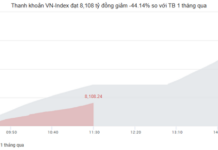
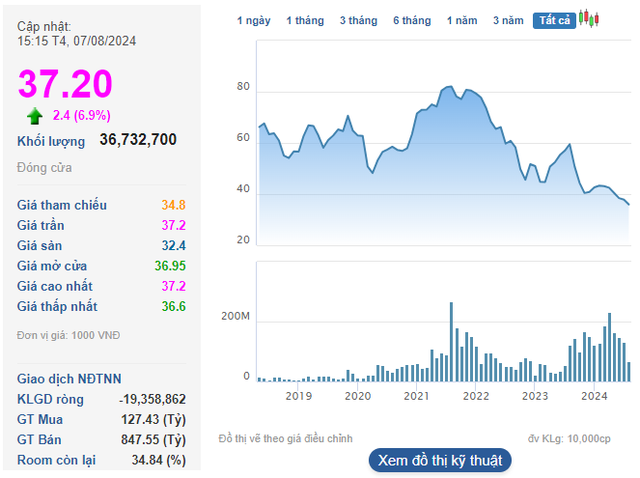
Despite FTSE’s announcement of a planned upgrade roadmap for September 2026, foreign investors continued to net sell VND 24 trillion in October. Year-to-date, foreign investors have withdrawn a record VND 125 trillion, the highest level compared to emerging markets of similar size.
In a newly released report, SGI Capital highlights that the most significant difference between Vietnam and other emerging markets is the VND’s depreciation of approximately 5% annually since early 2022. This substantial annual discount prompts foreign investors to demand more attractive valuations before committing capital.
SGI Capital notes that domestic capital inflows have also weakened, as local investors have had to absorb significant selling pressure from foreign investors while also participating in large IPO deals and new share issuances. Trading volumes have halved since the liquidity peak in August, reflecting diminished buying interest. Meanwhile, margin lending has surged to new highs, indicating strong domestic investor confidence in an uptrend.
“Margin lending spiked in Q3, doubling the 2022 peak, while the VN-Index and market capitalization rose only 10-20%. Record margin lending amid rising interest rates in a market with non-cheap valuations presents significant risks,” the report states.
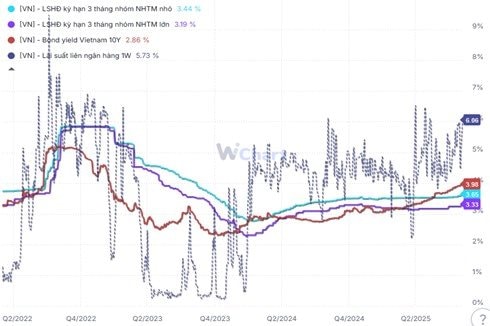
Additionally, recent surges in deposit and lending rates have begun to impact both liquidity and domestic investor sentiment, reducing buying demand and putting pressure on interest rate-sensitive sectors such as banking, securities, and real estate.
Following the recent drop below 1,600, SGI Capital believes market valuations are no longer expensive, primarily due to bank stocks trading at median levels, partially reflecting the challenges the banking sector faces. However, non-financial stocks remain overvalued, particularly large private conglomerates, whose valuations have risen far beyond reasonable levels, eroding their investment appeal.
According to SGI, the prolonged “cheap money” cycle since May 2023 is nearing its limits. Multiple indicators suggest tightening liquidity and impending interest rate hikes. In the short term, the stock market is most sensitive to interest rate trends.
The record number of new trading accounts, liquidity, and margin lending in recent times are outcomes of a prolonged low-interest-rate environment and high expectations for ambitious economic growth.
As in previous cycles, many individuals and businesses have leveraged borrowed funds and short-term capital to invest in stocks and other assets. These positions will only be exposed and forced to liquidate during significant market downturns.
“In this context, further valuation declines will create significant opportunities for long-term value investing, and we are fully prepared to capitalize on these opportunities,” SGI Capital asserts.
Key Macroeconomic Signals
Furthermore, the report highlights several recent macroeconomic signals indicating growing pressure on monetary policy and exchange rates.
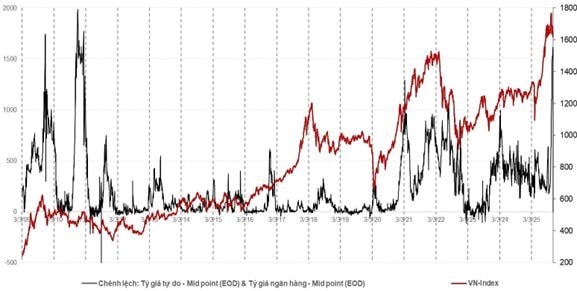
First, the unofficial exchange rate has repeatedly hit new highs, with a 6% spread against the official rate—the widest since 2011. This serves as both a warning sign and evidence of foreign currency outflows into gold, cryptocurrencies, and overseas markets. As a result, foreign reserves have fallen to just two months of import cover, below IMF standards. The State Bank of Vietnam may need to adopt more flexible VND interest rate management to stabilize the exchange rate, rather than direct USD interventions.
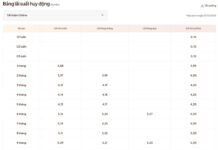
Second, foreign currency outflows have slowed bank deposit growth in Q3, while credit growth remains rapid, tightening liquidity and pushing interest rates higher. Despite record OMO injections by the central bank, systemic liquidity remains tight, sparking a deposit rate competition, particularly among private banks with high lending growth.
Third, credit growth (excluding bonds) has reached 140% of GDP, with 2025 credit growth nearing 20%—the highest since 2010—to achieve the 8% GDP growth target. This growth is primarily driven by real estate, increasing bad debt risks and interest rate pressures when the cycle reverses. Rapid credit expansion has also pushed property prices beyond affordability for many citizens.
Finally, SGI notes that accelerating GDP growth through public investment and large infrastructure projects relies heavily on external funding, rather than domestic credit, to avoid further interest rate pressures. With international borrowing costs high, Vietnam needs innovative financing solutions and institutional reforms to ensure macroeconomic stability and sustain 7% medium- to long-term growth.
Market Pulse 12/11: Green Wave Sweeps In, VN-Index Recaptures 1,630 Mark
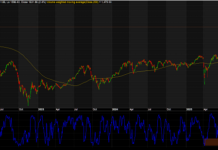
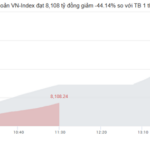
At the close of trading, the VN-Index surged by 38.25 points (+2.4%), reaching 1,631.86 points, while the HNX-Index climbed 3.71 points (+1.42%) to 264.79 points. Market breadth was overwhelmingly positive, with 361 advancing stocks versus 323 declining ones. Similarly, the VN30 basket saw a near-complete dominance of green, with 29 gainers and only 1 loser.
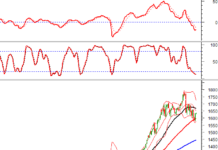
Vietstock Daily November 13, 2025: Recovery Momentum Continues
The VN-Index has surged, decisively breaking above its 100-day SMA. The Stochastic Oscillator is poised to generate a buy signal from oversold territory. Should this signal materialize in upcoming sessions, accompanied by trading volume surpassing the 20-day average, the index’s recovery prospects would be significantly strengthened.
Great News on Wages for Millions of Workers Starting Next Year
The government has mandated an increase in the regional minimum wage, ranging from 250,000 to 350,000 VND per month, effective January 1, 2026.