1. Principles for Selecting Land for Construction
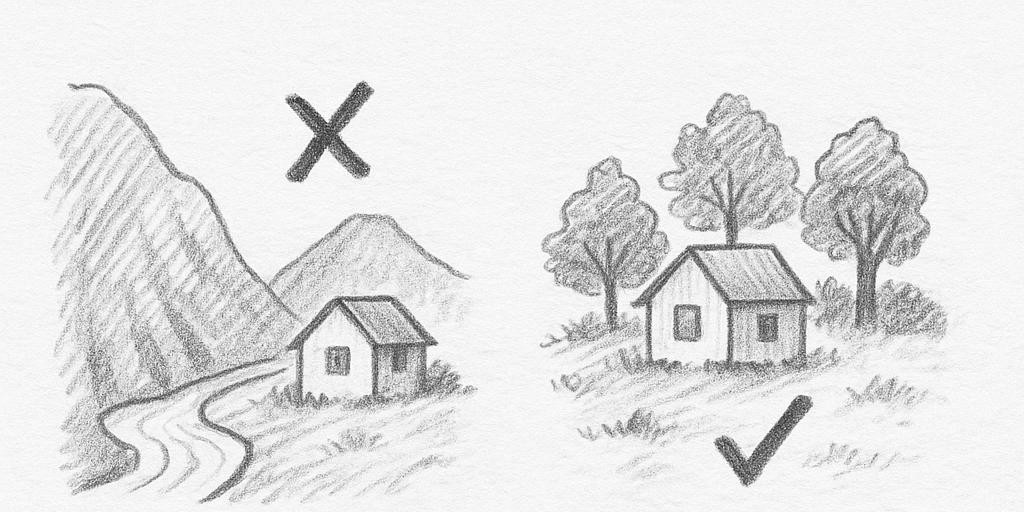
Avoid building homes at the base of mountains (especially on cleared slopes) and too close to rivers or streams.
– Steer clear of steep slopes: Avoid constructing homes on slopes exceeding 25–30°. Soil and rocks can easily slide during heavy rainfall.
– Maintain distance from streams: Flash floods can sweep away structures. Keep at least 15–50 meters from stream edges.
– Shun weak, weathered soil: Loose, cracked soil with underground cavities poses a high risk of collapse.
– Prioritize areas with natural cover: Forests and mature trees help stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
– Opt for gentle slopes (<15°) or elevated grounds: These ensure natural drainage and greater safety.
2. External Preventive Measures
– Risk zoning maps: Identify red zones (high-risk, no construction), yellow zones (construction with precautions), and green zones (safe for building).
– Erosion-control vegetation: Plant deep-rooted species like Vetiver grass, bamboo, and acacia to stabilize soil.
– Drainage trenches: Channel rainwater away to prevent saturation and slope instability.
– Early warning systems: Install loudspeakers, warning signs, and rain gauges for timely evacuation.
– Community flood shelters: Construct multi-story reinforced concrete buildings with open ground floors for floodwater passage and upper floors for safe refuge.
3. Safe Construction Solutions
a. Foundations and Footings
– Terraced leveling: Avoid cutting across slopes; use stepped grading instead.
– Retaining walls and gabions: Stabilize soil while ensuring proper drainage through these structures.
– Deep, secure footings: Anchor foundations into bedrock for maximum stability.
– Flood-prone areas: Use pile or elevated foundations to keep structures above water levels.
b. Recommended House Designs
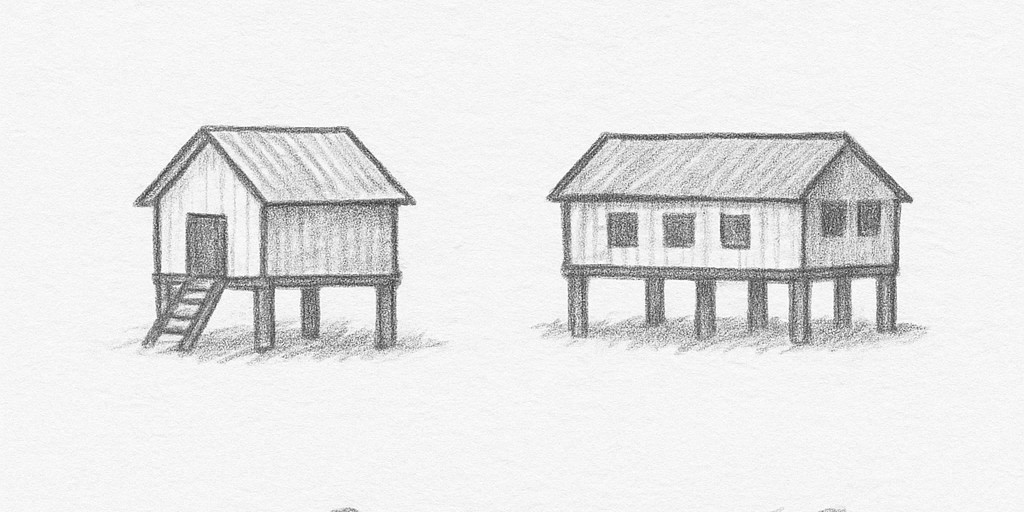
In flood-prone regions, stilt houses are ideal; villages should include at least one robust stilt structure for disaster shelter and community activities.
– Stilt houses (1.5–2.5 meters above ground): Prevent flood damage, improve ventilation, resist mold, preserve cultural practices, and utilize underfloor space.
– Lightweight framed structures: Minimize damage during landslides.
– Community centers: Multi-story reinforced concrete buildings with open ground floors and upper levels for shelter and communal use. (See Illustration 2)
c. Village Layout Strategies
– Avoid obstructing natural water flow with buildings.
– Align homes along mountain contours, parallel to elevation lines.
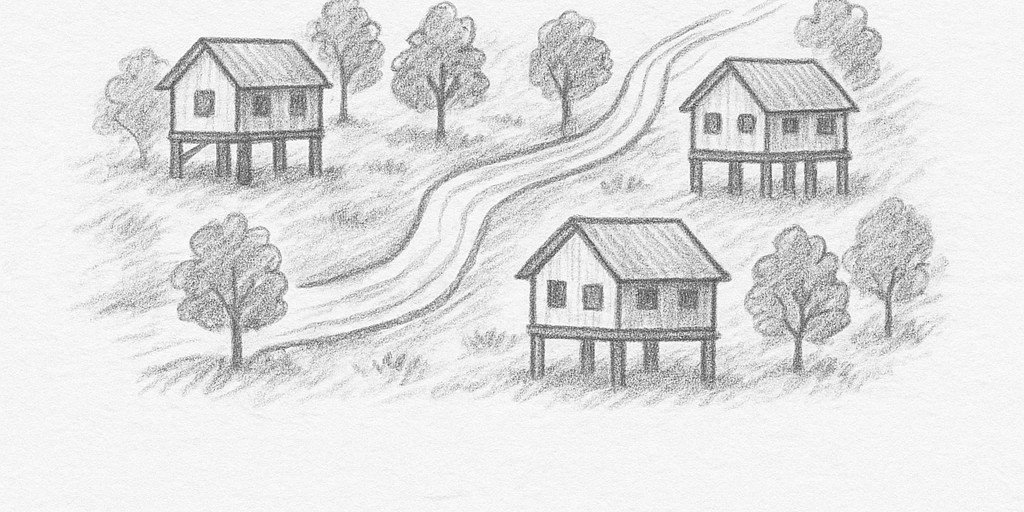
Space homes adequately to prevent water flow obstruction during floods.















