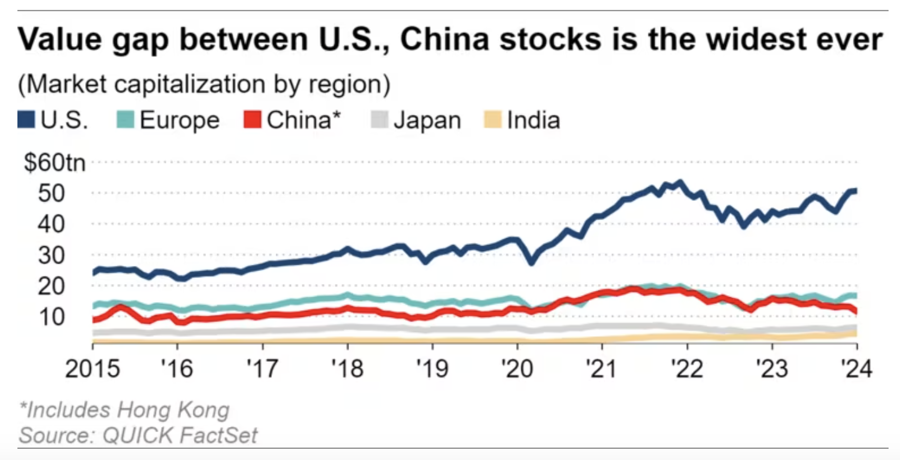
The Nikkei Asia newspaper quoted data from financial data provider FactSet as saying that the mainland China and Hong Kong stock markets have lost about $1.7 trillion in market capitalization since the end of 2023. As a result of this decline, the proportion of Chinese stocks in the global stock market’s total market capitalization in USD has dropped to about 10%, half of the peak of 20% set in 2015 when investors expected the world’s second-largest economy to accelerate.
Meanwhile, the total market capitalization of the US stock market has increased by $1.4 trillion from the end of last year to reach $51 trillion. The proportion of the US market capitalization in the global stock market as a result reached 48.1%, the highest since September 2003. The gap in the market capitalization proportion between the US and China in the global stock market has thus reached its highest level since this data began to be recorded in 2001.
The growth disparity mainly reflects the opposite fortunes of the largest technology companies in the US and China.
The US e-commerce “empire” Amazon and Meta – the parent company of the world’s largest social network Facebook – have seen their market capitalization grow by a total of $510 billion since the end of last year, partly due to more optimistic Q4 2023 financial reports than previous forecasts that these companies announced last week.
Meanwhile, China’s leading e-commerce company Alibaba and its leading game and social media company Tencent have seen a total of $31 billion in market capitalization “evaporate” over the same period.
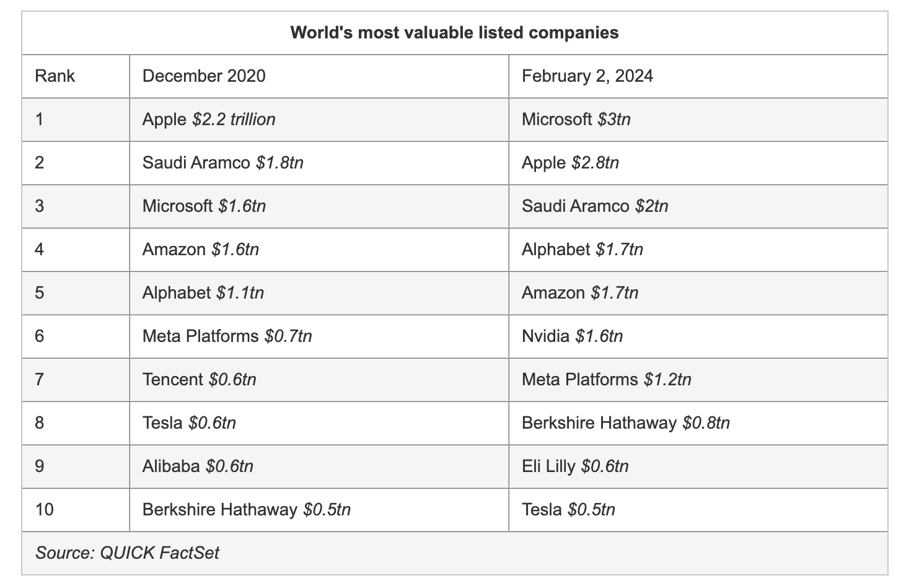
As of last Friday, among the top 500 companies in terms of market capitalization in the world, there were 236 US companies, an increase of 15% compared to three years ago. In contrast, China has 35 companies on this list, a decrease of 60% over the same period. The Baidu search engine, e-commerce company JD.com, and electric car manufacturer Nio are among the Chinese companies no longer on this list.
At the end of 2020, both Tencent and Alibaba were among the top 10 largest companies in the world in terms of market capitalization, closely chasing US companies. These Chinese technology giants had built a position as leading platforms in the market of 1.4 billion people. The high expectations for the growth of Chinese technology companies at that time had driven global investors to buy shares of these companies.
However, in recent years, Chinese technology companies have struggled noticeably. The disappointing recovery of the Chinese economy after the Covid-19 pandemic has forced the country’s leading technology companies to reconsider their expansion plans. For example, Alibaba is reportedly considering selling part of its consumer business, including grocery stores. If implemented, this will be a strategic shift for a company that has had strong expansion years transitioning from online business to traditional retail.
On the other hand, the impressive growth momentum despite the high interest rates of the US economy has strengthened the position of US technology companies. Recently, Alphabet – the parent company of the world’s largest online search engine Google – reported record revenue and net profit in Q4 thanks to strong growth in online advertising. The US’s leading position in the AI race has also attracted money to be poured into US technology stocks.
The US chip company Nvidia, the world’s sixth-largest market capitalization, is dominating the almost monopoly position on chips used for AI technology. Chinese companies like Tencent have lost direct access to these chips after the US Government imposed restrictions on the sale of advanced chips to China based on national security.
China is making efforts to develop its domestic chip production sector to achieve technological self-reliance, but the US restriction on exporting chip manufacturing equipment from suppliers such as Applied Materials has hindered China’s efforts. China’s largest chip maker SMIC has lost about a quarter of its market capitalization since the beginning of this year.
In addition, the Chinese Government is also implementing a campaign to limit the influence of domestic technology companies. Late last year, regulatory agencies unexpectedly imposed restrictions on the online gaming sector once again showing the legal risks that investors face.
In Q4 2023, US asset management company Baron Capital reduced its investment in China to zero in a global growth equity fund – the first time since the fund was launched in 2012. Portfolio manager Alex Umansky of Baron emphasized that the Chinese Government’s strengthening of supervision on technology companies and increasing geopolitical tensions are worrisome issues.
With less interest in Chinese stocks, international investors are increasingly seeking opportunities in other Asian markets such as India. The number of Indian companies named in the list of the world’s top 500 companies by market capitalization has increased nearly twofold in the past 3 years to 21 companies. High expectations for population growth and income growth in India have fueled demand for shares of companies focused on the country’s domestic market, such as state-owned life insurance company Life Insurance Corp.
The return of more interest in stable companies in Japan has helped slow the decline in the market capitalization proportion of the country’s stock market in the global stock market. Toyota’s market capitalization in USD is now nearly on par with Tencent, making the Japanese automaker race for the third most valuable company in Asia after Taiwan’s chipmaker TSMC and South Korean electronics company Samsung Electronics.