Huawei’s latest smartphones showcase a significant shift towards domestic components, with nearly 60% of their value sourced from China, according to a recent teardown analysis. This marks a substantial advancement in the production of central processors and memory chips, despite ongoing U.S. export restrictions.
In collaboration with Japanese teardown specialist Fomalhaut Techno Solutions, Nikkei dissected two of Huawei’s flagship models—the Mate 70 Pro (2024) and Pura 80 Pro (early 2024)—to evaluate component costs. The analysis reveals a strategic localization of supply chains, with the Mate 70 Pro boasting 57% domestically sourced components by value. The Pura 80 Pro, estimated at $380 in total component costs, maintains a similar 57% domestic sourcing rate.
This trend contrasts sharply with earlier models: Huawei’s 2020 equivalents relied on just 19% domestic components, rising to 32% in 2023. Meanwhile, reliance on parts from Japan, the U.S., and South Korea has plummeted by over 20 percentage points between 2023 and 2024.
The teardown highlights Huawei’s focus on high-value domestic components, particularly CPUs and memory, as a direct response to U.S. trade restrictions imposed in 2019 under the Trump administration. These measures barred U.S. firms from supplying critical hardware and software to Huawei.
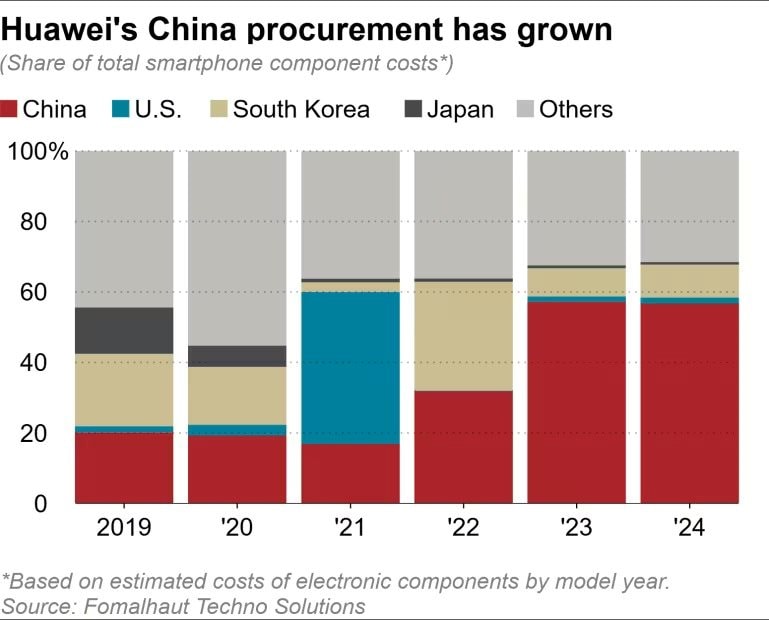
Huawei’s domestic component ratio in smartphones has surged in recent years, reflecting accelerated supply chain localization.
For the Pura 80 Pro’s multi-semiconductor chip, Huawei employed the Kirin 9020, designed by its subsidiary HiSilicon. DRAM and NAND flash memory now come from Chinese suppliers ChangXin Memory Technologies and Yangtze Memory Technologies, respectively. BOE Technology provides OLED screens, valued at over $64 per unit.
“Key components are almost entirely Chinese-made, bringing Huawei closer to full domestic production,” notes Fomalhaut CEO Minatake Kashio. However, challenges persist. Akira Minamikawa of Omdia estimates a 5-year gap in mass production capabilities, while Satoru Oyama of Grossberg highlights design-to-manufacturing hurdles for Chinese firms.
China’s government is accelerating talent acquisition by attracting domestic and foreign researchers to top universities through funded programs. According to Canada’s TechInsights, China’s semiconductor self-sufficiency reached 23.3% in 2023, up 8.4 percentage points over a decade.
Huawei Advances Sustainable Energy Ecosystem in Vietnam
On September 27th in Ho Chi Minh City, Huawei Digital Power hosted the Vietnam Installer Summit 2025, an annual large-scale event exclusively tailored for Vietnam’s solar installation community.
The iPhone Model That Could Save a Declining Smartphone Market
The foldable smartphone market is in a rut, but the launch of the iPhone foldable will be a game-changer.