While the deployment and expansion of generative AI capabilities present challenges such as model fine-tuning and data quality management, it can be faster and simpler than traditional AI projects of similar scope. High-impact use cases can be implemented in a matter of days or weeks. Based on practical experiences in applying generative AI, both internally and in collaborations with banks, the following critical aspects need solid capabilities to successfully scale generative AI across the enterprise and create sustainable value beyond initial proof-of-concepts.
First: Strategic Roadmap
To successfully scale generative AI, businesses often start by clearly defining the strategic role of generative AI and advanced analytics within the organization. This can range from transformative business model shifts to tactical initiatives aimed at enhancing productivity.
An asset management company recognized the potential of generative AI in improving client advisory and influencing the industry ecosystem, including operating platforms, partnerships, and economics. This led to a more agile approach to resource allocation and AI investment.
Second: Talent Development
The rapid evolution of generative AI has posed a significant challenge for bank leaders, leaving them with little time to prepare for its impact on employees, as well as skill enhancement and talent attraction necessary to stay competitive.
Additionally, banks need to continuously reassess their talent attraction and development strategies to align with technological changes. Skill-based recruitment, rational resource allocation, and comprehensive skill enhancement are crucial; many new positions will require knowledge in AI, cloud, data, and other technical domains. Ultimately, retaining talent depends not only on competitive salaries but also on clear advancement opportunities and jobs that provide long-term meaning and value to technology professionals.
Third: Operating Model
Bank leaders are seeking new operating models to support generative AI technology, but the concept of a “generative AI operating model” is not entirely accurate. Successful organizations have adopted a flexible, cross-functional, and interconnected operating model between business groups and providers. This ensures transparency and efficiency in deployment while ensuring that AI initiatives deliver against specific business outcomes.
As technology advances, banks need a more adaptable structure that enables departments to identify and prioritize appropriate activities. Organizations should reconsider why their current structure cannot integrate innovation capabilities and why this requires a special effort. Successful banks not only initiate new initiatives but also equip current teams with the necessary resources and skills to maximize generative AI.

Illustration
Fourth: Technology
Banks that successfully scale generative AI often carefully consider the “build, buy, or partner” dilemma when weighing the benefits of developing in-house solutions against leveraging proven solutions from ecosystem partners. Technologies such as platforms, cloud infrastructure, and MLOps can become commoditized due to the rapid evolution of open-source solutions. Clear strategic decisions, with a focus on creating real value, are indicative of successful expansion efforts.
This also presents a significant challenge for banks, which are accustomed to procuring IT solutions from third parties but struggle with next-generation AI models that require a high level of trust in providers to overcome risk barriers. Banks must carefully consider their AI application decisions, ensuring that risk levels remain within acceptable thresholds.
Additionally, generative AI integration is crucial. AI models should be complementary, compatible with legacy systems, and easily integrable with existing workflows, applications, and data sources. This is a complex task that requires multiple architectural elements such as context management, MLOps platforms, and risk management tools to ensure efficient integration and maintenance.
Fifth: Data
AI’s reliance on unstructured data adds complexity to banks’ current data strategies and architectures, as many banks lack the capabilities and infrastructure to handle such data. Unstructured data such as service interactions, social media posts, and news can be leveraged by generative AI to provide insights and support bank employees. The deployment of generative AI enhances services and customer experiences while unlocking the value of unstructured data for the entire organization.
To optimize data architecture, banks need to develop capabilities that support high-value applications, including vector databases and data handling tools. Data quality is even more critical in this context, and leading banks are using talent and automation to ensure data quality throughout its lifecycle. At the same time, leaders need to be mindful of security risks and act swiftly to comply with regulations.
Sixth: Risk and Controls
Generative AI brings opportunities but also introduces new risks, especially in the financial domain, where risk management remains inconsistent. Banks will need to redesign their risk governance frameworks and develop new controls to address these challenges.
The use of generative AI must be integrated into the expansion strategy from the outset, with close monitoring of model interpretability and decision objectivity. To mitigate risks from AI “hallucinations,” where models produce illogical outputs, banks are developing automation and result-checking methods, such as adjusting LLM parameter settings or using automated censorship tools to ensure accuracy and safety.
Seventh: Change and Adoption Management
The way a bank manages change can determine the success or failure of its scaling efforts, especially in ensuring the adoption of new technology. While the application has great potential, it won’t be effective if it’s not designed to encourage employee and customer usage. If employees don’t feel comfortable or understand the technology’s limitations, its potential won’t be fully realized. Transformational technology can even cause conflicts among leaders if there is a lack of consensus on goals.
To successfully deploy generative AI, banks need to shift their approach: start with the end-user experience and work backward. This helps build flexible AI systems that can learn and adapt from real-world feedback, ensuring continuous evolution based on human needs.
A comprehensive change management plan is key, including leadership and employee training and providing clear incentives for technology adoption. This requires transparency, engagement from leaders and influencers, and a clear vision of priorities and desired outcomes.
Generative AI has the potential to create significant value for banks, but scaling and convincing employees and customers to embrace this technology is not straightforward. For success, banks need a clear strategy to overcome barriers, optimize opportunities, and fully leverage the potential of generative AI.
Reference: Mckinsey & Company
Compiled by DTSVN – Digital Transformation Solutions for the Finance – Banking Industry.
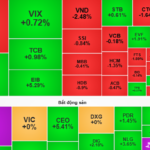
“Social Security Recovers $4.6 Billion; Workers Reap the Benefits”
With a stringent approach to technology and inspections, Vietnam Social Security has successfully recovered nearly VND 1,100 billion in overdue payments. This significant achievement is a testament to their unwavering commitment to protecting the rightful interests of tens of thousands of hardworking employees across the nation.
Biometric Identification Pilot at Tan Son Nhat Airport: Securing Borders, Streamlining Travel
Let me know if you would like me to provide any additional revisions or if you have another writing task for me!
“The Ministry of Public Security has embarked on a journey of technological innovation and digital transformation, introducing a plethora of convenient features. One notable initiative is the pilot program for biometric identification at Terminal 3, showcasing their commitment to embracing cutting-edge technology.”
“MB Bank’s Vice President Showcases the Talents of an Unsung Hero Team: The Elite Squad of ‘Ethical Hackers’ Protecting Over 30 Million Customers, Even Tricking Senior Leaders in the Process.”
“Mr. Vu Thanh Trung, MB, forgoes the traditional requirements of formal qualifications. Instead, he seeks individuals with proven practical abilities and a keen imagination to identify loopholes within the banking system and its customers.”