According to the General Department of Customs, in August 2025, Vietnam exported 216,649 tons of various rubber types, valued at USD 359.3 million. This marks a 5.1% increase in volume and a 7.4% rise in value compared to the previous month. Additionally, it reflects a 3.3% growth in volume and a 4.1% increase in value compared to August 2024.
In the first eight months of 2025, Vietnam’s rubber exports reached 1.11 million tons, valued at USD 1.98 billion. While volume slightly decreased by 0.6%, value surged by 12.6% year-on-year, driven by higher prices.
After hitting a one-year low last month, Vietnam’s average rubber export price in August 2025 rose by 2.2% month-on-month and 0.8% year-on-year, reaching USD 1,658 per ton.
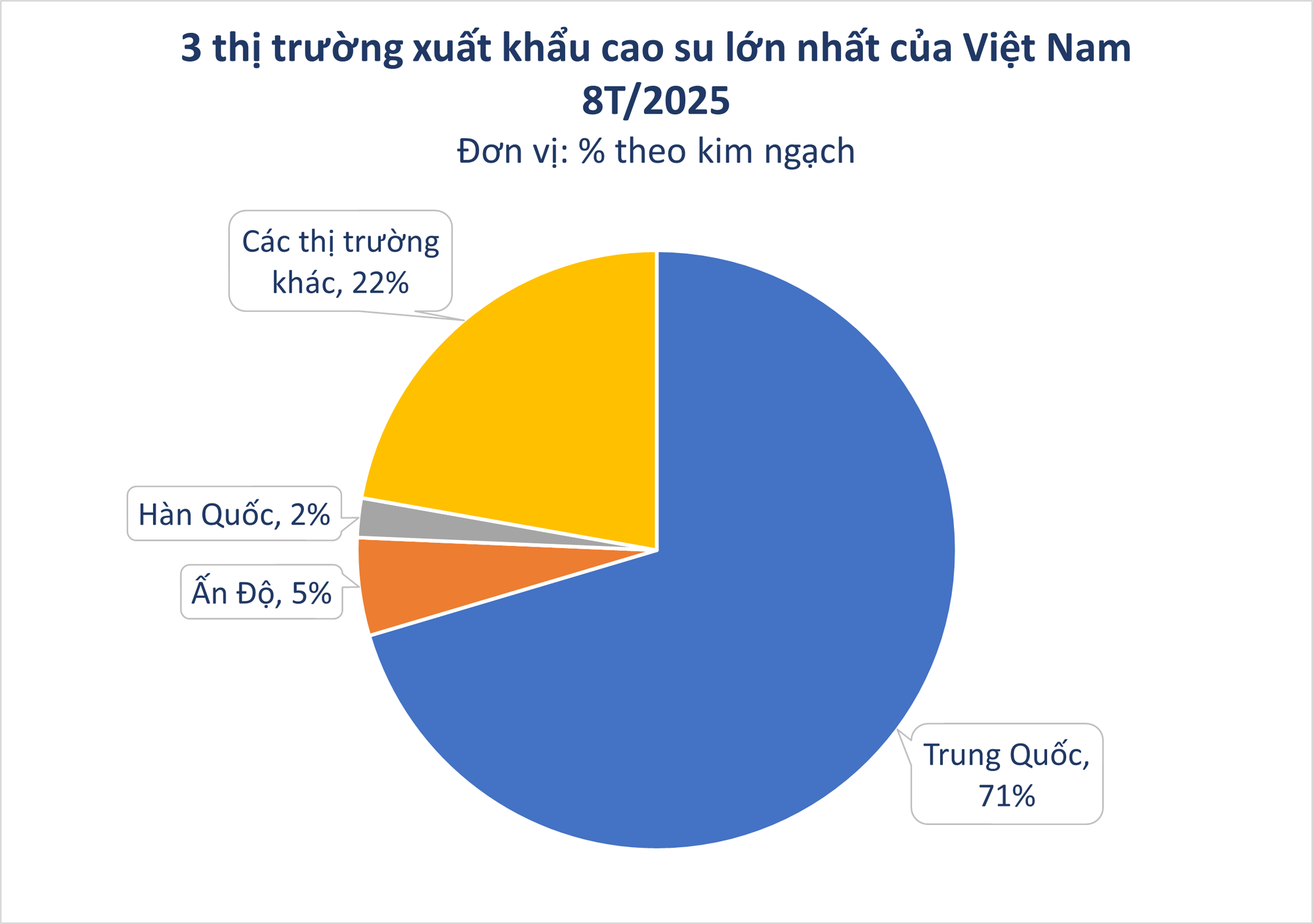
China remains Vietnam’s largest rubber export market, with 158,657 tons valued at USD 260.23 million, up 17.9% in volume and 20.7% in value compared to August 2024. In the first eight months of 2025, exports to China totaled 795,771 tons, valued at USD 1.4 billion, reflecting a 5.9% volume increase and a 22.3% value surge year-on-year. China now accounts for 71.3% of Vietnam’s total rubber exports.
India follows with 55,432 tons, a 42.5% decline year-on-year. Malaysia emerged as the third-largest market, with 30,239 tons, up 160%.
Notably, Indonesia significantly increased its rubber imports from Vietnam, reaching over 28,000 tons valued at USD 51.4 million, a 100% volume increase and a 96% value surge year-on-year. Its market share jumped from 1.3% in 2024 to 2.6% in 2025.
According to the Association of Natural Rubber Producing Countries (ANRPC), natural rubber prices fluctuated sharply in July 2025 due to trade tariffs, geopolitical tensions, and adverse weather conditions impacting production. After a period of weak demand and ample supply, concerns over supply disruptions spurred buying activity.
Meanwhile, U.S. President Donald Trump signed an executive order reducing auto import tariffs from Japan from 27.5% to 15%. South Korea is also awaiting a similar agreement to lower auto import tariffs from 25% to 15%. Auto sales could influence vehicle production and demand for rubber-based tires.
With growing demand from China and a rebound in global rubber prices, Vietnam’s rubber exports are projected to remain robust in the final months of 2025. However, increasing competition from Thailand, which is expanding its market share in China through zero-tariff export agreements, poses a significant challenge.
The Billion-Dollar Product from Vietnam: A Global Frenzy with Prices Soaring to a 2-Year High, China as its Top Patron
The export price of this commodity hit a 2-year high as of June 2022. This marks a significant peak, with prices soaring to levels not seen since 2020. This news is sure to capture the attention of investors and economists alike, as it indicates a potential shift in the market and could have far-reaching implications for the global economy. With such a dramatic rise, the question now is whether this upward trend will continue or if a correction is on the horizon.