According to the Vietnam Real Estate Brokers Association, the experience of other countries shows that credit policy is one of the essential tools for governments to regulate the real estate market. Many of the policies successfully implemented by other countries can be referenced, learned from, and applied in Vietnam.
Based on the lessons learned from these countries, the Association proposes several credit policy solutions to stabilize the market when it experiences fluctuations of more than 20% in three months or other real estate market fluctuations that impact socio-economic stability, without affecting the demand for housing from citizens.
 Real estate prices are soaring. |
The Association suggests tightening credit policies for speculators. Specifically, to reduce the number of people borrowing for speculative purposes or using excessive leverage, credit institutions can adjust loan limits by modifying the loan-to-value ratio, requiring a higher proportion of down payment, or applying higher interest rates for second-home buyers and beyond.
Secondly, enhance credit monitoring and management. As per the Association’s proposal, the government can impose regulations on credit quality control, requiring banks to provide more detailed reports on real estate-related loans, thereby strengthening risk oversight. Establish a credit mechanism for social housing projects, prioritizing capital allocation for projects that develop affordable and social housing to address the housing needs of low-income earners.
Additionally, the state should also implement credit relaxation policies, including reducing interest rates and providing long-term loans with preferential rates for first-time home buyers or other priority groups to maintain social stability, such as newly married couples.
To ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of these policies, the Association believes that the state needs to develop a large, precise, and up-to-date database to distinguish between genuine homebuyers and those engaging in speculation or profiteering.
Expediting the publication of real estate transaction price indices and other influential indicators is crucial to determining when government intervention is necessary, especially amid concerns about rising real estate prices.
For a more comprehensive regulation of the real estate market, credit policies should be combined with the implementation of real estate transfer taxes or property taxes. Moreover, when applying regulatory policies, flexibility must be considered to maintain stability in the real estate market and minimize risks.
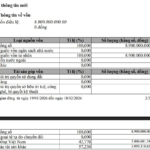
In the last two years, the condominium market in Hanoi has seen rapid and significant price increases. The price gap between Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City’s condominium markets has narrowed (in 2019, the primary price gap between the two markets was 30%; by 2024, the gap ranged between 5-7%).
As of the second quarter of 2024, according to surveys and reports from major provinces and cities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City, condominium prices have increased by an average of 5-6.5% quarterly and 25% annually, depending on the area and location.
The Ministry of Construction attributes the localized price increases in major localities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City to the continued limited new supply and the small number of new projects entering the market. The scarcity of middle- and lower-class housing supply has contributed to price increases in these projects.
Ngoc Mai