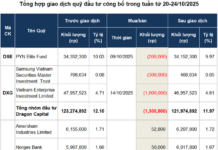
The stock market is a reflection of the economy, but investors are always interested in the most prominent events that have a significant impact on psychology and cash flow. The possibility of the Fed beginning to cut interest rates in September 2024 after three years of maintaining a tight monetary policy is a historic event. We are pleased to present an article by Dr. Nguyen Hong Diep, CEO of VICK Joint Stock Company, on this topic.
Will the US Economy Make a Soft Landing or Fall into a Recession?
The foundation of the free-market economy (American capitalism) is based on Keynesian economics. Keynes was an economist born in the late 19th century. He founded the General Theory of Economics during the Great Depression of 1929-1931. Its foundation is based on Employment, Interest Rates, and Money. Keynes also pointed out that effective demand will prevent recession. In other words, supply is determined by demand. As long as demand increases, production and employment will follow suit, preventing the economy from falling into recession.
So, what are the signs of an economic recession? There are a total of 11 signs, but five are extremely important.
1. Continuous GDP decline. According to modern economic theory, if GDP (US) declines for two consecutive quarters, it is a sign of recession.
2. Sudden weakness in the job market. Among the employment data, the most important is the unemployment rate. If this rate exceeds 5%, it is a dangerous sign. In addition, non-farm payrolls (decreased hourly earnings) and new jobs are also signs of an impending recession.
3. Inverted yield curve for bonds. If long-term interest rates are usually higher than short-term rates, but when this relationship is reversed, it is a sign of economic decline.
4. Increasing bad debt. Recall the time in 2008 when the bad debt of the US banking system suddenly increased, leading to a liquidity crisis, the bankruptcy of the prestigious Lehman Brothers, and the fire sale of real estate.
5. Fiscal and monetary policy conflicts between countries. When there are disagreements on interest rate management among key economies, it is a sign of an impending recession.
In addition to the five main reasons above, there are other signs of an economic recession, such as a weak shipping industry, reduced oil demand, tightened credit conditions, geopolitical tensions, wars, and epidemics.
A crisis is more severe than a recession. Based on the above, it has been determined that a global economic crisis has occurred only three times: 1930, 2001, and 2008. The 2020 pandemic was just a short-term recession due to the unexpected epidemic factor.
So, how is the US economy doing? Despite having to endure interest rate hikes and maintain a tight monetary policy for a long time, the US economy still appears healthy and has not fallen into a recession. Of course, there is always a lag, and policies gradually seep into the economy. All of this needs to be observed and tested through data in the coming months, and it may not be until mid-2025 that we can accurately determine whether the US economy has fallen into a recession or not.
The Role of the Fed
The Fed, or the US Federal Reserve, plays a role in shaping monetary policy and ensuring economic stability. The Fed will balance risks between prices, the job market, and interest rates. Therefore, the Fed will proactively raise or lower interest rates based on inflation and employment data. Of course, the Fed will also have to act to rescue the economy in emergencies during crises or recessions.
Therefore, it is essential to distinguish between two entirely different situations in nature: one is when the Fed acts according to a roadmap, and when certain goals, such as inflation, are achieved, it will start lowering interest rates. The second is when the Fed acts solely because the economy is in a recession or crisis. So, it is not always the case that a Fed rate cut indicates a weak economy that needs support.
When the Fed provides substantial support, it is usually accompanied by synchronized measures such as QE packages. The nature of QE is to inject money from the Fed’s balance sheet. We have witnessed how quickly and drastically the Fed can lower interest rates in previous cycles. Most of these emergency actions tend to sow fear among investors.
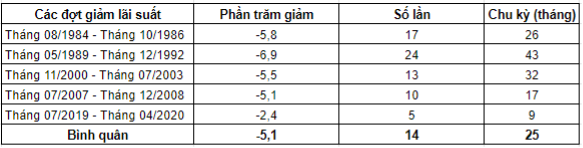
Table 1: Fed Interest Rate Cuts
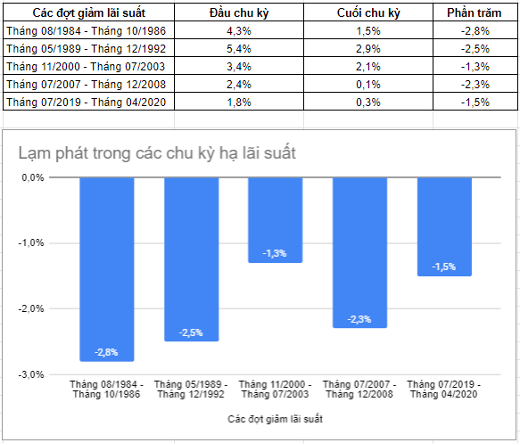
Table 2.1: Inflation during the Rate Cut Cycle
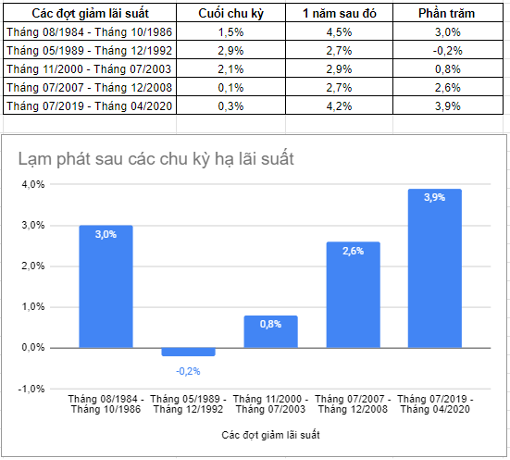
Table 2.2: Inflation after the Rate Cut Cycle (One Year Later)
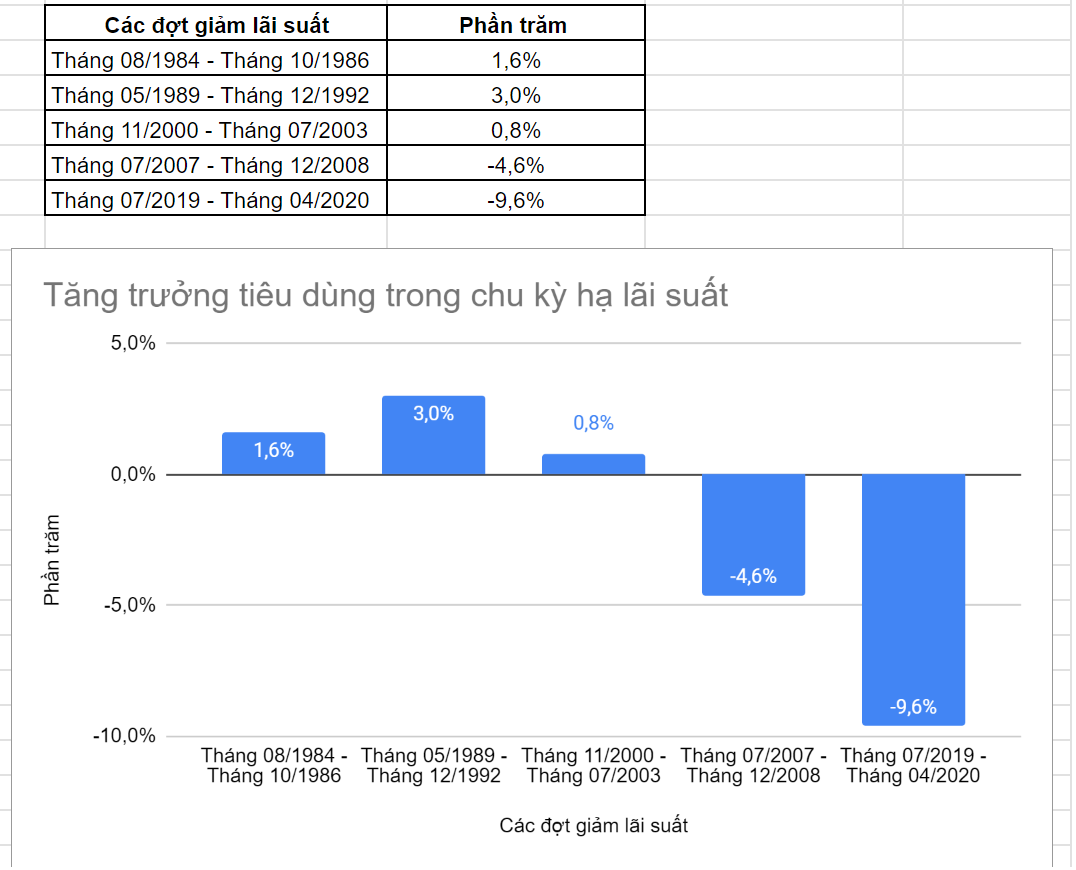
Table 3.1: Consumer Spending Growth during the Rate Cut Cycle
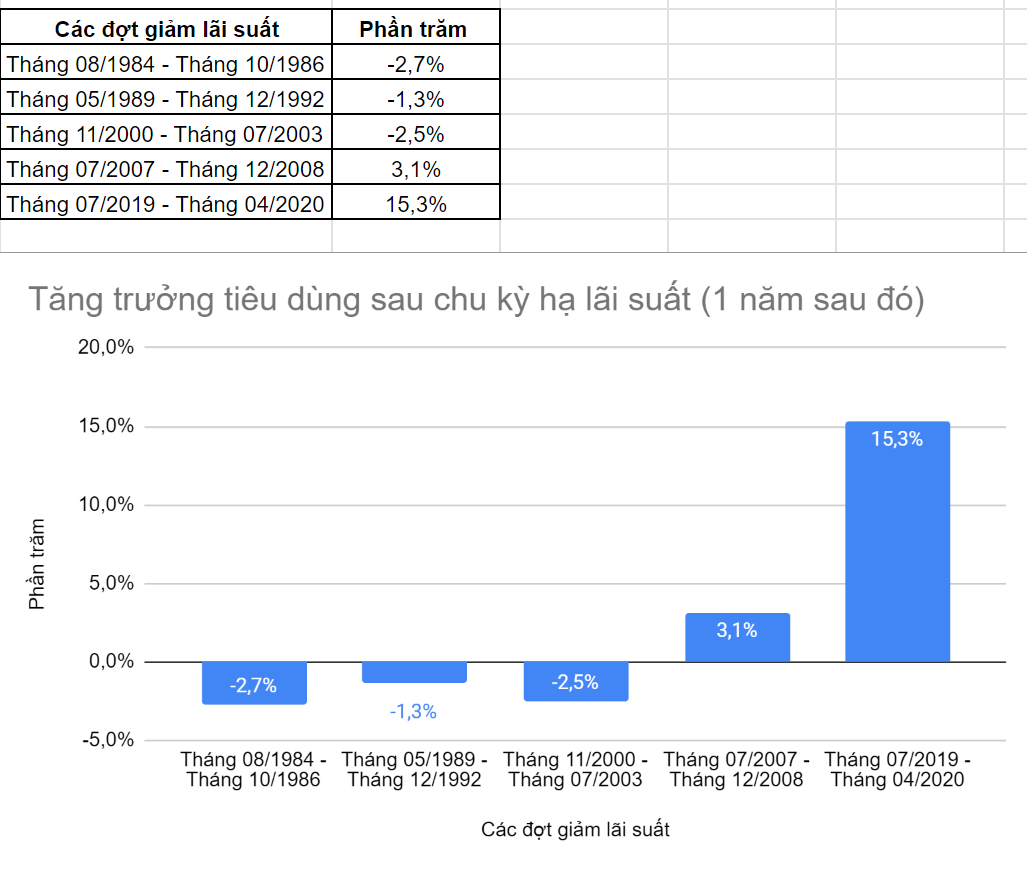
Table 3.2: Consumer Spending Growth after the Rate Cut Cycle (One Year Later)
Stock Market Reaction
According to a report by the American financial services company Charles Schwab, out of the 14 interest rate cycles of the Fed since 1929, 12 rate cut cycles recorded an increase in the S&P 500 index within 12 months after the cuts. The two remaining exceptions occurred after the Fed cut rates in 2001 and 2007. The report states that the economic environment at those two times was different from the present. In 2001, stocks fell amid the bursting of the dot-com bubble. In 2007, the US experienced a subprime mortgage crisis.
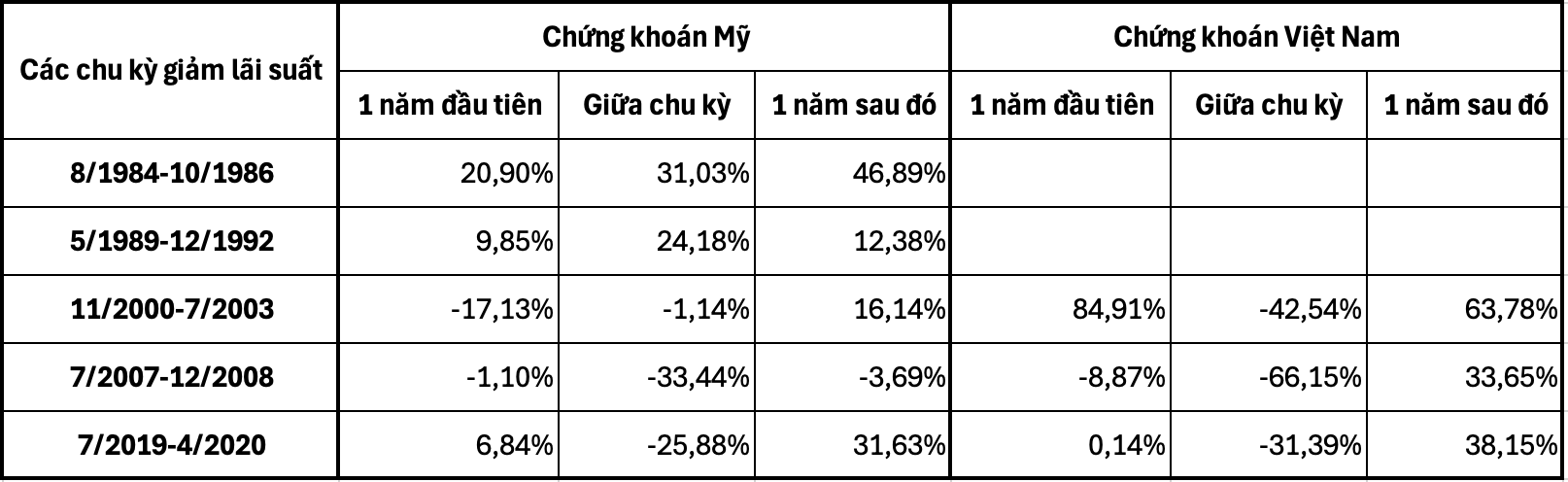
Table 4: Stock Market Reaction to Fed Rate Cuts
As analyzed above, it is crucial to distinguish between rate cuts following a roadmap and emergency rate cuts to rescue the economy. If the economy is stable and only experiencing a slowdown in growth, interest rate cuts will have little immediate impact. It will only react strongly when the economy shows signs of distress.
Analyzing the table above, we observe that, at the beginning of the cycle (one year or six months), stocks rarely fluctuate. In the middle of the cycle, there is often a significant decline, possibly due to investors taking profits. After the rate cut cycle ends and one year passes, stocks tend to surge, as this is when the benefits of cheaper money are fully realized.
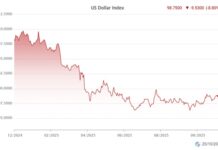
In the current context, it is challenging to predict whether the US economy will fall into a recession. The possibility of a soft landing has been mentioned numerous times by Fed officials and scholars. Interest rate cuts have positive effects that anyone can immediately see, such as weakening the dollar and driving money away from overly safe channels towards riskier investments like bonds and stocks.
The Vietnamese economy is highly open. Global economic impacts, especially from the US, always affect us. In the past, we have witnessed the pressure of rising exchange rates due to a strong US dollar, and this pressure was one of the reasons for continuous net foreign outflows.
Clearly, lowering interest rates will also significantly reduce this pressure. With a stable socio-economic situation, well-controlled inflation, and the potential for market upgrade, it is highly likely that the Fed’s rate cut this time will not negatively affect the Vietnamese stock market.
Overcoming Challenges in Dealing with Bad Debts
In the newly passed Revised Securities Law, securities companies (SCs) no longer have the privilege to hold collateral. Therefore, SCs need to recognize that debt collection is their responsibility, and they should be extremely strict in assessing borrowers, ensuring compliance with principles, procedures, and conditions before granting loans.
Declining profits at Bank increase in 2023
Throughout the year 2023, this bank achieved a pre-tax profit of over 928 billion VND, a decrease of 16.2% compared to 2022 and only 73% of the set plan was accomplished.