Shifting Credit Flows and Capital Strengthening Opportunities
The banking sector’s most notable highlight in 2025 is the qualitative shift in credit flows. Historically, growth was often constrained by limited credit room. However, this year, the State Bank of Vietnam (SBV) set a 16% growth target from the outset and allocated credit room to banks. As of November 27, total credit growth surpassed VND 18.2 trillion, up 16.56% year-to-date, compared to 11.8% in the same period last year—a 20% increase year-over-year.
More importantly, funds are now directed to where they’re most needed. Under the regulator’s guidance, capital has flowed into manufacturing, exports, and renewable energy. Green credit and ESG standards are no longer just annual report buzzwords but integral to lending assessments. This shift not only diversifies banks’ loan portfolios and reduces real estate dependency but also opens access to affordable international capital, fostering deeper financial integration for Vietnam.
SBV data shows that by November 30, 2025, green credit outstanding reached VND 750 trillion. Average growth from 2017 to 2025 exceeded 21% annually, outpacing overall economic credit growth. Commercial banks supply 88% of green credit, primarily through green bonds and international loans. IFC data reveals Vietnam issued over USD 1.5 billion in green bonds from 2020 to 2025.
While real estate lending remains significant, it’s now more differentiated. Funds are directed toward actual housing and industrial property projects, avoiding speculative land plots, ensuring steadier, lower-risk cash flows.
Alongside capital shifts, banks are racing to adopt technology and operational models. Digital transformation now means more than mobile app services—it’s a core competitive factor for cost optimization.
AI and big data analytics in credit scoring, fraud detection, and customer service have reduced cost-to-income ratios (CIR) to 27-32%, though some banks still exceed 40%.
Robotic process automation (RPA) and eKYC enhancements minimize human error and operational costs, explaining the closure of physical branches this year.
The Open Banking and data-sharing legal framework, highlighted by the 2030 Digital Transformation Strategy launched in November 2025, enables banks to share APIs with third parties, creating a seamless financial ecosystem. AI-driven solutions now offer real-time personalized financial advice and product designs.
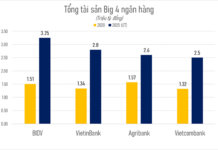
Another achievement is strengthening capital buffers and ownership transparency. The amended Law on Credit Institutions provides a robust legal framework to address cross-ownership issues. Stricter oversight of major shareholders has improved governance, ensuring bank capital serves legitimate purposes. Most listed banks maintain high CAR ratios of 11-12% (vs. the 8% requirement), aligning with Basel III standards and enhancing macro-resilience.
Foreign investment is another opportunity. The decree raising foreign ownership limits to 49% in banks acquiring weak institutions (from 30%) bolsters capital and strategic expertise.
Latent Risks: Bad Debt and Cybersecurity
Despite progress, 2025’s banking landscape faces risks. Bad debt remains the biggest challenge. While on-balance-sheet NPLs are controlled, asset quality is questionable.
Restructured loans maturing post-Circular 02’s expiry on December 31, 2024, and uneven real estate recovery have inflated latent NPLs. Third-quarter 2025 reports from 27 banks show NPLs at VND 44 trillion, with ratios rising from 1.94% to 2.01% (down from 2.05% in Q2) due to expanded credit.
NPLs are increasingly classified as loss-provisioned (Group 5), accounting for 55%, while substandard (Group 3) and doubtful (Group 4) debts make up 19% and 26%, respectively.
Smaller banks face profit erosion from provisioning costs. Legal hurdles and illiquid markets slow NPL resolution, despite the amended Law on Credit Institutions effective October 15, 2025, which strengthens the legal framework for NPL and collateral handling.
Net interest margins (NIM) are also under pressure. Banks must balance competitive deposit rates with lower lending rates to support the economy, squeezing profitability. This pushes banks toward fee-based income and forex services, creating a divide between large banks with cheap CASA funding and smaller banks with higher costs.
Cybersecurity risks escalate with digitalization. Deepfake scams and supply chain attacks targeting users and third parties in 2025 challenge customer trust, forcing banks to balance security and user experience.
For 2025 to set the stage for 2026, banks must address these bottlenecks. Those balancing growth, risk management, digital optimization, and diversified revenue will lead in the next economic phase.
– 07:59 31/12/2025
Prime Minister Highlights 8 Outstanding Achievements of the Banking Sector in Recent Times
On the morning of December 31st, in Hanoi, Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh attended and directed the conference summarizing the year 2025 and the term 2021-2025, while also outlining the banking sector’s tasks for 2026.
Hai Phong Port Targets Pre-Tax Profit of Over VND 1.5 Trillion by 2026
On the morning of December 30th, Hai Phong Port Joint Stock Company (UPCoM: PHP) held an expanded meeting of its Party Executive Committee to review the work of 2025 and outline tasks for 2026. The company is entering a new phase of development, focusing on deep-water ports and comprehensive digital transformation.
SHB and Thanh Nhàn Hospital Sign Comprehensive Partnership Agreement
Through its comprehensive partnership with Thanh Nhàn Hospital, SHB remains steadfast in its commitment to supporting administrative units. As a pioneering bank, SHB delivers cutting-edge financial solutions, drives digital transformation, and enhances operational efficiency. Together, we strive for the sustainable development of the healthcare sector and the well-being of our community.
Telecom Giants Emerge as Cambodia’s Special Envoys in the Digital Age
From its humble beginnings as a newcomer in a well-established market, Viettel Cambodia (Metfone) has orchestrated a remarkable turnaround, emerging as the leading telecommunications provider in the Kingdom of Cambodia. Beyond its economic success, the brand is now celebrated as a unique “digital bridge” fostering diplomatic ties between Vietnam and Cambodia.