According to the latest data from the US Geological Survey, the world currently has approximately 4.4 million tons of tungsten, an increase of 600,000 tons from last year (3.8 million tons). The top five countries with the largest tungsten reserves are: China (1.8 million tons), Australia (570,000 tons), Russia (400,000 tons), Vietnam (74,000 tons), Spain (66,000 tons), and South Korea (29,000 tons).
Tungsten is used as an anti-abrasive material in metalworking, mining, oil and gas, and construction industries. It is an irreplaceable metal in a range of industrial applications, including the production of high-performance machines and steel alloys. As a result, tungsten is also utilized in the automotive, energy, construction, aerospace, aviation, and power generation industries.
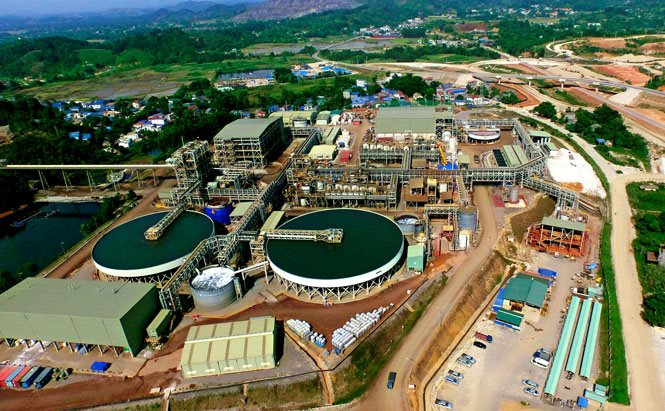
In Vietnam, Thai Nguyen province holds the largest tungsten reserves in the country, accounting for 90% of the national reserves. According to the Dai Tu District’s website in Thai Nguyen province, the output from the Nui Pao mine in Thai Nguyen accounts for approximately 33% of global tungsten production, excluding China, making it the second-largest mine of its kind in the world. This mine is one of the largest identified tungsten reserves outside of China.
Notably, Masan High-Tech Materials (MHT) has mastered the world’s leading tungsten recycling technology, according to the People’s Committee of Thai Nguyen province. By owning this exceptional recycling technology, MHT has identified recycling as a strategic pillar that will bring success in terms of revenue and reinforce its leading position in the global high-tech materials market.
The company has developed and refined a recycling process through research projects and simulation experiments, enabling the complete recovery of lithium, nickel, copper, cobalt, and manganese from discarded batteries. They have also developed specific refining formulas to achieve higher tungsten recovery efficiency.
MHT now possesses a novel recycling technology for sludge containing cobalt and black powder from discarded batteries. This new technology holds the promise of recycling various types of hard cutting tool powders while having a lesser environmental impact than traditional recycling processes. Scientists believe that this technology has the potential to be a “game-changer” for the global recycling market of copper, cobalt, nickel, manganese, and lithium.
These technological achievements enable MHT to move away from natural mineral extraction and embrace a circular business model. This model involves urban waste mining, collection and treatment of production waste, and recycling of scrap materials. End-of-life assets are then transformed into new resources, creating new materials and products.
MHT is working diligently to realize its ambition of building a tungsten recycling plant, positioning Vietnam as a leading global supplier of high-quality and sustainable tungsten. The company is collaborating with its subsidiary, H.C. Starck (Goslar, Germany), to develop the first and largest tungsten recycling plant in Asia, located in Vietnam.
The technology for the tungsten recycling plant in Thai Nguyen will initially be provided by H.C. Starck, one of the few companies with exclusive patents and a comprehensive and environmentally friendly tungsten recycling foundation. The technology is continuously improved and innovated to develop environmentally friendly processes based on world-leading research and development experience in Germany, as well as research activities in Vietnam.
Masan Realizes Retail Consumer Opportunities, Shifts Focus for Profitable Growth
On May 30, 2024, Masan High-Tech Materials (MHT), a publicly traded company on the UPCoM exchange under the ticker symbol “MSR,” announced that it had entered into a sales contract with the Mitsubishi Materials Corporation Group (MMC Group).