Vietnam’s central bank has been navigating a delicate path with its interest rate policy, carefully considering market dynamics, macroeconomic conditions, inflation, and monetary policy goals.
According to the State Bank of Vietnam, when inflationary pressures mount, they proactively adjust interest rates upward to curb inflation. Conversely, when inflation is under control and aligns with the set targets, the focus shifts to supporting economic growth by lowering interest rates.
As of 2023, the State Bank has consistently reduced key interest rates and maintained these reduced rates in the early months of 2024. This strategic move is intended to provide financial institutions with access to low-cost capital, ultimately boosting the economy.

State Bank reduces interest rates to boost economic growth.
|
The State Bank encourages financial institutions to streamline costs, simplify loan procedures, and embrace digital transformation in their lending processes. By doing so, they aim to reduce lending rates and provide much-needed support to the economy.
Lending rates have witnessed a notable decline compared to previous years: the average lending rate decreased by 1.1% in 2023 and 1.24% in 2024. Furthermore, in the first seven months of 2025, lending rates for new transactions by commercial banks dropped by 0.4% compared to the end of 2024, providing a significant boost to businesses, individuals, and the overall economy.
Additionally, the State Bank has directed financial institutions to channel credit towards productive sectors and priority areas as outlined by the government, while closely monitoring credit exposure in high-risk sectors.
Credit growth has been managed in tandem with the economy’s capacity to absorb capital, with a focus on maintaining credit quality. As a result, between 2021 and 2024, average credit growth stood at 14.17% annually. As of July 31, 2025, capital mobilization reached over VND 16 trillion, marking a 7.14% increase, while credit outstanding exceeded VND 17 trillion, reflecting a 10.24% rise compared to the end of 2024.
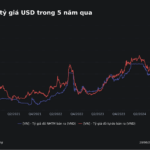
In tandem with the development of the foreign exchange market, the State Bank has gradually increased the flexibility of exchange rates, striking a balance between market demands and macroeconomic stability.
Since 2016, the central bank has introduced a daily flexible exchange rate adjustment mechanism for the mid-point rate, taking into account both domestic and international market conditions, macroeconomic and monetary balances, and monetary policy objectives. This approach has proven effective in absorbing external shocks and mitigating their impact on exchange rates. Concurrently, the trading band for the USD/VND exchange rate has been widened gradually, starting from ±1%, then moving to ±2% and ±3% (in 2015), and eventually reaching ±5% in 2022.
During periods of intense pressure on exchange rates and the foreign exchange market, stemming from international market fluctuations and domestic challenges, the State Bank has intervened proactively using diverse tools. These interventions, coupled with other monetary policy instruments, have successfully stabilized the foreign exchange market, contributing to macroeconomic stability and inflation control.
As a result of these strategic interventions, the USD exchange rate has demonstrated agility, aligning with market conditions and mirroring trends among regional and global currencies. Notably, during periods of intense international market volatility, the Vietnamese dong has maintained greater stability compared to many other currencies. The foreign exchange market has functioned smoothly, ensuring that the economy’s legitimate foreign currency needs are met.
Ngọc Mai
– 07:53 01/09/2025
What’s Affecting Interest Rates?
In a thriving economic landscape, with surging credit growth and intense competition for funds, banks are offering varying lending rates. Experts predict a slight upward trend in interest rates by the end of 2025, creating a diverse landscape for borrowers.
Why Are Exchange Rates Constantly Rising?
The State Bank of Vietnam (SBV) announced the reference exchange rate for August 28 at 25,268 VND per USD. Bank USD selling prices remained at the ceiling level of 26,531 VND/USD. The free market saw record highs for USD at 26,720 VND. Since the beginning of 2025, the Vietnamese dong has depreciated by 3.8% against the US dollar in the banking system and 3.4% in the free market.
A Minimum Wage Increase of 7.2%: Strategies to Prevent a Price ‘Hike’
The minimum wage is set to increase by 7.2% from the beginning of 2026, a move aimed at counteracting the effects of inflation and ensuring workers can afford the rising cost of living. Historically, such wage increases have been followed by a rise in the price of goods. To prevent this, authorities must take action to stop businesses from simply passing on these increased labor costs to consumers, ensuring that this wage increase truly benefits workers.