Benefits of Custard Apple for Anemia
Custard apples are an excellent source of iron, a mineral crucial for the production of hemoglobin, the main component of red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. Iron deficiency is one of the leading causes of anemia.
Custard apples also contain high levels of vitamin C, which enhances iron absorption from food. The combination of iron and vitamin C in custard apples optimizes iron intake, supporting the treatment and prevention of iron-deficiency anemia.
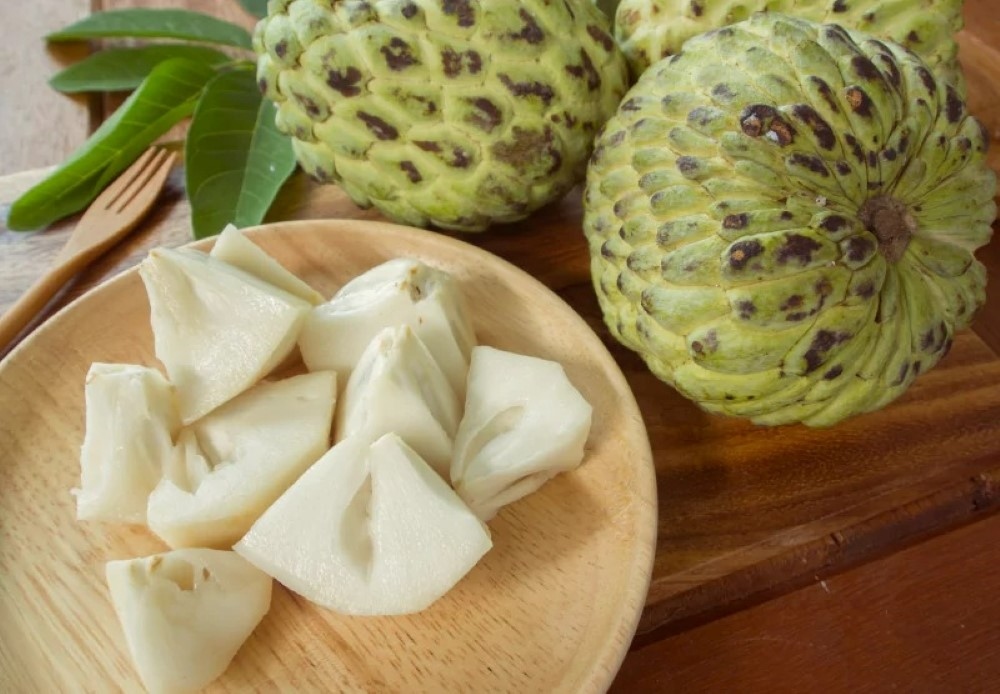

Custard apples offer blood-boosting and cancer-preventing benefits. Image: Getty Images
Eye Health Benefits
Custard apples are rich in vitamin A, a powerful antioxidant that protects the cornea, maintains eye moisture, prevents dry eyes, and reduces the risk of age-related macular degeneration. The vitamin C content in these fruits also safeguards the eyes from free radical damage, aids in collagen production, and ensures the elasticity of blood vessels in the eyes.
Additionally, custard apples contain carotenoids like lutein and zeaxanthin, known for their ability to shield eyes from harmful blue light emitted by digital screens and the sun. Lutein and zeaxanthin also lower the chances of cataracts and macular degeneration. Custard apples provide a small amount of riboflavin, a B vitamin that protects against eye conditions such as cataracts and dry eye syndrome.
Cancer Prevention
Custard apples are abundant in flavonoids such as quercetin and kaempferol, which are potent antioxidants that protect cells from free radical damage, thereby reducing the risk of cancer. Research has shown that acetogenins found in custard apples can inhibit the growth of cancer cells and destroy them without harming healthy cells.
As a significant antioxidant, vitamin C in custard apples neutralizes free radicals and lowers the chances of DNA damage, a critical factor in cancer development. Meanwhile, the high fiber content in custard apples promotes digestion and eliminates toxins from the body, reducing the risk of gastrointestinal cancers.
Custard Apple Benefits for Cardiovascular Health
Custard apples are rich in magnesium and potassium, two minerals essential for regulating blood pressure. Magnesium helps relax blood vessels and prevents spasms, while potassium balances sodium levels in the body, thereby lowering blood pressure. Vitamin B6 in custard apples reduces homocysteine, an amino acid that can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
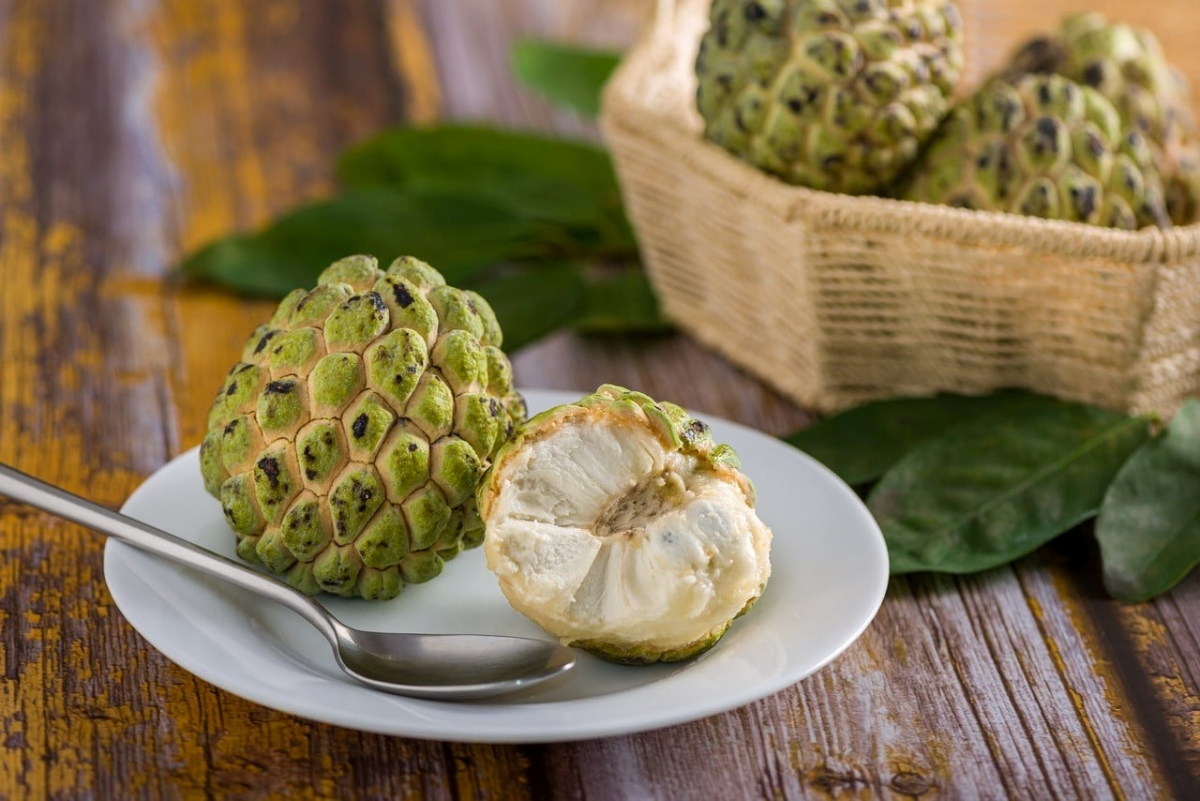

Custard apples are highly beneficial for cardiovascular health. Image: Shutter Stock
Furthermore, custard apples are rich in antioxidants like vitamin C and flavonoids, which protect heart cells from free radical damage, reduce inflammation, and prevent the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in arteries. Due to their high fiber content, custard apples also help lower bad (LDL) cholesterol and increase good (HDL) cholesterol, thereby promoting cardiovascular health.
Benefits for Pregnant Women
Vitamin B6 in custard apples helps alleviate nausea and vomiting, common symptoms during pregnancy. Vitamins A and C in custard apples are vital for the development of the fetus’s eyes, skin, hair, and immune system.
Custard apples may also reduce the risk of miscarriage, lessen labor pain during childbirth, and increase breast milk production post-delivery. The potassium and magnesium in custard apples help regulate blood pressure, lowering the risk of preeclampsia and other cardiovascular complications during pregnancy. However, pregnant women should consult their doctors before consuming custard apples, especially if they have a history of diabetes or allergies to the fruit.
Preventing Arthritis
As a potent antioxidant, vitamin C in custard apples neutralizes free radicals that cause inflammation in the body. Research indicates that individuals with low blood levels of vitamin C have an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
Custard apples also contain magnesium, a mineral essential for maintaining bone and joint health, reducing inflammation, increasing bone density, and alleviating joint pain. Moreover, kaempferol, present in custard apples, exhibits strong anti-inflammatory properties. Studies have shown that kaempferol can help reduce arthritis-related inflammation and symptoms.