The 8% growth target faces challenges
In February 2025, the government proposed to the National Assembly to adjust the growth rate of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2025 to 8% and above. This is higher than the target set by the National Assembly at its meeting three months ago at 6.5%, along with a target inflation rate of 4.5-5%.
According to the government’s proposal, the basis for achieving this target includes:
• Promoting public investment and FDI: The government plans to have the total social investment capital in 2025 reach about $174 billion, equivalent to 33.5% of GDP. Of which, public investment is about $36 billion (VND 875,000 billion), an increase of VND 84,300 billion compared to the plan in 2024. Private investment is expected to reach $96 billion, and FDI about $28 billion.
• International trade: Vietnam aims to achieve a trade growth rate of about 12% in 2025, with an expected trade surplus of $30 billion. In 2024, exports grew by 14.3%, while imports increased by 16.7%, resulting in a trade surplus of $24.77 billion.
• Ensuring financial stability and controlling inflation: The government aims to maintain inflation at 4.5-5%, ensuring macro-economic stability and creating favorable conditions for production and business activities.
This is a notable adjustment reflecting the government’s ambitious economic stimulus plan for 2025, serving as a springboard for the “double-digit growth” target mentioned by Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh at the end of 2024.
However, TPS believes that achieving the 8% target will be challenging due to the following reasons:
Global economic fluctuations: According to the United Nations, global economic growth is expected to reach 2.8% in 2025, unchanged from 2024. This is lower than the average of 3.2% during 2010-2019, reflecting weaknesses in investment, labor productivity, and mounting financial pressures. OECD also forecasts global growth of 3.3% in 2025, with the Eurozone growing by only 1.3%. This poses significant challenges for Vietnam’s exports, especially in industries such as textiles, electronics, and agriculture, which rely heavily on major markets like the US and Europe. The average forecast for Vietnam’s GDP growth in 2025 by prominent organizations remains around 6.5%. If US President Donald Trump restarts the trade war, particularly with China, it could disrupt global supply chains. An escalation of trade tensions may hinder Vietnam’s exports due to new tariff policies and put pressure on domestic production costs.
USD/VND exchange rate may reach 26,000: The strength of the US dollar could reduce Vietnam’s appeal to international investors, making FDI inflows more cautious. This is especially true if the Federal Reserve delays its interest rate reduction plan.
Inflationary pressures and rising production costs: Inflation in Vietnam is still largely influenced by input costs and logistics expenses. Currently, logistics costs in Vietnam account for about 16.8% of GDP, higher than the global average of 10.6% (according to the Vietnam Logistics Business Association – VLA). The recent upward trend in fuel prices and transportation costs is adding pressure to the inflation target.
TPS believes that achieving the ambitious 8% growth target will be challenging. However, Vietnam can still aim for a growth rate of 6.5% – 7% (the initial target), and the new goal signifies the government’s strong commitment to prioritizing economic growth in 2025.
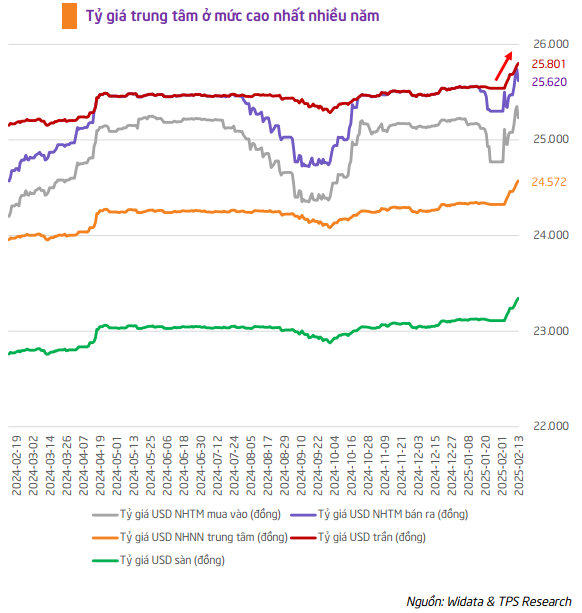
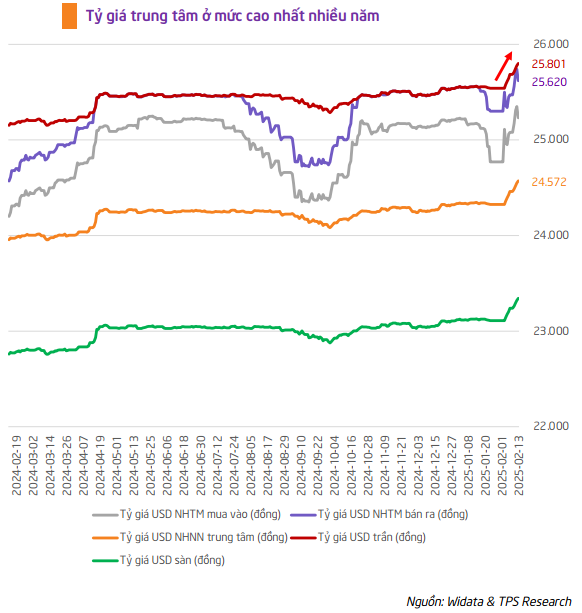
USD/VND exchange rate may reach 26,000 by year-end
The financial market is witnessing a strong upward trend in the USD/VND exchange rate since the end of 2024. The rate is currently at its highest level in many months, with the State Bank of Vietnam’s (SBV) central exchange rate reaching 24,572 VND/USD. Some commercial banks have even offered rates as high as 25,740 VND/USD.
TPS predicts that the USD/VND exchange rate will continue to face upward pressure in 2025 and may reach 26,000 VND/USD by the end of the year due to strong external factors.
One of the most significant influences on the USD/VND exchange rate is the inflation situation in the US. With inflation rising to 3% in January 2025, the Fed’s plan to cut interest rates has become more challenging. The Fed’s limited room to reduce interest rates, coupled with stable US economic conditions and a robust job market, has kept the USD strong. Additionally, the US tax policies, particularly under President Donald Trump, have created uncertainty in international trade, impacting not only the country’s trade relations but also putting pressure on global currencies, including the Vietnamese Dong (VND). These tariff policies are likely to continue pushing the USD/VND exchange rate higher as international money flows into the USD as a safe investment option.
In response to these developments, the SBV has adjusted the central exchange rate and increased the ceiling selling rate. This move provides the SBV with additional tools for potential market intervention if needed, especially considering the potential impact on foreign reserves.
TPS believes that the sharp rise in the exchange rate at the beginning of the year took the investment community by surprise, leading to an overly anxious market reaction on February 12, 2025. However, given the government’s economic stimulus orientation and the volatile global political and trade environment, a USD/VND exchange rate of up to 26,000 VND/USD is a positive scenario.
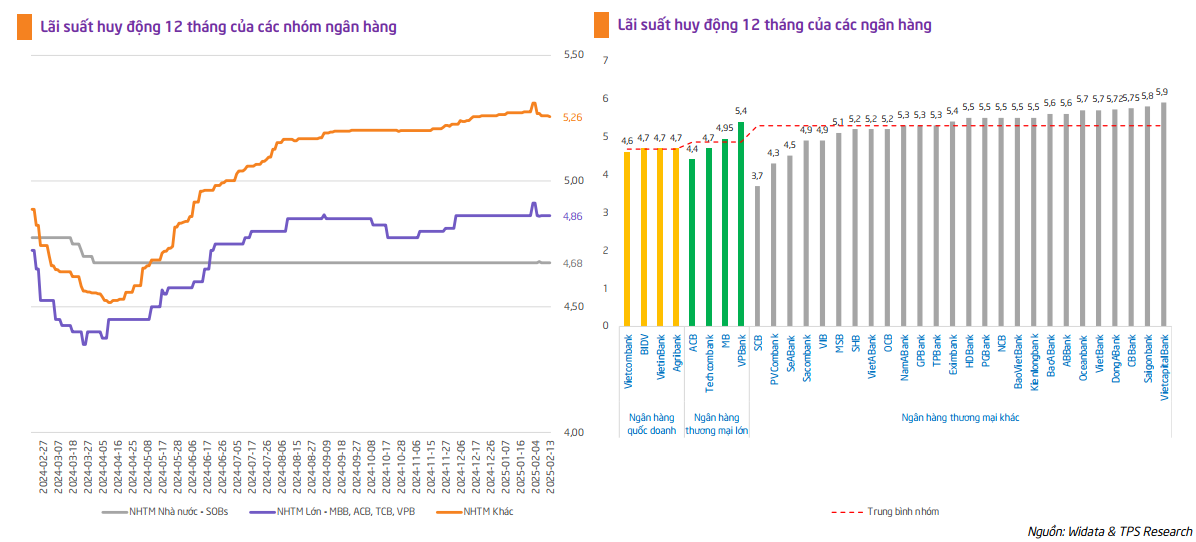
Bank deposit interest rates remain low
TPS observes that bank deposit interest rates in Vietnam during 2025 have mostly remained low, with only a few small banks making short-term adjustments. Most banks have kept their 12-month term deposit rates at around 5% per annum, reflecting stable liquidity and ample room to maintain low lending rates to support the economy.
Han Dong
– 09:29 15/02/2025
Unlocking Vietnam’s Economic Potential: Navigating the Path to 2025 with Optimism and Caution
According to the latest report by Standard Chartered Bank, Vietnam’s economy is projected to grow by 6.7% in 2025. With a forecasted growth of 7.5% in the first half and 6.1% in the latter half compared to the same period last year, this expansion is driven by robust business activity and sustained foreign investment.
Unleashing Public Investment to Spur 2025 Growth
Public investment is seen as the spearhead to boost growth this year, supporting a scenario of declining international trade and affected domestic consumption.