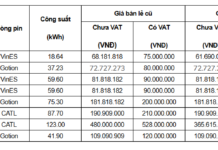
Deputy Governor of the State Bank of Vietnam, Pham Thanh Ha
At the Q3/2025 Banking Operations Press Conference, Deputy Governor Pham Thanh Ha stated that since the beginning of 2025, the global economic and political landscape has been highly unpredictable. Concerns over U.S. tariff policies and the risk of a global trade war, geopolitical conflicts, commodity price shocks, and lingering inflationary pressures—despite some cooling—pose significant challenges. These factors complicate global financial and monetary markets, exerting pressure on domestic monetary policy, exchange rates, and interest rates, while also impacting efforts to achieve the 2025 economic growth target of over 8%.
Closely monitoring domestic and international macroeconomic trends, and adhering to the Party’s guidelines, National Assembly resolutions, and the Prime Minister’s directives, the State Bank of Vietnam (SBV) has proactively and flexibly managed monetary policy tools. This includes close coordination with fiscal and other macroeconomic policies to control inflation, stabilize the macroeconomy, promote economic growth, and ensure the safety of credit institutions.
These monetary policy efforts have significantly contributed to GDP growth, with inflation well-controlled at an average of 3.25% over eight months, and core inflation at 3.19%—lower than general inflation. This has helped stabilize the macroeconomy amid global and regional uncertainties, as emphasized by the Deputy Governor.
Regarding interest rate management, the SBV has maintained low operational interest rates since the start of 2025 to encourage market reductions in lending rates, supporting businesses and individuals. The SBV has also directed credit institutions to cut operational costs, enhance digital transformation, and implement other measures to lower lending rates, which have shown a downward trend.
In the foreign exchange market, the SBV has flexibly managed exchange rates, coordinating with other monetary policy tools. This has ensured smooth market operations, meeting legitimate foreign currency demands and maintaining a flexible exchange rate aligned with market conditions.
To support credit institutions in meeting economic growth needs, the SBV issued a document on December 30, 2024, announcing the 2025 credit growth targets and principles for proactive implementation.
With inflation under control and in line with National Assembly and Government targets, and following Government and Prime Minister directives, the SBV adjusted credit growth limits on July 31, 2025, ensuring transparency and proactiveness. This adjustment was initiated by the SBV without requiring requests from credit institutions.
As a result of these measures, credit growth in 2025 has consistently outpaced 2024, with a 13.37% increase by September 29, 2025, compared to year-end 2024. Credit has focused on production and business sectors, particularly priority areas and growth drivers aligned with Government policies.
Looking ahead, the Deputy Governor noted that the global economy faces continued challenges and risks, requiring agile and timely policy responses. The SBV will maintain proactive and effective monetary policy, coordinating with fiscal and other macroeconomic policies to control inflation, stabilize the economy, and support growth in line with national development goals.
Key focus areas include: First, flexibly managing monetary policy tools to balance exchange rates and interest rates, supporting production and growth while maintaining macroeconomic stability. Second, continuing flexible exchange rate management and market intervention when necessary. Third, directing credit institutions to reduce costs and enhance digital transformation to lower lending rates. Fourth, aligning credit management with macroeconomic conditions to meet economic capital needs. Fifth, collaborating with ministries to address policy challenges and improve access to bank credit for businesses and individuals.
Quang Hưng
ACB Set to Launch Exclusive Branded Gold Bars
On October 1, 2025, Asia Commercial Bank (HOSE: ACB) published its “Terms and Conditions for Buying and Selling Gold Bullion” on the ACB website, in compliance with Clause 8, Article 1 of Decree 232/2025, which amends and supplements Clause 4, Article 12 of Decree 24/2012. This regulation mandates that enterprises and credit institutions engaged in the buying and selling of gold bullion must publicly disclose customer rights and obligations on their electronic information pages or at their transaction headquarters.
Central Bank Digital Currency: Viettel, MobiFone Tasked with Pre-Technical Research, Having Prepared for Years as Industry Leaders
Vietnam is racing to develop its central bank digital currency (CBDC), with major industry players actively participating in the initiative.