Credit up nearly 2%, bad debt up 14%
After two months of negative growth at the beginning of the year, credit turned positive again in March (up 0.98%); by the end of March 2024, it reached approximately 13.6 million billion VND, up 0.26% from the beginning of the year.
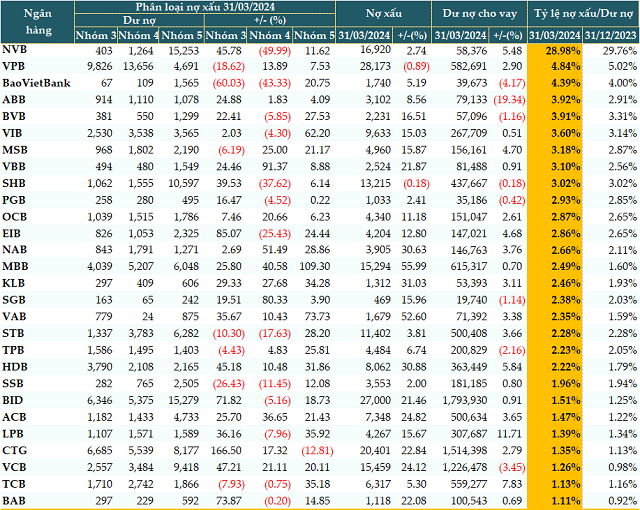
Data from VietstockFinance shows that as of March 31, 2024, the total outstanding debt of 28 banks in the system was more than 10.2 million billion VND, a slight increase of nearly 2% from the beginning of the year.
8 out of 28 banks had negative credit growth compared to the beginning of the year. Of these, ABBank (ABB) decreased the most – more than 19% (79,133 billion VND), followed by BaoVietBank, which decreased by more than 4% (39,673 billion VND), and Vietcombank (VCB) decreased by more than 3% (over 1.2 million billion VND)…
The remaining banks achieved positive growth with an average rate of 3.5%. Notably, LPBank (LPB) had the strongest credit growth (+12%), followed by Techcombank (TCB, +8%), HDBank (HDB, +6%), and NCB (+5%).
Meanwhile, bad debt continued to increase compared to the beginning of the year. As of the end of the first quarter, the total bad debt of the 28 banks was 224,146 billion VND, an increase of more than 14%. Two banks improved their loan quality: VPBank (VPB) reduced bad debt by nearly 1%, and SHB slightly decreased by 0.1%. The remaining banks in the system reported an increase in bad debt with an average growth rate of over 18% compared to the beginning of the year.
The structure of bad debt also showed a more negative development. Substandard debt (Group 3) increased the most at 21%, followed by debt with potential loss (Group 5), which rose by nearly 18%, and doubtful debt (Group 4) increased by over 4%.
|
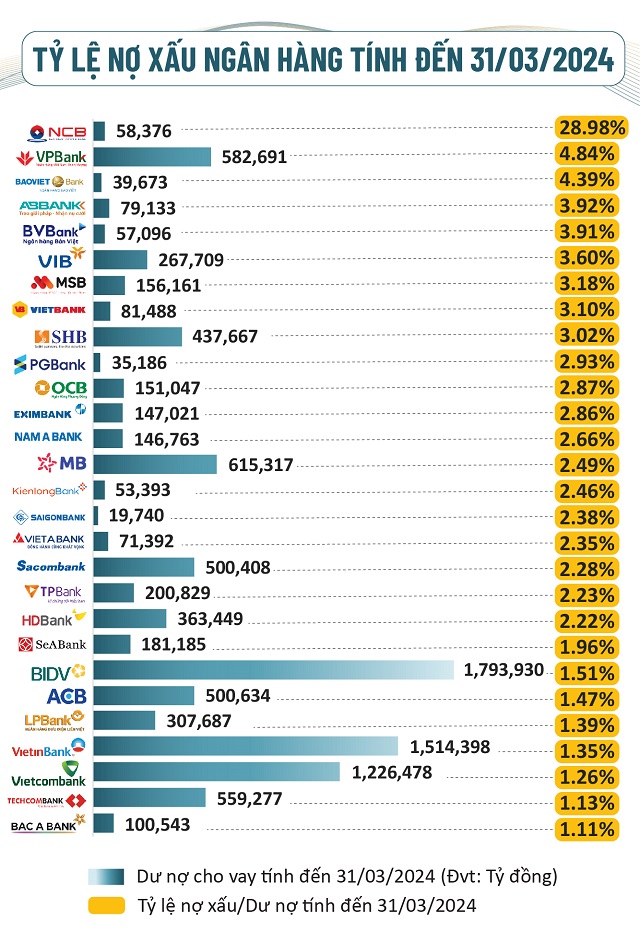
Loan quality of banks as of March 31, 2024 (Unit: Billion VND)
Source: VietstockFinance
|
24 banks increased the ratio of bad debt to total loans
As of March 31, 2024, 24 out of 28 banks increased the ratio of bad debt to total loans compared to the beginning of the year. Notably, 9 banks had a ratio above the allowable threshold of 3%, while at the beginning of the year, only 5 banks were in this situation.
However, there were 4 banks that improved their bad debt ratios: VPB, NCB, SHB, and TCB.
 Source: VietstockFinance
|
Will the end of the second quarter be the peak for bad debt?
Bad debt in banks continues to rise amid the extension of Circular No. 02/2023/TT-NHNN, which allows for debt restructuring and postponement until the end of 2024. Commenting on this, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Dinh Trong Thinh, an economic expert, explained: “The restructured debts do not become bad debts, but there are still debts that are not eligible for restructuring and will turn into bad debts. Not all enterprises are subject to debt restructuring, and those that are not eligible, when due and unable to pay, will turn into bad debts.”
When Circular No. 02 expires, the bad debt level will surely increase significantly, as currently, with the extension, the bad debt ratio has already exceeded the regulations.
Mr. Thinh further shared that the Prime Minister has requested banks to cut costs to reduce lending rates and support businesses. However, deposit rates will have to increase gradually according to market adjustments, and since April, many banks have started to raise deposit rates as bank deposits are declining. To maintain low lending rates, banks need to keep deposit rates low as well. Therefore, deposit rates may increase for some long-term maturities, usually those longer than one year.
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nguyen Huu Huan, a lecturer at the University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City, assessed that the current economic situation is growing linearly rather than recovering strongly. Therefore, the pressure of bad debt in the economy remains. Surely, bad debt in the coming time will continue to increase. Although Circular No. 02 has been extended until the end of 2024, if the world economic situation remains the same and recovers, and there are no negative factors, and the Federal Reserve (Fed) cuts interest rates by the end of the year, the bad debt of Vietnamese banks will peak in the second quarter or early third quarter. But that is the peak due to Circular No. 02, and when it expires, bad debt will increase even higher due to adjustments.
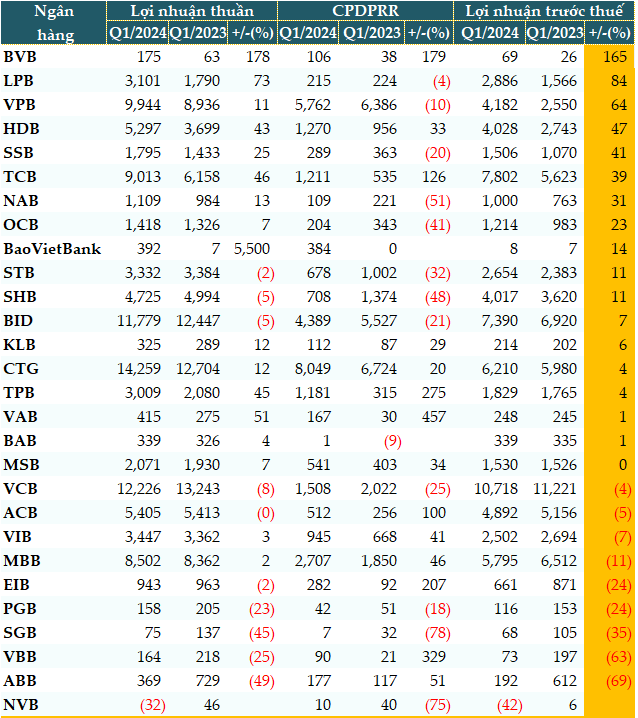
When bad debt increases, the cost of credit risk provisions also needs to increase, reducing bank profits in the first quarter.
The total credit risk provision expenses of the 28 banks in the first quarter of 2024 were 31,656 billion VND, up nearly 7% over the same period last year. Fourteen out of 28 banks increased their credit risk provisions, eroding bank profits. As a result, 9 banks reported a decrease in pre-tax profit in the first quarter, and 1 bank reported a loss.
|
Pre-tax profit of banks in the first quarter of 2024 (Unit: Billion VND)
Source: VietstockFinance
|
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nguyen Huu Huan forecast that in the second quarter, bad debt and credit risk provisions would continue to increase. When bad debt peaks and shows a downward trend, the provisions will also decrease.
Cat Lam