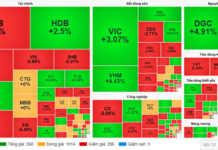
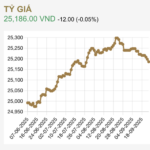
The USD/VND exchange rate has been on an upward trajectory since the beginning of the year, driven by the U.S. Federal Reserve’s tight monetary policy aimed at curbing inflation, which has strengthened the U.S. dollar.
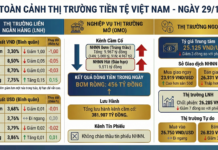
Additionally, as we enter the third quarter, import businesses are ramping up their USD purchases to settle year-end orders and prepare for peak production and consumption seasons. As of September 20, 2025, the central exchange rate set by the State Bank of Vietnam (SBV) stands at 25,186 VND/USD, marking a 3.5% increase since the start of the year.
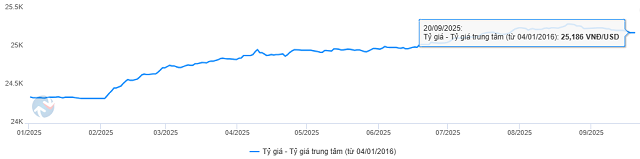 Source: VietstockFinance
|
At Vietcombank, the USD buying and selling rates on the morning of September 22 were listed at 26,178 and 26,448 VND/USD, respectively, reflecting a 3.5% increase year-to-date.
Multifaceted Impact
Mr. Jung Hyo Chang, Director of Foreign Exchange and Derivatives at Shinhan Bank Vietnam, notes that the recent depreciation of the local currency has increased capital costs, particularly for businesses heavily reliant on imported materials or foreign currency loans.

Mr. Jung Hyo Chang – Director of Foreign Exchange and Derivatives, Shinhan Bank Vietnam
|
Conversely, export businesses gain a competitive edge in international markets due to improved pricing. However, if exporters rely on imported raw materials, their financial costs and profits are also affected, with the impact varying based on their foreign exchange exposure.
“We are closely monitoring these developments and offering tailored risk management solutions, including currency hedging products, to help businesses navigate effectively,” added a representative from Shinhan Bank Vietnam.
Mr. Nguyen Quang Huy, CEO of the Faculty of Finance and Banking at Nguyen Trai University, observes that exchange rate fluctuations present both opportunities and challenges for the banking sector in risk management.

Mr. Nguyen Quang Huy – CEO of the Faculty of Finance and Banking, Nguyen Trai University
|
When the local currency weakens, businesses with foreign currency loans face higher repayment pressures, increasing credit risk. Even VND loans for imports can negatively impact repayment capabilities due to rising input costs, necessitating stricter credit quality monitoring by banks.
Exchange rate volatility has a dual impact on international payments and foreign exchange trading. Exporters benefit from converting foreign earnings into VND, while importers face higher costs. Banks must enhance their advisory role, offering derivative tools to mitigate risks. The surge in foreign exchange demand (spot, forward, swap, option) boosts service profits but requires stringent currency position management to avoid liquidity risks during market turbulence.
Banks must strike a delicate balance between seizing business opportunities and effective risk management.
 Ms. Ho Truc Lam – Director of Horeca Food Joint Stock Company
|
From a business perspective, Ms. Ho Truc Lam, Director of Horeca Food Joint Stock Company, notes that her export-focused business to the U.S. and Europe benefits from a stronger exchange rate. In contrast, importers face higher costs and reduced domestic purchasing power, leading to profit declines. However, high exchange rates favor domestically produced goods over imports, limiting import competition.
Ms. Lam mentions that U.S.-bound export orders in the final months of the year are planned for 3 months, compared to the previous 6-8 month cycles.
A representative from a tent exporter to South Korea with a factory in Ninh Binh notes that the tent market caters to the upper-middle class. Global economic factors like tariffs and inflation are impacting various sectors, including the tent industry.
Solutions for Businesses
Mr. Nguyen Quang Huy advises businesses to proactively develop exchange rate risk management strategies rather than reacting passively.
Exporters can use forward currency sales to lock in rates or put options for a minimum insurance rate with upside potential. Matching export earnings with import payments is also beneficial.
Importers can use forward currency purchases to fix input costs. Currency swaps are ideal for mismatched cash flows. Negotiating risk-sharing clauses in trade contracts is also advisable.
All businesses should establish robust exchange rate risk policies, collaborate closely with banks for derivative solutions, and diversify markets to reduce currency dependence.
At the banking level, Mr. Jung Hyo Chang highlights the increased credit risk from foreign currency loans, necessitating stricter collateral requirements and liquidity management to ensure smooth global financial transactions.
Exchange rate volatility offers opportunities but also poses risks in foreign exchange trading. Banks must cautiously manage market risks and capital allocation to avoid profit volatility.
Shinhan Bank has developed comprehensive solutions to support exporters and importers in managing exchange rate risks, including market reports, derivative products, and cash flow management advice. The effectiveness and cost of these tools depend on business size, risk exposure, and operational cycles.
Exchange Rate Expected to Decline Gradually
Mr. Jung Hyo Chang predicts continued exchange rate volatility due to global interest rate policies and geopolitical uncertainties. Expectations of a Fed rate cut in September and a weakening USD suggest a gradual decline in the VND exchange rate, aligned with the USD-Index trend.
Mr. Nguyen Quang Huy forecasts a more stable exchange rate by year-end, supported by global monetary easing, potential market upgrades attracting foreign capital, and strong remittance and FDI inflows. These factors will help balance the market and enable the SBV to stabilize the exchange rate effectively.
– 10:00 22/09/2025
How Will the Fed’s 0.25% Rate Cut Impact Vietnam’s Exchange Rates?
The USD/VND exchange rate is expected to ease as the Federal Reserve initiates its monetary policy loosening cycle, marked by the first interest rate cut of the year.
Central Bank Conducts Net Withdrawal in Open Market Operations
During the week of September 3–8, the State Bank of Vietnam (SBV) continued to flexibly manage system liquidity through open market operations.