The chemical company Duc Giang Chemical Group (DGC) has just announced its annual shareholders’ meeting documentation for 2024, with a business plan that continues to lag behind 2023. In 2024, the chemical giant sets a revenue target of VND 10.2 trillion, a 4.7% increase from 2023, with a post-tax profit of VND 3.1 trillion, a slight 4% decrease, and a dividend plan at 30%.
In terms of revenue structure, gold phosphorus is still expected to be the main source of income for DGC, with a target production volume of 43,000 tons, bringing in over VND 4.1 trillion. Food-grade phosphoric acid 85% and technical-grade phosphoric acid (WPA 50%) are expected to bring in nearly VND 2 trillion and over VND 1 trillion, respectively. DAP fertilizer is expected to bring in VND 560 billion, MAP fertilizer VND 520 billion, and various types of Superphosphate VND 450 billion.
In 2024, DGC plans to propose the construction of several projects, including the Plasticizers Complex in Nghi Son (Phase 1), with an investment capital of VND 500 billion; Continued research on the Alumina project, conducting surveys to obtain investment licenses; expanding and upgrading the reserves at Mine 25, with an investment capital of VND 10 billion.
In addition, DGC plans to propose the merger of Phosphorus 6 with Duc Giang Lao Cai Chemical Co., Ltd. (a subsidiary of DGC). At the same time, they will consider merging Phosphorus Apatite Vietnam JSC (UPCoM: PAT) into DGC.
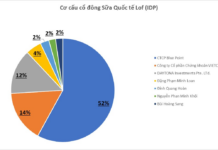
PAT is owned by DGC through Duc Giang Lao Cai. Accordingly, Duc Giang Chemical Company currently holds 51% of PAT’s capital through Duc Giang Lao Cai. In addition, Mr. Dao Huu Huyen – Chairman of the company and his son Mr. Dao Huu Duy Anh – CEO of the company together own 16.7% of PAT’s capital.
PAT was listed in June 2022. In terms of business performance, in 2023, PAT generated nearly VND 286 billion in profit, less than 1/3 compared to the extraordinary year of 2022 (VND 963 billion), but the second-highest profit since its establishment in 2014.

Prior to 2023, Duc Giang Chemical recorded net revenue of VND 9.748 trillion, a 32.5% decrease compared to 2022, and a post-tax profit of VND 3.241 trillion, a 46.3% decrease.
On the consolidated financial statements, the audited post-tax profit differed by 10% compared to the separate financial statements. According to the explanation of the company’s leadership, the sharp decrease in revenue was mainly due to the decrease in domestic and global market prices. The total operating expenses, including financial, sales, business management, and corporate income tax expenses, decreased by 18% in 2023. The higher decrease in revenue led to a significant decrease in profit.
VCSC Securities (VCSC) forecasts global demand for gold phosphorus will grow at a single digit rate in the medium term, driven by EV battery demand and chip demand from artificial intelligence. In this regard, DGC will benefit and continue to gain market share in the industrial phosphoric acid (IPC) market in the medium term as China no longer exports gold phosphorus.
The International Association of Semiconductor Equipment and Materials (SEMI) forecasts that global semiconductor sales will increase by 12% compared to the same period in 2024. In addition, the stable inventory levels of chip manufacturers also support chip production activities, thereby increasing the demand for industrial phosphoric acid in the future.
In the semiconductor field, DGC has established a dominant presence in East Asia (excluding China) in the gold phosphorus market and is rapidly entering the US market. The company’s top-quality gold phosphorus purity surpasses all competing companies in the global export market. According to Vietcap, DGC expects to benefit from the increased chip production by the US and its allies, regardless of the location of the plants.