Analyzing the VinFast VF 9’s Exterior: A Magnetic Exploration

A captivating video emerged on social media featuring a curious individual testing the exterior of the VinFast VF 9 with magnets. This unique experiment revealed the different materials used in the construction of this premium vehicle.
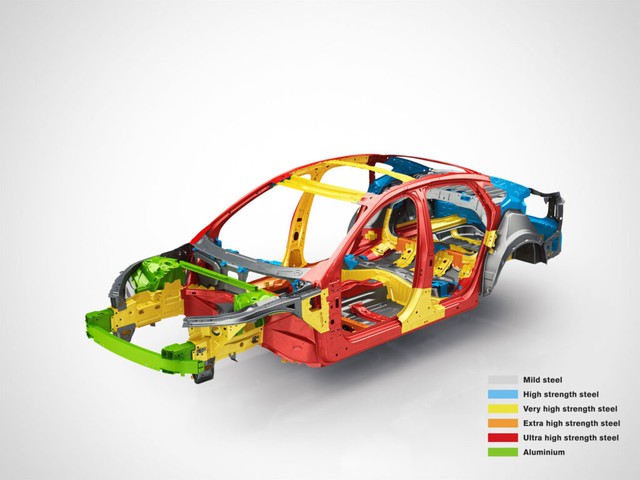
The video showcased that the front and rear wheel arches, as well as the roof, are made of steel or iron-containing alloys, while the doors, trunk, and other body panels are crafted from non-ferrous metals or alloys. Additionally, the front and rear bumpers, along with the hood, are likely made of plastic, as they did not react to the magnets.
This diverse use of materials underscores VinFast’s thoughtful engineering and cost-effective approach to manufacturing, repair costs, and, most importantly, safety. Modern automobiles are designed with varying levels of softness and hardness in different areas to optimize their performance in collision scenarios.
While plastic components often serve to absorb impact and reduce shock during accidents, the vehicle’s frame is typically constructed using stronger and more rigid materials to minimize cabin deformation.

Moving beyond traditional metals, today’s automotive industry embraces a wide range of alloys and composite materials. Steel remains the most prevalent choice, with different grades such as HSS, AHSS, and UHSS, each offering distinct strength characteristics.
Aluminum is increasingly favored for hoods, doors, and trunks due to its lightweight nature, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and handling. Additionally, technical plastics like polypropylene and ABS are go-to options for bumpers, trim, and exterior details thanks to their corrosion resistance and ease of shaping.
In the realm of premium and performance vehicles, carbon fiber and fiberglass shine for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, although they come at a higher price point. Some manufacturers are also exploring magnesium alloys and advanced composites to strike the perfect balance between weight and durability.
With sustainability at the forefront, there is a growing interest in bio-based and recycled materials, heralding a new era of eco-conscious automotive design.
| Material | Key Advantage | Limitation | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel (HSS/AHSS/UHSS) | Durable, safe, and cost-effective | Heavier than aluminum/composites | Structural components, body of standard vehicles |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, stiff (varies with alloy) | Expensive, challenging to weld | Hood, doors, premium vehicles |
| Plastic, Composite | Lightweight, inexpensive, easy to form, corrosion-resistant | Prone to deformation | Bumpers, windows, exterior trim |
| Fiberglass | Lightweight, durable, corrosion-resistant | Poor heat resistance, difficult to repair | Luxury vehicles, trim, exterior accents |
| Carbon Fiber | Extremely lightweight, exceptionally strong | Very expensive, challenging to produce and recycle | Supercars, high-performance vehicles |
| Magnesium | Ultra-lightweight | Expensive, prone to corrosion | Gearbox casings, steering components, frames |
| Bio-based Materials | Sustainable, eco-friendly | Not yet widespread, lower performance | Future applications in research |