The US stock market fell on Thursday (March 14) after officials released a report showing higher-than-expected inflation. Crude oil prices rose sharply to the highest level in 4 months after new forecasts suggested that global oil supply will be tighter than initially expected.
At close, the Dow Jones fell 137.65 points, or 0.35%, to 38,905.66. This decline ended a 3-session winning streak for the blue-chip index.
The Nasdaq fell 0.3% to 16,128.53. The S&P 500 dropped 0.29% to 5,150.48.
Stock prices faced pressure from rising yields on US treasury bonds after the US Labor Department released another report showing that inflation in the country was not decreasing as quickly as expected.
The Producer Price Index (PPI) for goods and services rose 0.6% in February from the previous month, double the predicted increase of 0.3% according to a Dow Jones survey of economists. The core PPI rose 0.3%, also higher than the expected increase of 0.2%.
The persistence of inflation raises the possibility that the US Federal Reserve will keep interest rates higher for longer. This expectation is reflected in the rising yields on US treasury bonds. A high interest rate environment is not beneficial for stocks or other assets such as gold and crude oil. Prior to the PPI report, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) report released earlier this week also showed that inflation was not decreasing as much as expected.
While Wall Street investors are still betting on the Fed beginning rate cuts in June, they believe the central bank will find it difficult to cut rates quickly and strongly due to the risk of resurgent inflation.
“The question now is whether investors will reconsider the timing of the Fed’s rate cuts. And if so, whether that change in expectations will change the upward trend of the market a lot”, said Chris Larkin, director of trading and investment at E-Trade, in an interview with CNBC.
The yield on 10-year US treasury bonds rose about 10 basis points to 4.29%. Technology stocks were the hardest hit by the rising yields. Nvidia, a chip manufacturer, saw its stock fall for the fourth time in the past 5 sessions, recording a decline of more than 3%.
“I believe the question now is whether interest rates will continue to rise, and if so, whether the market will decline further. I think the answer to both of these questions is yes”, said Thierry Wizman, chief strategist at Macquarie.
The PPI report is the last important economic data to be released before the Fed’s next regular monetary policy meeting scheduled for March 19-20.
“The concern about monetary policy has changed. In early this year, the market believed that the Fed would cut interest rates 6-8 times throughout the year. Now, the market believes the Fed will only cut interest rates 3 times this year. Inflation figures are still hot, but employment figures seem to be weak. The conflict of this data shows that the easiest thing for investors to do now is to do nothing much”, said JJ Kinahan, chairman of TastyTrade, to Reuters.
According to data from CME’s FedWatch Tool, traders are currently betting on a 59.9% chance that the Fed will start cutting interest rates in June. One week ago, the betting rate was 81.7%.
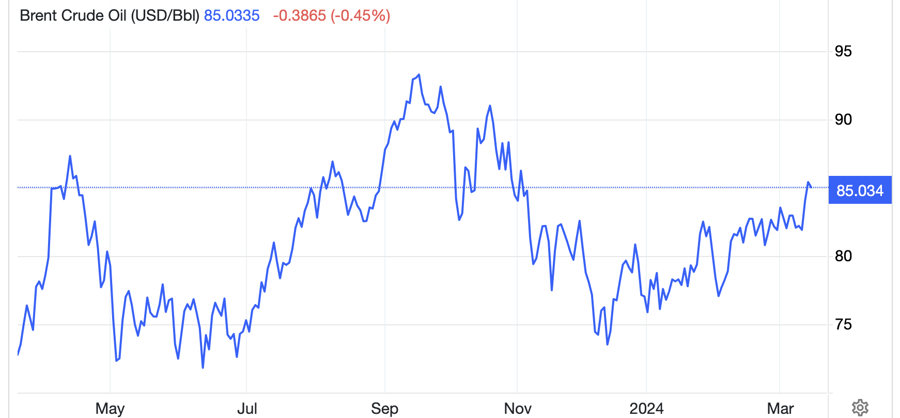
Brent crude oil futures rose $1.39/barrel, or 1.7%, to close at $85.42/barrel in London. WTI crude oil futures rose $1.54/barrel, or 1.9%, to close at $81.26/barrel in New York.
This is the highest closing price for both types of oil since the beginning of November last year. Prior to this rise, Brent and WTI oil prices both rose nearly 3% in Wednesday’s trading session.
In its monthly report on the global energy market situation and outlook, the International Energy Agency (IEA) raised its forecast for global oil demand this year. This is the fourth consecutive month since November that the IEA has raised its forecast for world oil demand in 2024, but also warned that “the deceleration of the global economy could hinder oil demand”.
The IEA forecast global oil demand to increase by 1.3 million barrels/day this year, an increase of 110,000 barrels/day from the forecast given last month. However, this forecast growth rate is still lower than the increase of 2.3 million barrels/day recorded in 2023.
In addition, the IEA lowered its forecast for global oil supply this year, stating that global oil supply will only increase by 800,000 barrels/day, reaching 102.9 million barrels/day.
“Oil consumption remains high while supply tightens. Refining margins are also very high, which is a positive factor driving crude oil demand”, commented Dennis Kissler, vice chairman of BOK Financial.
The rise in oil prices is also supported by escalating tensions in the Russia-Ukraine war, as Ukraine has recently used drones to launch attacks on major Russian refineries. The Russian Energy Ministry said the country’s seaborne exports of gasoline and diesel fell 1.5% in February from the previous month due to these attacks.
According to Kissler, the damage caused by the aforementioned attacks to Russian refineries could reduce the country’s gasoline production by more than 10%.