VPA), prolonged dry weather conditions have led to a 10% decrease in Vietnam’s pepper output this year, amounting to approximately 170,000 tons. This reduction in supply from Vietnam has significantly impacted global prices. In the second quarter of 2024, domestic black pepper prices surged by 93% compared to the beginning of the year and tripled compared to the same period in 2023. Pepper prices are expected to continue rising due to increasing demand and constrained supply.
Forecasts indicate a growing global demand for pepper, with the EU remaining a significant market for Vietnamese pepper. Moreover, Vietnamese businesses possess substantial pepper processing capabilities, with an annual capacity of 140,000 tons, presenting opportunities for the development of the Vietnamese pepper industry in the coming years.
Currently, consumers worldwide are willing to pay a premium for high-quality pepper. Markets such as the US, EU, and the Middle East are increasingly seeking products that meet sustainability standards across social, environmental, and economic dimensions throughout the supply chain.
Experts also attribute the expected price increase in import markets to a supply shortage compared to global demand, coupled with rising freight costs and port congestion in Asia.