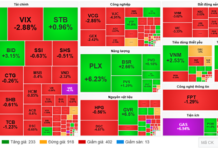
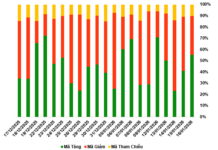
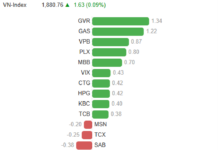
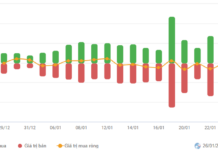
Illustrative Image
Qatar is one of the world’s leading liquefied natural gas (LNG) exporters. According to Reuters, the country plans to increase LNG production by 85% from the current 77 million tons per year (mtpa) of the North Field to 142 million tons by 2030, up from the previous estimate of 126 million tons.
Market experts say Qatar’s expansion plans in LNG production could help the country control nearly 25% of the global market share by 2030 and squeeze out projects from competitors, including the United States – where President Biden has temporarily halted new exports approvals.
Qatar has the advantage of being the world’s lowest-cost producer. Some market experts believe this move will impact global projects in the United States, East Africa, and elsewhere.
Fraser Carson, Global LNG Research Senior Analyst at Wood Mackenzie, said Qatar’s timing of the announcement was random. Meanwhile, other major LNG competitors are running into setbacks due to the Biden administration’s pause on LNG export approvals, Russia facing sanctions, and ongoing instability in Mozambique.
Competition between Qatar and the United States is intensifying following the European Union’s decision to reduce dependence on Russia’s gas through pipelines after the conflict with Ukraine. US gas suppliers have quickly filled the void, asserting themselves as the world’s largest LNG exporter by 2023, surpassing Qatar.
US LNG capacity will almost double over the next 4 years. However, the US has unexpectedly decided to pause approving applications for new LNG export terminals to assess the environmental impact. This move has raised concerns among gas importers that it will affect energy security in the future worldwide.
Senior LNG analyst Alex Froley at ICIS data intelligence company said that the planned expansion will lead to a more stable, lower-priced period in this decade and encourage greater acceptance of LNG by Asian buyers.
Ramesh of Rystad said, “Producing 16 million tons per year at low cost is positive for Asia and exactly what the LNG market needs to ensure a long-term future in the region.”
The global gas market will increase to 580-600 mtpa by 2030, from the current 400 mtpa, mostly driven by Asian demand. Qatar is expected to control 24-25% of that market by then.
Henning Gloystein, Director of Energy and Resources Practice at, said, “Qatar has the geographical advantage of meeting high existing demand in Northeast Asia, in China, Japan, South Korea, as well as future demand in the only growth region in South Asia, especially in India.”
Leading global energy companies, including Exxon Mobil, Shell, TotalEnergies, and ConocoPhillips, have been central to Qatar’s LNG industry for decades. Industry sources expect Qatar to continue seeking partnerships with global firms as they have a lot of LNG volumes to sell. Some sources forecast Woodside’s Australia project and the Lake Charles project in the US may seek partnerships with Qatar as they recently abandoned a smaller $52 billion partnership plan with Santos.
In 2023, Qatar was the fourth-largest LNG supplier to Vietnam with a production of 235,117 tons, worth over $131 million.
According to Reuters