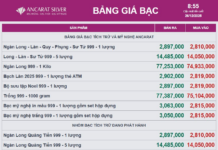
On October 28, Hanoi People’s Committee Chairman Tran Sy Thanh issued a directive on the development of the city’s 2026-2030 socio-economic plan, setting a target of an average GRDP growth rate exceeding 11%.
The directive emphasizes that the plan’s formulation must ensure continuity, practicality, consistency, and feasibility, while closely aligning with central policies, particularly the upcoming Resolution of the 18th Congress of the Hanoi Party Committee (2025-2030 term).
Strengthening Growth Foundations
Agencies are required to comprehensively assess the implementation of the 2021-2025 socio-economic development plan, focusing on analyzing favorable conditions, challenges, achievements, and limitations.
Reports should clarify growth rate and quality, macroeconomic stability, investment capital efficiency (ICOR), labor productivity, total factor productivity (TFP), budget revenue and expenditure, and the implementation of the city’s special mechanisms and policies.
Specifically, Hanoi requests an in-depth analysis of the implementation of Central Conclusion No. 123-KL/TW and Government Resolution No. 226/NQ-CP, targeting a national growth rate of 8.3-8.5% by 2025.
Additionally, agencies must evaluate the dual goals of COVID-19 prevention and economic recovery, as well as the implementation of the Government’s Socio-Economic Recovery and Development Program.

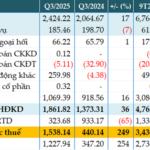
Hanoi People’s Committee is developing a plan to achieve an average GRDP growth rate exceeding 11% for the 2026-2030 period. Photo: Trong Phu |
A key focus is evaluating economic restructuring linked to growth model innovation. Hanoi aims to develop high-tech industries, smart manufacturing, clean agriculture, eco-tourism, and e-commerce.
The city also requires assessing the implementation of Resolution No. 68-NQ/TW on private economic development, promoting green and circular economies, and the contribution of the digital economy to GRDP.
This includes perfecting the socialist-oriented market economy, establishing legal frameworks for emerging fields like science-technology, digital transformation, education, healthcare, energy security, capital markets, and labor.
Hanoi mandates a thorough evaluation of strategic infrastructure development, including ring roads, urban railways, science-technology infrastructure, telecommunications, digital infrastructure, irrigation, and rural infrastructure.
Regarding human resources, agencies must report on the implementation of resolutions on breakthroughs in science, technology, innovation, and national digital transformation (Resolutions 57-NQ/TW, 193/2025/QH15, and 71/NQ-CP).
They should also clarify the implementation of central resolutions on comprehensive education reform, e-government, digital society, and digital citizenship.
Striving for Over 11% Growth
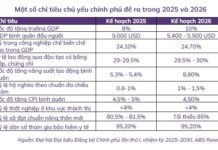
For the 2026-2030 period, Hanoi aims for an average GRDP growth rate exceeding 11%, with increased per capita income and labor productivity.
The city targets maximizing social resources, boosting public investment, developing the private sector, and attracting foreign investment.
To achieve these goals, Hanoi outlines 10 key tasks and solutions:
First, enhancing legal reform, governance efficiency, and a law-abiding culture. The city aims to reduce administrative procedures, shift from ex-ante to ex-post checks, and lower costs for citizens and businesses.
Second, establishing a new growth model, promoting industrialization and modernization through science, innovation, and digital transformation. The city focuses on resolving bottlenecks in capital, labor, and land markets, and restructuring weak credit institutions.
Third, developing the private sector as a growth driver. Hanoi will implement Party and Government resolutions, fostering regional and global private conglomerates, and supporting small businesses and households.
Fourth, advancing science, technology, innovation, and national digital transformation, investing in digital infrastructure, AI, data technology, sharing economy, e-commerce, and smart manufacturing.
Fifth, improving human resource quality through education reform, STEM, digital skills, entrepreneurship, and English as a second language in schools.
Sixth, developing modern, synchronized infrastructure, prioritizing urban railways, ring roads, science-innovation infrastructure, and digital infrastructure.
Seventh, enhancing culture, society, and living standards, implementing the 2025-2035 National Cultural Development Program, and social welfare policies.
Eighth, managing resources efficiently, promoting green and circular economies, climate adaptation, disaster mitigation, and waste recycling.
Ninth, strengthening defense, security, and social order, building a modern, elite military force.
Tenth, enhancing international integration, focusing on economic and technological diplomacy, and implementing Party resolutions on foreign affairs.
The directive assigns tasks to relevant departments for drafting plans, consulting experts, and finalizing the plan for submission to the Party Committee and People’s Council in early 2026.
TRONG PHU
– 09:00 29/10/2025
OneShop Launches: A New Milestone in the Digital Transformation of Vietnamese Small Businesses
OneShop, the brainchild of One Mount Group, builds upon the legacy of VinShop to create a comprehensive digital commerce platform. Its mission is to empower millions of Vietnamese small businesses, propelling them into the modern retail era.
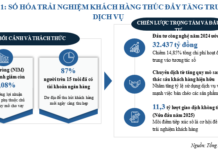
MSB: System Security as the Foundation for Innovation and Growth
In the digital age, data has become a cornerstone asset for organizations, with security emerging as the linchpin of customer trust. Against this backdrop, Maritime Bank (MSB) is committed to crafting a secure digital ecosystem, prioritizing information security, data protection, and a seamless digital experience as the pillars of its long-term growth strategy.
Over 5 Million Household Businesses to Halt Lump-Sum Tax Payments Starting 2026
The implementation of electronic invoices, transparent supply chains, and the elimination of lump-sum tax from January 1, 2026, presents a critical challenge for business management capabilities. This shift demands that all business households adapt and evolve to meet the new requirements.