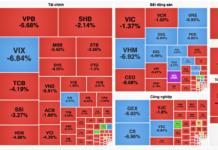
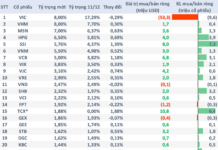
The latest report on foreign direct investment (FDI) revealed a 2% decline in global FDI inflows in 2023, totaling $1.33 trillion. However, ASEAN stood out with a record-breaking performance, marking its third consecutive year of growth. ASEAN’s FDI inflows rose by 1.2% to $226.3 billion, driven by robust economic growth and strong integration into global value chains.
Global FDI Inflows: A Tale of Volatility
According to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), global FDI inflows stood at $1.33 trillion in 2023, marking a 2% decrease from the previous year. This volatility was largely attributed to “wild swings” in a handful of European conduit economies. The introduction of a global minimum tax (GMT) for large multinational enterprises (MNEs) and a significant drop in cross-border M&As in developed markets also played a role. Excluding these conduits, the decline in global FDI inflows was more pronounced, exceeding 10% year-on-year. Developing markets, led by Developing Asia, experienced a 7% shrinkage in inflows, with the largest FDI recipient, Developing Asia, witnessing an 8% drop, as per UNCTAD’s analysis.
Despite the global downturn in foreign direct investment (FDI), ASEAN has defied the odds by achieving three consecutive years of growth, with a 1.2% increase in 2023, totaling $226.3 billion.
Asia remains a significant recipient of FDI inflows, despite a general decline. The region attracted $621 billion in investments, accounting for nearly half of global inflows. Notably, the East Asian region, encompassing China, Japan, and South Korea, experienced significant declines due to China’s economic slowdown. However, stable flows into ASEAN were maintained, buoyed by robust economic growth and strong connections within global value chains.
Within Developing Asia, China witnessed a 14% drop in inflows to $163.3 billion, while India saw a staggering 43% year-on-year plunge to $28.2 billion. In contrast, ASEAN’s inflows rose by 1.2% to $226.3 billion in 2023, although the distribution was uneven due to tight monetary policies worldwide. Singapore remained the top investment destination within ASEAN, with a 13% increase to nearly $160 billion. Vietnam also saw a smaller but notable 3.4% rise to $18.5 billion. However, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand reported declines of 15-59% year-on-year, mirroring broader global trends as economic activities slowed in response to tight monetary policies.
The United States has consistently been the largest contributor to ASEAN’s FDI inflows since 2019. In 2023, the US accounted for 32% of total inflows to ASEAN, more than double its 13% share in 2022 and surpassing the average of 12% from 2010-2019. This shift underscores the impact of rising US-China tensions, supply chain reconfigurations, and the growing emphasis on de-risking and “friend-shoring.”
Similar to the US, but on a smaller scale, Europe has also significantly increased its investment in ASEAN. Inflows from countries like Switzerland and Germany have multiplied compared to the 2010-2019 period, indicating a shift in investment patterns.
A Bright Outlook for ASEAN in the Near Future
Will ASEAN continue to attract FDI in the coming years? And will the decline in key ASEAN markets like Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand be reversed?
Economic experts are optimistic about ASEAN’s prospects, forecasting that the region will remain an attractive destination for FDI in the next 3-5 years. In 2024, the ASEAN region is expected to maintain strong economic growth, particularly in major consumer markets such as Indonesia, the Philippines, Vietnam, and Malaysia. Stable demand and improved export activities of goods and services contribute to this positive outlook.

Mr. Suan Teck Kin, Head of Research and Executive Director of Global Economics and Markets Research at UOB Group, highlighted several factors supporting ASEAN’s FDI attraction prospects:
- The signing of an MOU between Singapore and Malaysia in January 2024 to establish the Johor-Singapore Special Economic Zone (JS-SEZ) demonstrates a commitment to regional integration.
- Increased regional integration, as evidenced by the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) coming into force in 2022, substantial intra-ASEAN trade and FDI flows, and the growing adoption of cross-border payments via QR and digital channels.
- Demographic dividend: The large pool of young people in the region will contribute to economic growth as their income and wealth increase.
- Domestic political stability: Smooth power transitions in Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand after recent elections ensure policy continuity and stability in these key ASEAN members for the next 3-5 years.
Mr. Teck Kin emphasized, “ASEAN remains a unique location for companies that are progressively localizing their production capabilities as supply chains evolve to become more robust and extensive, especially in the electronics sector.”
However, the global investment landscape is also facing challenges due to geoeconomic fragmentation, with trade networks and regulatory environments diverging. This creates both obstacles and isolated opportunities, and governments and businesses must adapt to stay competitive.
Vietnam’s Rising Star
As China’s growth slows, ASEAN, and particularly Vietnam, is attracting attention as a new hub for global supply chains and investment. Vietnam is now a “gateway” to the ASEAN region, offering attractive opportunities for investors.

Vietnam has established itself as a prominent destination for foreign investment in the ASEAN region, ranking third after Indonesia and Singapore. As a vital link in global supply chains, Vietnam has become a preferred choice for corporations seeking to diversify their operations, especially in light of the “China+1” strategies adopted by many businesses.
Vietnam’s actual foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows reached a record high of $23.2 billion in 2023, surpassing the previous year’s record. Registered FDI for 2023 also increased by 32% to $36.6 billion, nearly matching the historic high of $38 billion in 2019. Vietnam is expected to maintain its attractiveness for FDI this year, as indicated by the disbursed FDI capital in the first half of 2024, which amounted to $10.8 billion, more than double the $4.6 billion in Q1 2024.
This impressive performance is a result of significant improvements in Vietnam’s infrastructure, including investments in seaports, highways, and industrial parks. Additionally, efforts to promote sustainable development through green products, coupled with investment incentive policies, interest rate reductions, tax breaks, and price stabilization, have made Vietnam one of the most attractive destinations for FDI in the region.
The positive outlook for foreign direct investment inflows is expected to continue, driving Vietnam’s growth in 2024. This is supported by optimistic projections from various financial institutions, including UOB Bank, which forecasts Vietnam’s GDP growth to remain at 6% in 2024.
The World Bank’s recent report, released on August 26, 2024, further bolsters this positive outlook. They have raised Vietnam’s economic growth forecast for 2024 to 6.1%, driven by a recovery in manufacturing and processing exports, tourism, consumption, and investments. Moreover, the World Bank predicts that Vietnam’s growth rate will reach 6.5% in both 2025 and 2026, indicating the potential for Vietnam to become the fastest-growing economy in ASEAN in the coming years.
To explore these growth opportunities further, UOB will host its annual “Gateway to ASEAN” conference on September 6th in Ho Chi Minh City. The event, themed “ASEAN: Crossroads to the World,” will bring together leaders from various departments in Vietnam and top businesses in the region. As “One Bank for ASEAN,” UOB is committed to fostering sustainable cooperation within the region and providing comprehensive financial solutions to support businesses in seizing development opportunities.
The most extensive bribery case ever in Thanh Hoa: Numerous suspects prosecuted for “Giving and Receiving Bribes”
The Provincial Security Investigation Agency (PSIA) of Thanh Hoa province announced on January 31st that it has made the decision to initiate a prosecution against 23 individuals in connection with the offenses of “Accepting bribes” and “Giving bribes” as stipulated in Article 354(3) and Article 364(2) of the Criminal Code.
Dragon Capital Chairman: “Long-term vision is needed, accepting necessary adjustments for a safer, more efficient, and higher quality market”
According to Mr. Dominic Scriven, Chairman of Dragon Capital, the role of the finance industry in the stock market will be significant in 2023 and possibly in 2024. The roles of other industries, such as real estate or consumer goods, will depend on their respective challenges.