Tungsten is a rare transition metal, commonly used in the filaments of incandescent light bulbs. Due to its unique properties, tungsten is also an essential metal in several key industries such as machinery and tool manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, oil and gas, chemicals, medical engineering, and electricity.
According to the United States Geological Survey, Vietnam’s tungsten reserves are estimated at about 100,000 tons, ranking third in the world, after China (1.9 million tons) and Russia (400,000 tons). The Nui Phao mine in Thai Nguyen province accounts for approximately 33% of global tungsten production, excluding Chinese sources.
Nui Phao is one of the world’s largest identified tungsten mines outside of China, with 52.5 million tons of WO3 ore of average grade 0.21%. The mine is considered a safe and reliable source of tungsten for automobile and aircraft manufacturers, with no other minerals or chemicals able to substitute.
The Nui Phao mine is operated by Nui Phao Mining Company Limited – a wholly-owned subsidiary of Masan High-Tech Materials (MSR). At the 2023 Annual General Meeting, MSR’s CEO shared that the results of drill testing at the Nui Phao mine indicated that the ore reserves could be mined for an additional 12 years, as opposed to the previous estimate of 8 years in 2019.
In June 2023, Masan High-Tech Materials completed the acquisition of Chemitas, a German-based company providing warehousing, energy management, and waste management services. This strategic move allows the company to control the entire tungsten supply chain, enhance production and logistics capabilities, and align with their strategy of creating comprehensive solutions for global customers.
In 2023, Masan High-Tech Materials recorded a net revenue of VND 14,093 billion, a 9% decrease from the previous year. Tungsten revenue accounted for VND 11,422 billion, a 15% drop from 2022 due to lower sales and market demand. The company incurred a record loss of VND 1,530 billion, compared to a profit of over VND 105 billion in 2022.
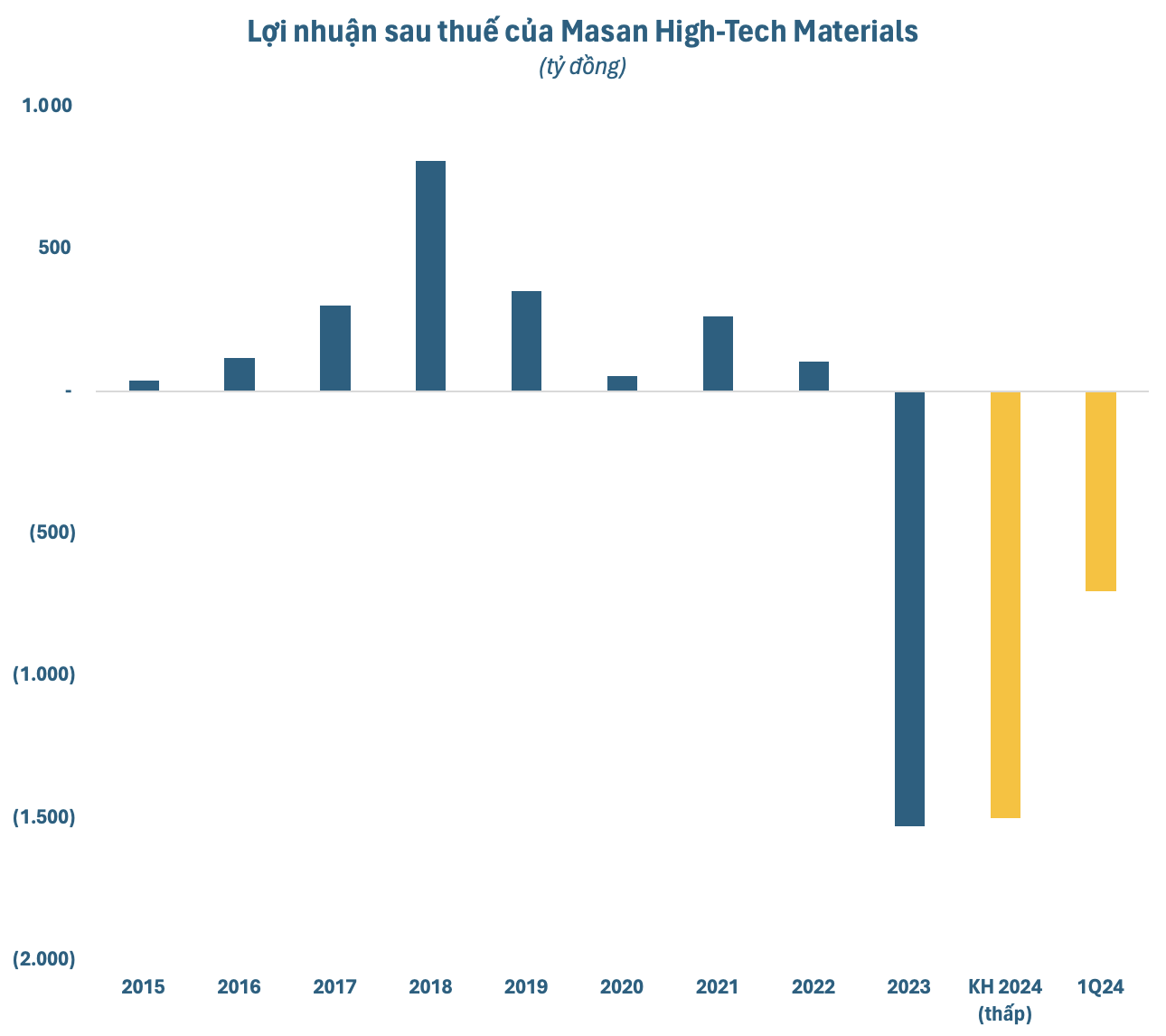
In 2024, Masan High-Tech Materials outlined two business scenarios. In a challenging environment, the company aims for a net revenue of VND 15,000 billion and a net loss of VND 1,500 billion. If conditions improve, they expect to achieve a net revenue of VND 15,800 billion and break even.
In the first quarter of 2024, Masan High-Tech Materials reported a net revenue of over VND 3,089 billion, an 18.4% decrease from the same period in 2023. Net profit after tax was negative, at over VND 702 billion, compared to a profit of VND 13.6 billion in the previous year. The net loss attributable to the company’s shareholders was VND 718 billion, a significant decrease from the first quarter of 2023.
Despite unremarkable financial performance, MSR’s stock unexpectedly soared. On May 15, the share price surged by the daily limit of nearly 15% to VND 16,900/share, the highest in seven months since mid-October last year. It is rare for MSR to reach the daily limit; the last time this occurred was almost a year ago, on May 26, 2023.
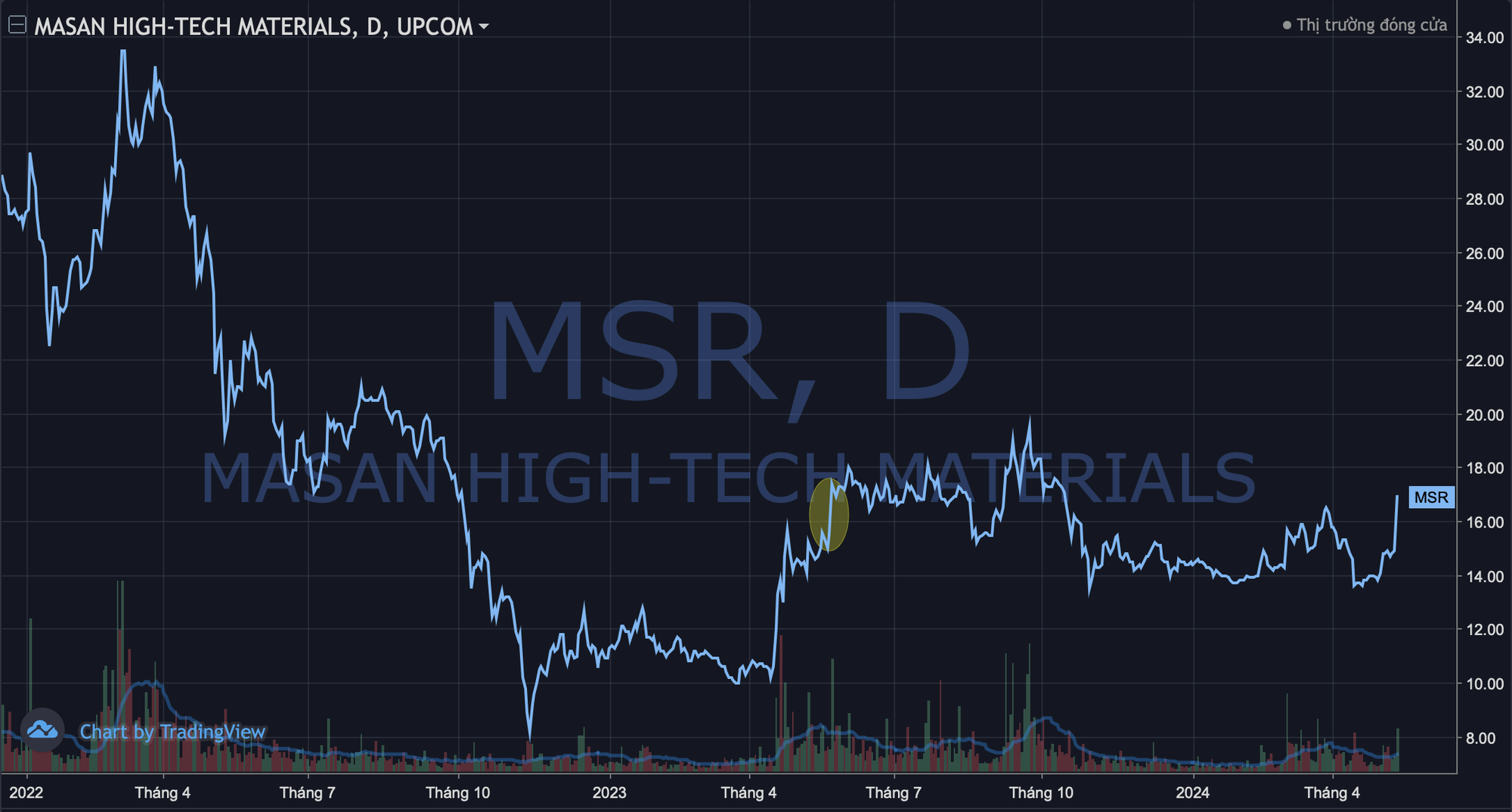
As the stock price skyrocketed, Masan High-Tech Materials’ market capitalization also surged to nearly VND 18,600 billion. This figure is only half of its peak in early March 2022 when the company entered the billion-dollar capitalization list. The current market capitalization of Masan High-Tech Materials ranks 11th on the UPCoM exchange.
The dramatic surge in MSR’s stock price on the stock market followed the company’s new move regarding the restructuring of its tungsten business. Masan High-Tech Materials has reached a framework agreement to sell 100% of H.C. Starck Holding (HCS) to Mitsubishi Materials Corporation Group (MMC).
HCS, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Masan High-Tech Materials, is a manufacturer of high-quality tungsten powder. In 2020, Masan High-Tech Materials invested in HCS with the goal of bringing tungsten refining and recycling technology to Vietnam to transition to a sustainable circular business model. Also, in the same year, MHT and MMC Group signed a cooperation agreement to establish a global tungsten value chain alliance.
However, the legal conditions in Vietnam were not yet conducive to importing tungsten scrap, hindering Masan High-Tech Materials’ plans for on-site recycling. Therefore, the company intends to divest from HCS to focus on domestic operations. This framework agreement marks another step forward in the business collaboration between the two entities.
Masan High-Tech Materials’ tungsten segment comprises two crucial facilities:
MTC plant of Masan High-Tech Materials is designed to process all the tungsten concentrate from NPMC and externally sourced raw materials containing tungsten into high-grade Ammonium Para-tungstate (APT) through chemical processing with physio-chemical refining steps and finally, the crystallization step. The APT product is then packaged for external sales or calcined to produce Blue Tungsten Oxide (BTO) and Yellow Tungsten Oxide (YTO) for external sales or further processing within Masan High-Tech Materials.
Goslar plant of H.C.Starck is designed to process tungsten intermediates produced at MTC and serves as a critical recycling facility globally for most tungsten-bearing scrap and secondary materials. The scrap is processed into premium Ammonium Paratungstate (APT) with physio-chemical refining steps and finally, the crystallization step. The APT and Tungsten Oxides produced at HCS are further processed into Tungsten Metal Powder, Tungsten Carbide Powder, and Tungsten Carbide Powder for Castings for use in related industries.