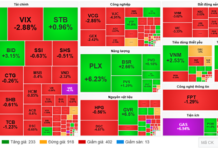
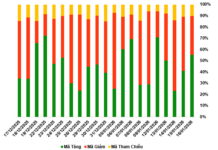
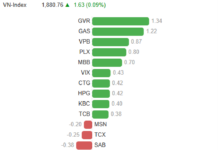
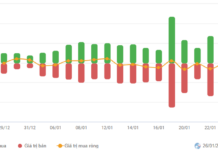
Under Article 25, Section 7 of the 2025 Tax Administration Law (Law No. 108/2025/QH15), detailed provisions are outlined regarding tax assessment for exported and imported goods.
1. Cases where customs authorities assess taxes on exported and imported goods:
a) Taxpayers rely on illegal documents, data, or records to declare or calculate taxes; fail to declare taxes or inaccurately, incompletely, or dishonestly declare information related to tax obligations;
b) Beyond the legal deadlines stipulated by customs laws, related regulations, or written requests from customs authorities, taxpayers fail to provide, refuse, or delay the submission of records, accounting books, documents, data, or figures necessary for accurately determining taxable amounts, exemptions, reductions, refunds, non-collection, or non-taxable status;
c) Taxpayers fail to provide evidence or explanations, or exceed the prescribed deadlines without justifying matters related to determining tax obligations as required by law;
d) Taxpayers fail to record or inaccurately, dishonestly, or incompletely record data in accounting books, records, documents, or data used to determine tax obligations;
e) Customs authorities have sufficient evidence to confirm that declared values, codes, or origins of goods do not match reality, impacting taxable amounts or incentives;
f) Transactions are executed inconsistently with their economic substance or actual occurrences, affecting taxable amounts, exemptions, reductions, refunds, non-collection, or non-taxable status; g) Taxpayers are unable to self-calculate their taxable amounts;
h) Taxpayers fail to comply with customs inspection decisions; i) Other cases identified by customs or other authorities where tax declarations or calculations violate legal provisions.
According to the 2025 Tax Administration Law, customs authorities determine taxable amounts based on: actual exported or imported goods; tax bases and calculation methods; tax and trade databases; customs records; accounting documents, books, records, data, inspection results, conclusions from competent authorities, or court rulings with legal effect, and other relevant information related to exported or imported goods.
Additionally, the Government specifies detailed provisions for clauses 1 and 2 of this Article, including: tax assessment methods; competent authorities and procedures for tax assessment; and the responsibilities of taxpayers, tax declarants, and customs authorities in the tax assessment process.
Proposed Regulation: Sole Proprietors Must Declare All Business and Production-Related Accounts
The Ministry of Finance is seeking public input on a draft decree regarding tax declaration, calculation, deduction, and the use of electronic invoices for business households and individual entrepreneurs.