The banking sector demonstrated continued stability and growth in Q3 2024, thanks to flexible governance measures from the State Bank of Vietnam (SBV). Circular 06, with its provisions on debt restructuring and maintaining loan classifications, provided significant support to the financial system in the past period in maintaining stable non-performing loans and limiting provisioning costs. However, the non-extension of Circular 06, expected by the end of 2024, will usher in a new chapter in risk management, putting pressure on banks to strengthen their internal capabilities to ensure long-term stability.
Financial Health Update from CAMELS Ratings
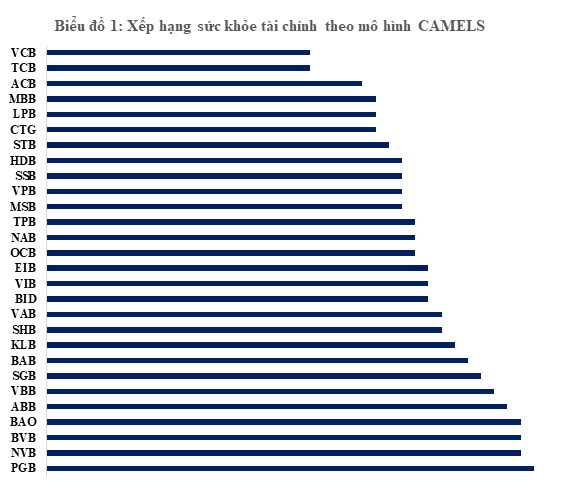
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the banking sector’s financial health, insights from the CAMELS model provide valuable information. We will rely on the ratings of banks by Yuanta Securities applying the CAMELS model to assess the performance and risk levels of commercial banks. This model encompasses six key factors: Capital Adequacy, Asset Quality, Management Quality, Earnings, Liquidity, and Sensitivity to Market Risk. Each factor is assigned specific weights and scores, forming a comprehensive scoring system for comparing performance across banks.
According to Yuanta’s scoring convention, lower scores reflect better financial health, stable profitability, and lower risk, while higher scores indicate areas for improvement. This ranking method combines quantitative and qualitative analysis to ensure objectivity and accuracy. Firstly, the system utilizes data from audited financial statements and periodic reports from the SBV to ensure reliable information. Secondly, the company applies historical analysis and forecasting, not limited to past data but also leveraging econometric models to predict future financial performance. This allows for an assessment of not only current health but also the ability to cope with potential fluctuations.
Source: Yuanta Vietnam
Note: Lower CAMELS scores indicate higher rankings |
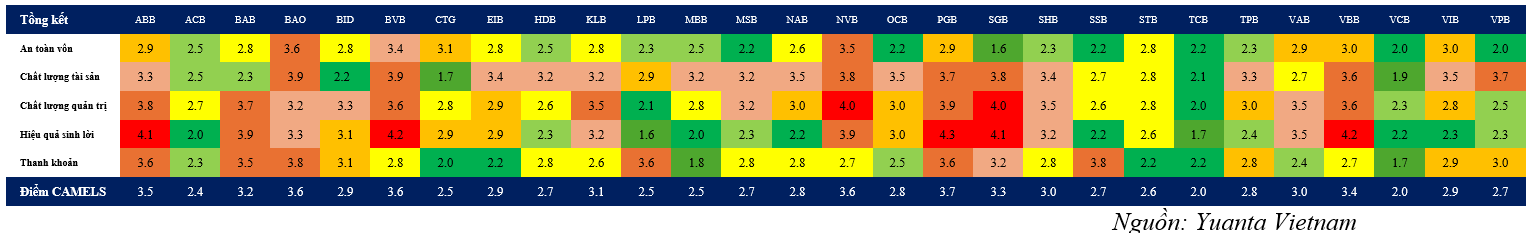
The Q3 2024 CAMELS ratings revealed a distinct performance differentiation among banks. Vietcombank maintained its leading position due to its strong equity ratio and high-quality assets, while large private banks like Techcombank and MB Bank excelled in the Earnings factor through their credit portfolio optimization and CASA ratio enhancement strategies. A notable highlight in this ranking was the significant improvement in Vietinbank’s financial health, reflected in its robust business results in recent quarters. It sustained healthy credit growth while maintaining a stable NIM, unlike other banks that experienced a decline.
On the other hand, small-scale commercial banks were ranked lower due to the pressure of increasing non-performing loans and limited liquidity. Notably, the Sensitivity to Market Risk factor is becoming more critical in the context of volatile interest rates and exchange rates. This trend underscores the necessity of enhanced risk management and maintaining reasonable provisions to ensure financial stability in the coming periods.
Chart 2: Details of Financial Capability Ratings of Banks
 |
Financial Health Expected to Improve with the End of Circular 06
Net interest income for banks in Q3 2024 increased by 17% year-on-year due to improved lending activities and lower funding costs. Stable credit growth, coupled with flexible monetary policies from the SBV, enabled banks to optimize profits. Vietcombank and MB stood out with high net interest income growth, positively contributing to the after-tax profits of the entire system. Notably, retail and small business segments drove the growth in net interest income during this period.
The NPL ratio for the industry remained at 2.26% in Q3, a slight increase from Q2, indicating that banks effectively managed their asset quality. Vietcombank continued to lead with the lowest NPL ratio in the system at 1.22%, attributable to its effective risk management strategies and enhanced provisioning. Although the industry’s NPL ratio increased slightly from the beginning of the year, this increase was within expectations and did not exert significant pressure on banks’ balance sheets. The stability of asset quality led to a considerable reduction in risk provisioning in Q3 2024, facilitating robust growth in pre-tax profits. This reflected not only improved control over non-performing loans but also a positive signal for financial prospects in Q4 and the full year 2024.
The SBV’s decision not to extend Circular 06 demonstrates confidence in the stability of the banking system and the quality of assets. Banks will face new challenges without the support provided by this Circular, but it also presents an opportunity for institutions to strengthen their risk management capabilities, self-regulate their credit activities, and build a more robust foundation.
The expiration of Circular 06 may cause some short-term fluctuations in the market. However, it also creates attractive opportunities for investors, especially in high-quality bank stocks like ACB, HDB, and VCB. These banks, with their high provisioning rates, are likely to benefit from reduced provisioning in the future, thus improving profitability. Looking ahead to 2025, banks such as Techcombank and VPBank are expected to continue their growth trajectory due to their ability to expand credit and the recovery of the real estate market. The business environment is anticipated to stabilize, enabling the banking sector to sustain long-term growth.
The Vietnamese banking sector in Q3 2024 exhibited positive signals with stable asset quality and robust profit growth. However, long-term success will hinge on agile risk management capabilities and adaptability to changes in the legal environment. The decision not to extend Circular 06 will present new challenges for the banking system but also opens up opportunities to enhance operational efficiency and strengthen market confidence.
“Renowned Expert Pham Chi Lan Unveils Four Common Weaknesses of Vietnamese Entrepreneurs: The Misguided Belief that Exporting is Superior to Domestic Market Conquest.”
The vast openness of the market has turned Vietnam into a ‘red ocean’ in numerous industries. Renowned economist Pham Chi Lan asserts that domestic competition is now fiercer than ever, even more so than international competition.
“Interest Rates: Sustaining Stability to Support Economic Growth”
The macroeconomic stability and consistent results, coupled with the growth in deposits and credit expansion, attest to the effectiveness of the State Bank’s monetary and credit policy framework and its implementation. This solid performance is a testament to the State Bank’s successful navigation of the economic landscape, fostering an environment conducive to business growth and financial stability.
What is a Credit Score?
Credit scores are a familiar term in finance, but for those who have never borrowed money, it may be an unfamiliar concept.