From an economic expert’s perspective, Dr. Nguyen Minh Phong believes that the processing and manufacturing industry has yet to fully tap into its potential and meet realistic development requirements, resulting in low value-added creation. Key export products to major markets (EU and the US) face challenges in market expansion and diversification for industrial enterprises.
Additionally, the majority of Vietnam’s supporting industry enterprises are small and ultra-small in scale, leading to low technology and management levels, as well as limited human resources. This makes it challenging to meet the increasingly high demands of partners regarding standards, quality, pricing, and delivery times.
 Economist Nguyen Minh Phong
|
Citing statistics, Vietnam’s annual machinery and equipment renewal rate has only reached about 10% in the past five years, while other countries in the region renew at a rate of 15-20%. Many industrial sub-sectors have low localization rates, heavily relying on imports of raw materials, intermediate products, and production machinery and equipment. Export-oriented industries such as textiles, leather, and electronics import 60-70% of their raw materials.
“The lack of linkage between enterprises is hindering the development of the supporting industry. As a result, domestic enterprises have not deeply engaged in the ecosystem and value chain of leading enterprises and foreign-invested enterprises,” said Mr. Phong.
Notably, the industry is quite dependent on imports, and the domestic market demand is low. Moreover, most of the large corporations in Vietnam are multinational corporations, while local enterprises are limited to processing and assembly stages, not focusing on new industries or high-tech industries.
“The most significant challenge in developing the processing and manufacturing industry is that local enterprises are heavily focused on processing and transformation, dependent on FDI enterprises, lacking resources and raw materials, and overly reliant on foreign markets, especially for imported raw materials from China and South Korea,” emphasized Mr. Phong.
From a business perspective, Mr. Cao Van Hung, Director of International Market Development at Smart Vietnam Precision Mechanics Joint Stock Company, shared that alongside the new wave of relocation, his company also faced challenges in implementing and meeting the surging demand for orders from international markets such as the UK, the US, Australia, and Canada.
According to Mr. Hung, the first challenge is the lack of a highly skilled workforce. Currently, meeting market and customer demands requires a large workforce, especially those directly involved in production.
Additionally, foreign partners have very high standards, requiring enterprises to connect with relevant parties to create a complete product. However, finding units with the same export-oriented mindset and meeting high export standards is challenging.

Mr. Cao Van Hung – Director of International Market Development, Smart Vietnam
|
Pointing out the obstacles faced by processing and manufacturing enterprises in general and Smart, in particular, Mr. Hung attributed them to objective factors such as geo-political tensions and increasing competition between major powers. At the same time, the recovery of major trading partners has been slow.
Additionally, Vietnamese enterprises lack internal strength and are hungry for information about markets, customers, and policies, which creates difficulties for many businesses.
Regarding subjective reasons, Mr. Hung observed that Vietnamese enterprises are not proactive enough in exploring and directly connecting with partners and customers in international markets. As a result, obtaining an order takes a considerable amount of time, and involving a third party to find customers can reduce profits.
Notably, enterprises lack a clear direction and are primarily focused on the Vietnamese market, lacking the ambition to expand globally.
Discussing solutions, Mr. Hung emphasized that to enhance their position and competitiveness, Vietnamese enterprises need to directly explore markets and listen to partner feedback, enabling them to improve their products and capture markets.
It is crucial for enterprises to have mechanisms in place to invest in human resources early on and offer attractive material and spiritual incentives to employees, especially those with high-level skills. This investment in human capital will create a competitive advantage in the context of integration.
In terms of policies, Mr. Hung suggested that the government, ministries, sectors, and associations should provide more support to enterprises in exporting goods to demanding markets. They can do this by regularly organizing workshops, forums, and exhibitions to help enterprises stay updated on market information, partners, and new business opportunities.
Sharing his perspective, Dr. Nguyen Minh Phong believed that in the future, the economy and industrial production would face numerous challenges. To enable industrial products, particularly those from the processing and manufacturing industry, to access demanding markets, comprehensive, effective, and feasible solutions are required, along with strong determination from the government and relevant ministries and sectors.
|
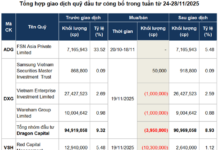
The processing and manufacturing industry is a large sector comprising eight smaller groups and sub-sectors: Chemicals, Rubber, and Plastics; Textiles, Leather, and Footwear; Food and Beverage Processing; Wood Processing; Mechanics; Electronics; Metal Production; and Building Materials Production. In 2023, the processing and manufacturing industry attracted over 23.5 billion USD in FDI, accounting for 64.2% of the total FDI registered in Vietnam, and representing a 39.3% increase compared to 2022. Following the recovery trend since the end of 2023, the added value of the entire industry in the first nine months of 2024 is estimated to increase by 8.34% compared to the same period last year. The industrial production index for the first nine months of 2024 compared to the same period last year increased in 60 localities and decreased in three localities nationwide. The consumption index of the entire processing and manufacturing industry in the first nine months of 2024 increased by 12.5% over the same period in 2023 (in the same period in 2023, it increased by 0.6%). |
Vietbank Proudly Opens New Branch in Bac Ninh
On September 26, the Vietnam Thrift Bank, more commonly known as Vietbank, inaugurated its 120th transaction office: Vietbank Bac Ninh Branch in Bac Ninh city, Bac Ninh province.
The Least Populous District in Binh Duong Province Will Have Four Urban Areas
The projected population size of Bac Tan Uyen district by 2040 is an estimated 300,000 people. This forecast highlights the potential growth and development of the area, offering a glimpse into the future of Bac Tan Uyen. With a thriving community and a vibrant economy, the district is on a trajectory to become a prominent hub in the region.