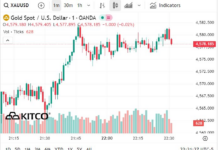
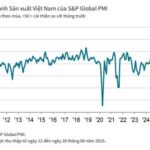
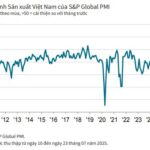
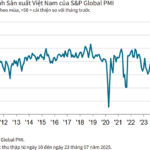
Vietnam’s Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI®) remained steady at 50.4 in September, unchanged from August. This indicates a continued modest improvement in the manufacturing sector’s health, marking the third consecutive month of enhanced operating conditions.
The recovery in business conditions during September was primarily driven by a rebound in new orders, following a slight decline in August. However, the growth in new orders was marginal.
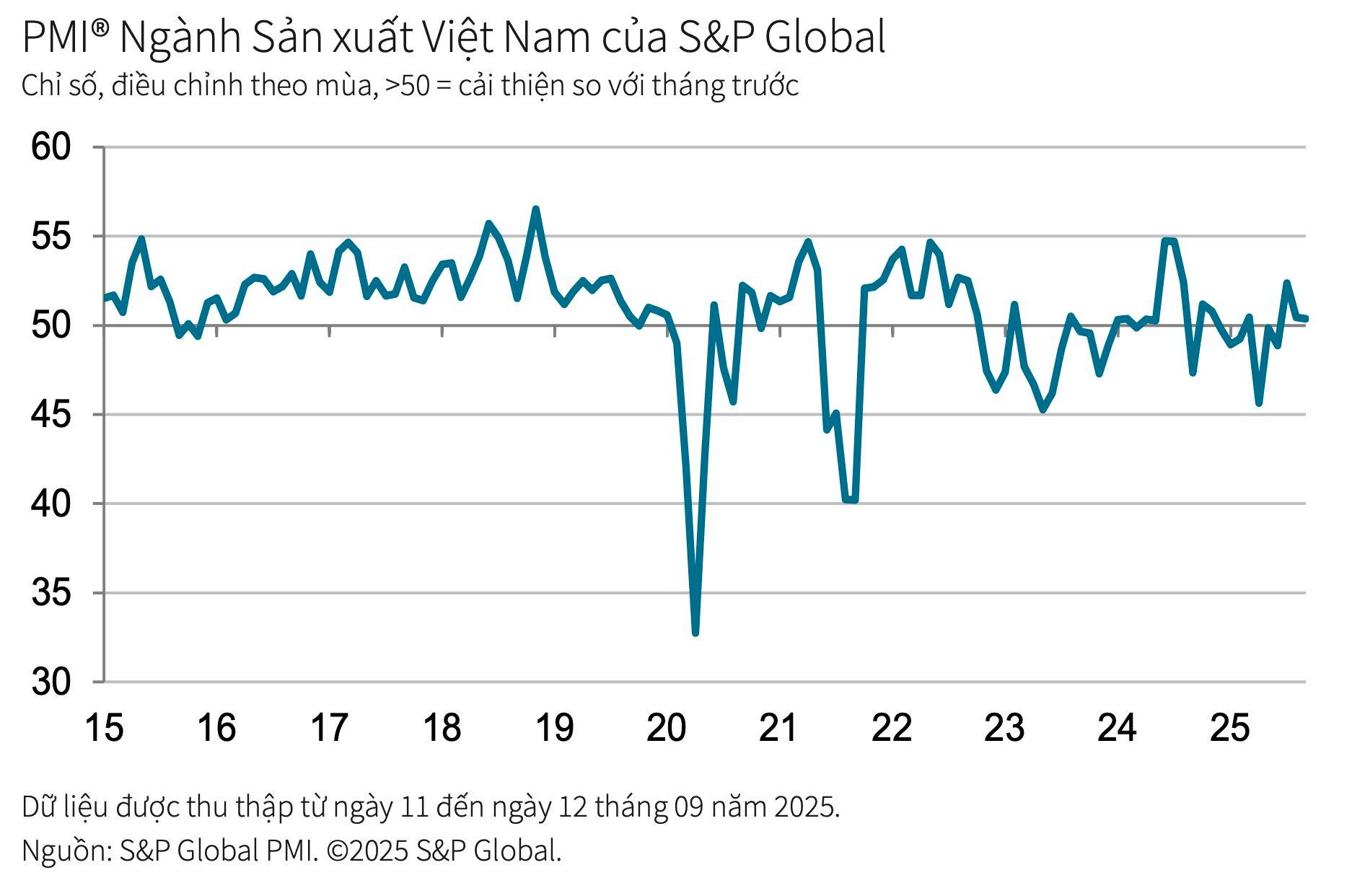
Meanwhile, new export orders continued to decline, though at the slowest pace in 11 months. International demand remained weak, but stabilized U.S. tariff policies reportedly helped some companies secure new overseas orders.
With overall new orders rising due to improved customer demand, manufacturers increased production at the end of Q3. This also contributed to a sharp reduction in backlogs of work.
On the employment front, manufacturers continued to reduce their workforce. Survey respondents attributed this to relatively low workloads and unreplaced retirements.
On a positive note, companies increased purchasing activity for the third consecutive month, driven by higher production needs. The use of purchased inputs supported production, leading to further declines in input inventories. Finished goods stocks also decreased, with the sharpest drop since July 2024.
According to S&P Global, survey participants cited supply shortages and transportation issues as key factors behind the 13th consecutive month of lengthened supplier delivery times.
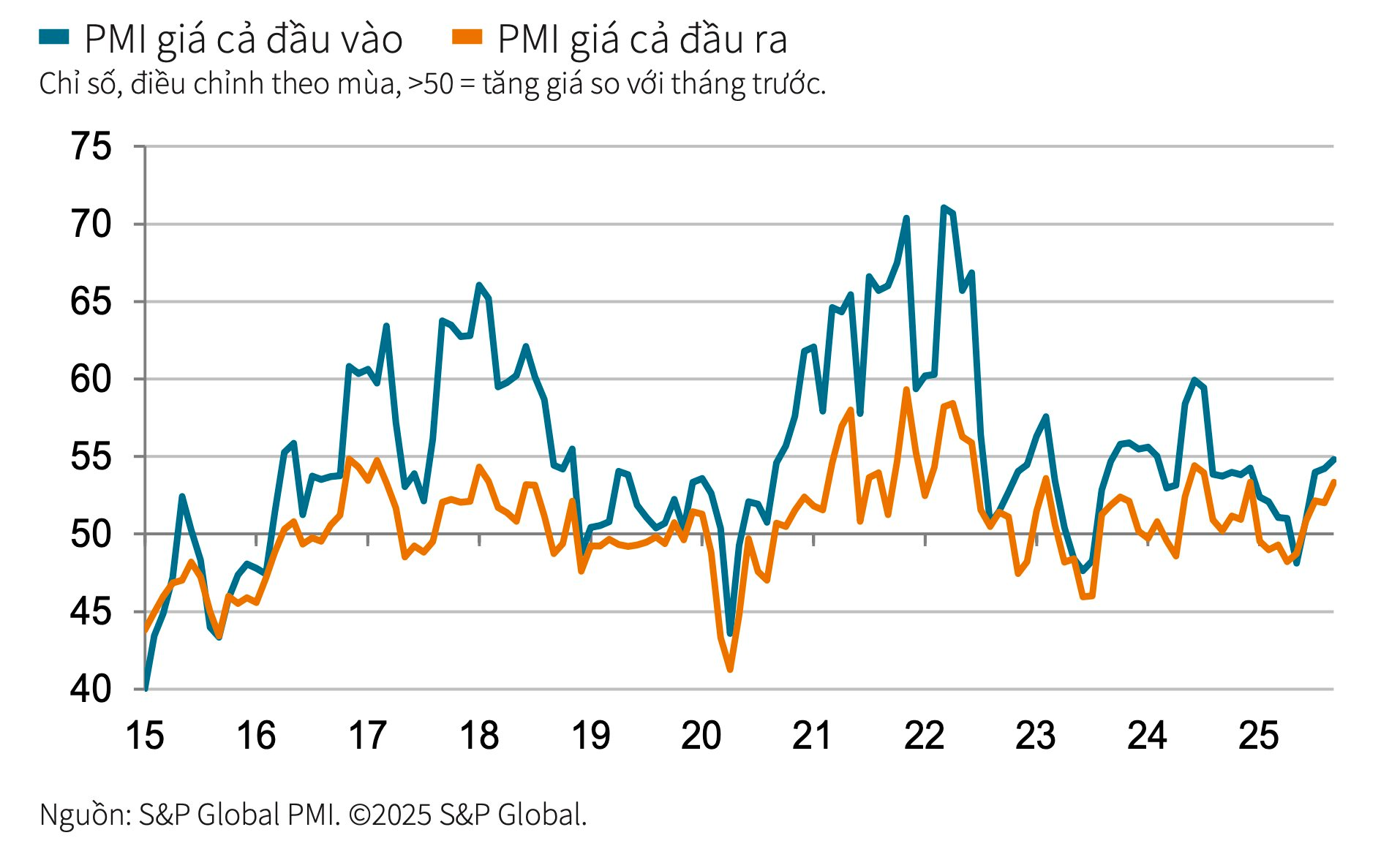
Inflationary pressures intensified in late Q3, with both input costs and output prices rising at faster rates. The latest increase in input costs was the steepest since July 2024, attributed to higher market prices and unfavorable exchange rate fluctuations. Consequently, selling prices rose at the fastest pace in 14 months.
A more stable economic environment is expected to boost new orders and production in the coming year. Public sector investment is also projected to support growth. While companies remain optimistic about the outlook, confidence levels have dipped since August and are below the long-term average.
Commenting on Vietnam’s September PMI, Andrew Harker, Economics Director at S&P Global Market Intelligence, stated: “There was positive news for Vietnamese manufacturers in September as new orders rebounded. Even exports, which have been declining since late last year, showed signs of stabilization. Greater clarity on tariffs appears to have bolstered customer demand for Vietnamese firms.”
Increased stability is anticipated to support growth next year, but business confidence remains subdued due to recent weak demand trends.
“A key area to watch in the coming months is inflation. Both input costs and selling prices have been rising at stronger rates recently. If this trend persists, we may begin to see price pressures constrain demand,” the expert cautioned.
August 2025 PMI: New Orders and Employment Slump
The S&P Global Vietnam Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), a pivotal gauge of the health of the manufacturing sector, remained above the 50.0 no-change mark in August. This indicated a second successive monthly improvement in the sector’s health. However, with the PMI falling from 52.4 in July to 50.4, the latest data highlighted only a mild improvement in business conditions.
July 2025 PMI: New Orders Rise for the First Time in Four Months
The S&P Global Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) for Vietnam stood at 52.4 in July, up from 48.9 in June and above the 50-point threshold for the first time in four months. This indicates an improvement in the overall health of the manufacturing sector. Indeed, the strengthening of business conditions was the most notable in nearly a year.
“PMI Surges Past 52: Vietnam’s Manufacturing Sector Booms Despite US Tariff Turbulence”
The Vietnamese manufacturing sector rebounded in July 2025, with the PMI index reaching an impressive 52.4 points. This marks the first time in four months that the index has crossed the 50-point threshold, indicating a return to growth. Notably, this expansion occurred despite ongoing weaknesses in export activity due to US tariff impacts.
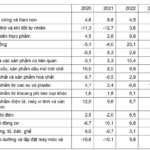
Industrial Production in 2024: Surpassing Targets
Surmounting numerous challenges, industrial production in 2024 achieved an impressive 8.4% growth rate. This figure not only surpasses the initial target set at the beginning of the year (a planned increase of 7-8%) but also marks the highest growth rate in the period from 2020 onwards.