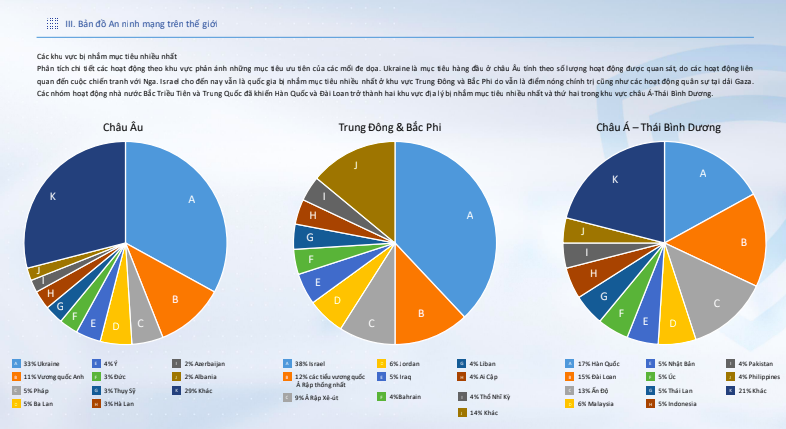
The Vietnam Cybersecurity Company (VSEC) has recently released a report on the 2023 cybersecurity overview and 2024 trends. According to the report, the global cybersecurity landscape in 2023 shows that Ukraine is the most targeted country in Europe, mainly due to its ongoing conflict with Russia.
In the Middle East and North Africa region, Israel remains the most targeted country due to political tensions and military activities in the Gaza Strip.
In the Asia-Pacific region, South Korea and Taiwan are the most targeted countries, largely because of state-sponsored hacking groups from North Korea and China.
Regarding the most targeted sectors, national-level cyber operations tend to target various sectors globally. Soft targets such as research institutions, non-governmental organizations, and universities remain the top targets, as they are considered easier to access and provide valuable information about a country’s policies, science, and technology.
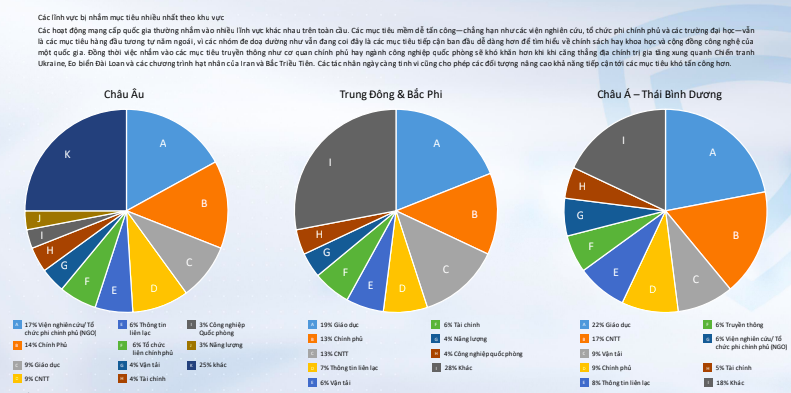
However, targeting media organizations and government agencies or defense industries has become more challenging due to increased geopolitical tensions surrounding the conflicts in Ukraine, the Taiwan Strait, and the nuclear programs of Iran and North Korea. Cyber threat actors have become more sophisticated, enabling them to target harder-to-attack objectives.
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, global damages from cyber attacks in 2023 reached approximately $8 trillion USD. This translates to $11.2 billion USD in damages per day, $466.7 million USD per hour, $7.8 million USD per minute, and $130,000 USD per second.
In addition, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected that the global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) would reach $105 trillion USD in 2023, implying that cyber attack damages would account for 8% of the world’s GDP.
The most common cyber attack methods in 2023 include identity theft, phishing, ransomware, business email compromise (BEC), and denial-of-service (DoS/DDoS) attacks.
In Vietnam, the Department of Information Security (Ministry of Information and Communications) recorded and addressed 9,503 cyber attacks targeting information systems in the country during the first nine months of 2023. These attacks included 8,168 cases of phishing, 451 cases of website defacement, and 884 cases of malware attacks.

Moreover, ransomware attacks on organizations and industrial infrastructure have nearly doubled compared to 2022. Manufacturing industries were the primary targets, accounting for over 70% of ransomware attacks, highlighting the significant impact on critical sectors.
According to a study by Cyberint, Vietnam ranked among the top 10 countries with the highest number of targets attacked by Infostealer malware in the Asia-Pacific region in 2023.
In terms of incidents, unauthorized access and privilege escalation were the most common security incidents, primarily targeting banking, financial, and insurance institutions. In 2023, VSEC monitored and recorded a total of 148,615 security incidents and identified 2,630 security vulnerabilities.
For the banking, finance, and insurance sector, unauthorized access and privilege escalation accounted for 28% of incidents, followed by web security incidents (26%), combined multiple techniques (23%), malware (8%), and phishing (7%). Denial-of-service (DoS/DDoS) attacks accounted for only 1%.
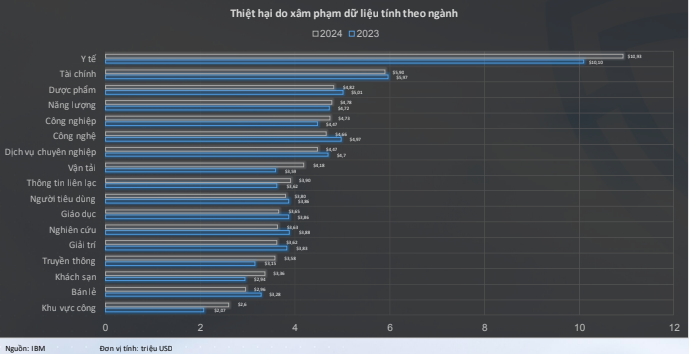
Notably, web-based attacks accounted for 62% (enterprise sector) and 59% (public sector) of incidents, while malware attacks accounted for 38% and 41%, respectively. Websites remain the primary targets for cyber attackers due to their widespread presence and accessibility on the internet.
Looking ahead to 2024, ransomware attacks and artificial intelligence-related cyber threats are expected to be the key trends. Open-source systems, IoT devices, operational technology (OT) systems, business email compromise (BEC), and cloud computing environments will be popular targets for cybercriminals.




![[Photo Essay]: Experts, Managers, and Businesses Unite to Forge a Path Towards Sustainable Green Industry](https://xe.today/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/z678592918-150x150.jpg)


![[Photo Essay]: Experts, Managers, and Businesses Unite to Forge a Path Towards Sustainable Green Industry](https://xe.today/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/z678592918-100x70.jpg)






