1. AI in Retail Banking: Trends, Applications, and Potential
In recent years, AI applications have become a prominent trend in the retail banking industry. Amid this transformative wave, banks globally are investing heavily in AI to enhance customer experiences, optimize operational processes, and improve competitive capabilities, transitioning from traditional retail banking or Digital Bank to AI Bank.
The banking industry is among the sectors with the highest levels of AI development, with 85% of banks having strategies to apply AI in new product and service development. Over 50% of staff are actively using AI in their daily work. It is forecasted that banks’ budgets for GenAI will increase significantly from $6 billion in 2024 to $85 billion by 2030.
The potential for AI applications in banking is enormous as almost all departments can leverage this technology.
In the front office, where direct interactions with customers and core business activities take place, employees are equipped with advanced AI tools to personalize experiences and increase sales effectiveness. These tools also free up time for employees to focus on customers, delivering more comprehensive experiences.
For middle and back offices, which provide support and handle transactions, data management, and systems, AI automates many processes. This not only enhances speed and accuracy, reducing errors and costs, but also allows employees to focus on higher-value activities, thereby improving service quality for customers.
2. Applications and Benefits of AI in Retail Banking
The latest financial forecasts indicate that the adoption of AI in next-generation banking will bring significant benefits to pioneering banks in the next three years, with expected productivity gains ranging from 22% to 30%. Hundreds of AI use cases in retail banking have been explored and developed by major specialized units:
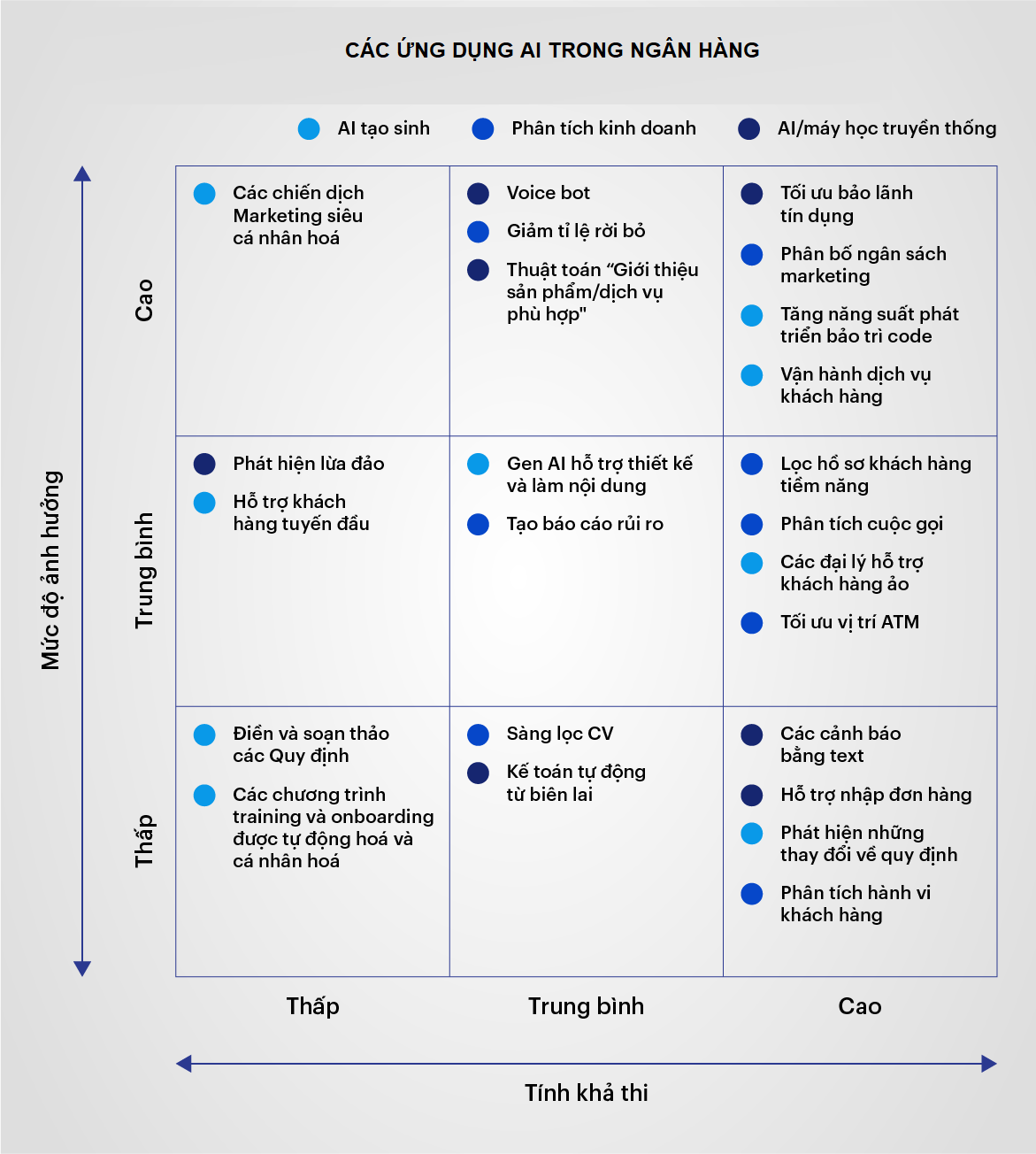
These use cases promise to benefit all areas of banking. Most banks choose to prioritize improving customer service, increasing employee productivity, and developing applications to automate internal processes. Some of the most common applications and their benefits to banks include:
Enhancing Customer Experience
AI systems improve the efficiency of chatbots and virtual assistants, enabling data analysis to understand customer behavior, preferences, and needs. This allows banks to save costs, reduce employee workload, and maintain consistent service quality. AI also automates responses to frequently asked questions and handles basic transactions such as balance inquiries or bill payments quickly and accurately.
Strengthening Security and Fraud Detection
AI uses algorithms to detect abnormal transactions and signs of fraud. The system can monitor and analyze millions of transactions daily, identify risky transactions, and alert employees promptly, safeguarding bank assets and reinforcing customer trust.
According to surveys, 58% of banks currently rely on AI for fraud detection. Research by Javelin Strategy & Research also shows that AI applications reduce fraud cases in the industry by up to 30%.
Optimizing Operational Processes
AI automates various business processes such as loan application processing and credit checks, saving time and operational costs. With its ability to handle data quickly and accurately, AI helps banks cut costs by 20% to 30%.
Developing New Products and Services
AI enables banks to build more precise and effective marketing campaigns by identifying potential customers, suggesting suitable products, and optimizing advertising costs. Research shows that using AI in marketing can increase bank revenue by 10% to 15%. Additionally, AI helps banks better understand customer needs and behaviors, allowing them to develop more appropriate products and services.
Credit Analysis and Risk Assessment
In the past, credit analysis relied on manual methods with basic indicators. Today, AI can handle more extensive and multi-dimensional data, including transaction history, credit information, and financial data from multiple sources, quickly and accurately. This enables banks to conduct more comprehensive credit risk assessments and make informed credit decisions.
AI can also predict customers’ repayment capabilities, helping to minimize risks when granting loans that match their financial capabilities. AI can automatically update and adjust risk models based on new data, ensuring banks always have an accurate assessment of customers’ creditworthiness.
3. Risks in AI Implementation in Retail Banking
To minimize errors, banks need to identify potential risks and their solutions in advance. Some common risks and their management strategies in AI implementation for retail banking include:
Ethical Risks: AI models may have biases due to data quality or user biases. This can lead to discrimination between different customer segments in decision-making.
To address these risks, the following strategies can be employed:
(1) Ensure compliance with AI impact assessments
(2) Develop methods to identify biases
(3) Regularly update models, continuously add data, and improve data quality.
Security and Privacy Risks: Banks may inadvertently violate customer privacy by collecting data for AI model training or predictive algorithms without specific customer consent. This could potentially lead to data breaches.
To mitigate these risks, consider the following strategies:
(1) Incorporate security and privacy requirements in AI model design
(2) Collect customer data only with consent
(3) Maintain strict security protocols throughout AI model operations.
Legal Risks: Regulations may not keep pace with the rapid development of AI. Additionally, banks operating in multiple jurisdictions may face different rules.
To navigate legal risks, consider the following strategies:
(1) Stay updated on legal regulations related to AI
(2) Increase transparency of AI models
(3) Design explainability into AI processes and outcomes, focusing on justifying reasons, responsibilities, data, safety, performance, and impact.
Workforce Risks: AI has the potential to transform the workforce, especially for jobs requiring computational and language skills. Additionally, banks may incur costs for retraining employees to use AI tools to support their work.
To manage workforce risks, consider the following strategies:
(1) Provide AI training and knowledge-sharing sessions for employees to enhance their skills
(2) Utilize AI to support existing jobs and empower employees to make better decisions.
(3) Ensure AI models are collaborative and incorporate human judgment.
Risks of AI Investment on Legacy Infrastructure: Banks that do not invest in upgrading their IT infrastructure may encounter limitations in graphics processing (GPU), network connectivity, memory, and storage capacity. This could lead to risks in AI execution and operations.
To address these risks, consider the following strategies:
(1) Use AI-enabled encryption to accelerate legacy code conversion, software development, and migration, and integrate legacy IT infrastructure.
(2) Invest in higher-performance networks.
4. Recommendations for AI Implementation in Retail Banking
AI implementation in banking should follow a well-defined process to ensure a selective approach that aligns with the bank’s needs. The complexity of AI applications also implies that the journey from idea generation to evaluation, prioritization, and MVP (Minimum Viable Product) development should be an iterative process, guided by competent units, to ensure effective AI utilization.
Conclusion
To effectively leverage AI in retail banking and achieve breakthrough benefits, banks need a clear strategy, investment in technology and human resources, and close collaboration with AI experts and specialized organizations. Effective change management, along with continuous communication and awareness-raising, will enhance understanding and acceptance of an AI-powered banking future.
Reference: Accenture
Compiled by: DTSVN Group – Digital Transformation Solutions for the Financial and Banking Sector.
TPBank’s Strategies Fueling Its Rapid Ascent
As a customer-centric strategy has long positioned TPBank amongst the front-runners shaping the landscape of retail banking in Vietnam, the superior and trendy nature of its products backed by cutting-edge digital banking technology that “anticipates and moves fast,” has also made TPBank the primary transaction bank for many customers.