“OCB: A Leading Bank in Risk Management and International Standard Compliance”

As a pioneer in enhancing risk management capabilities, OCB has undertaken a series of key projects to improve its risk management framework to international standards. As early as 2018, the State Bank of Vietnam recognized OCB as one of the first three banks to complete the Basel II risk management requirements. By 2022, OCB successfully implemented the Basel III liquidity risk management standard and the internal models approach (IMA) for market risk management, along with adopting the “Internal Liquidity Adequacy Assessment Process (ILAAP)” as per the regulations of the European Central Bank.
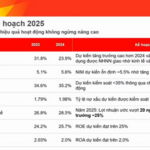
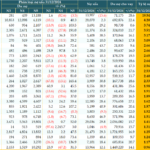
In 2023, OCB announced the completion of the implementation and application of the Basel II Advanced (Internal Ratings-Based) cloud-based capital computation platform, becoming the first bank in Vietnam to fulfill all the advanced requirements of Basel in international risk management standards. Over the following two years, OCB continuously enhanced its capital adequacy and liquidity resilience indicators. Specifically, in 2024, the capital adequacy ratio (CAR), liquidity coverage ratio (LCR), loan-to-deposit ratio (LDR), and the ratio of short-term funds for medium and long-term loans complied with the State Bank of Vietnam’s regulations. Additionally, OCB maintained high levels of liquid assets, such as cash, government bonds, and interbank lending, to ensure compliance with the current LCR requirements.
The bank also monitors the CAR, LCR, and net stable funding ratio (NSFR) on a monthly basis, striving for international standard Basel compliance. This approach has shaped OCB’s development towards sustainability, transparency, efficiency, and safety.
“In 2024, we regularly conducted internal assessments of capital adequacy (ICAAP) and liquidity (ILAAP) under complex scenarios, affirming OCB’s ability to meet our financial obligations to customers and partners in potential situations,” shared OCB’s leadership. “We ensure stable short-term business operations and have a stable capital plan to support our business growth.”
OCB’s 2024 risk appetite was constructed with stringent and flexible risk control targets to ensure the bank’s financial safety while aligning with its business strategy. Consequently, critical risk control indicators are consistently maintained, monitored, evaluated, and adjusted promptly, enabling OCB to expand its scale while maintaining tight risk management.
Due to its safe, efficient, and transparent operations, underpinned by a robust QLRR foundation and continuous improvements in line with international standards, OCB has consistently received high ratings from Moody’s over the years. Specifically, in 2024, the bank’s credit rating was Ba3 with a stable outlook. This rating reflects OCB’s stable financial position throughout economic cycles, a good capital adequacy ratio, and expectations for improved asset quality in the coming years. Additionally, Moody’s maintained the long-term foreign and local currency Counterparty Risk Assessments (CRRs) and the long-term Counterparty Risk Rating at Ba3(cr).
These ratings have opened up numerous opportunities for OCB to continuously attract foreign capital from international financial institutions. The stringent review and evaluation process conducted by these organizations ensures OCB’s operational quality, solid risk management, and commitment to safe, transparent, and efficient development. Furthermore, throughout the loan maintenance process, the bank must strictly adhere to financial health commitments regarding capital adequacy, asset quality, liquidity, and more.
This capital has enabled OCB’s SME customer segment, particularly women-owned businesses, to access preferential loans to invest in and develop their production and business operations, aligning with the bank’s sustainable development strategy.
In 2025, with the goal of placing OCB among the top five private joint-stock commercial banks in Vietnam in terms of efficiency and ESG, the bank will not only focus on business objectives, products and services, digital transformation, and human resources but will also continue to optimize governance, restructure its organizational model, and manage capital sustainably, while further solidifying its risk management foundation.
Kim Ngan
– 08:01 05/06/2025
Clearer Criteria Needed to Distinguish Between Three Types of Digital Assets: Virtual, Crypto, and Other Digital Possessions.
“During the afternoon session on May 9, discussions on the draft Law on Digital Technology Industry, pertaining to regulations on digital assets, took place. National Assembly Deputy Dong Ngoc Ba proposed a clearer distinction between three groups of digital assets: virtual assets, encrypted assets, and other digital assets.”
How to Prevent Bad Debt from Becoming an Economic Hindrance?
The rising tide of non-performing loans is a significant challenge for Vietnam’s banking system. It is not merely about managing bad debt but also about building a foundation for businesses to thrive and grow in an ever-changing world, ensuring that non-performing loans do not hinder the development of the financial system.
VCBS Ranks in the Top 10 Brokerage Firms by Market Share in 2024
Recently, the Ho Chi Minh City Stock Exchange (HOSE) unveiled the top 10 securities companies with the largest brokerage market share in Vietnam. This list showcases the leading firms in the industry, commanding a significant portion of the market and playing a pivotal role in shaping Vietnam’s burgeoning investment landscape.