Positive Growth Signals
The ADB assessment indicates that weakening global demand and elevated global interest rates have impacted Vietnam’s growth outlook for 2023. However, a timely shift towards a supportive monetary policy and a substantial public investment program are among key measures being undertaken to sustain the growth recovery in 2023. A relatively broad-based recovery in export-oriented manufacturing, services, and continued resilience in agriculture is expected to support Vietnam’s rebound. Strong foreign direct investment (FDI) and remittance inflows, a sustained trade surplus, recovering domestic consumption, and continued fiscal stimulus—with a significant public investment program—are seen as key to driving growth in 2024.
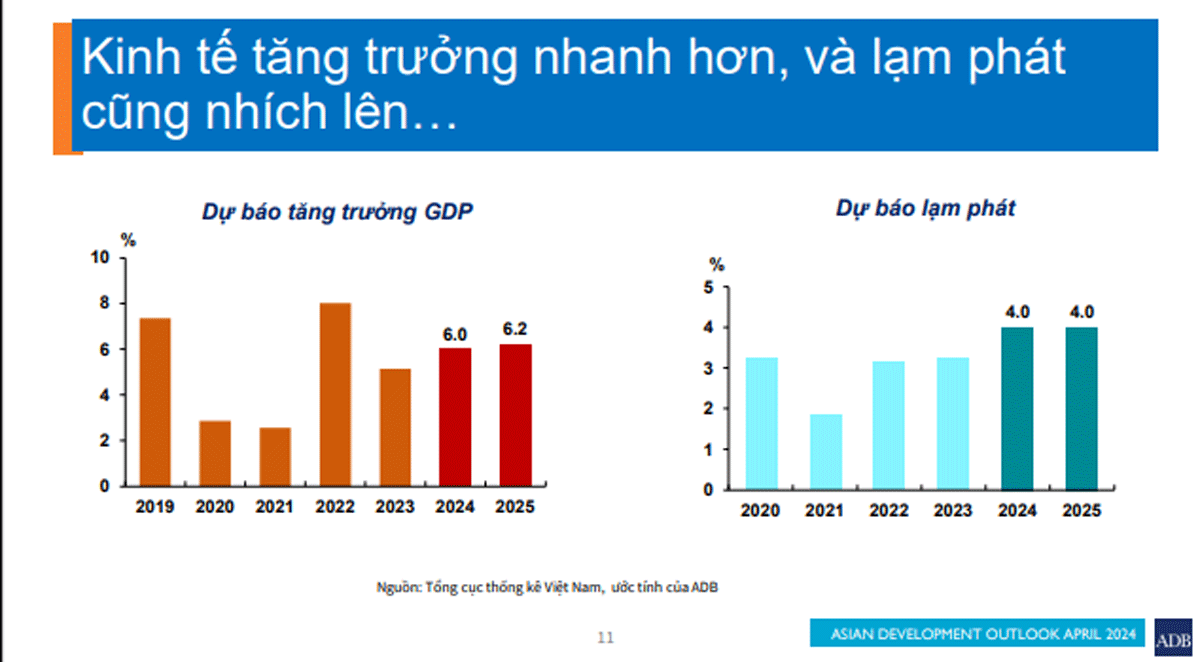
The early signal is that in the first quarter of 2024, economic growth accelerated to 5.7% year-on-year, from 3.4% in the same period last year. However, downside risks from global geopolitical uncertainties and domestic structural vulnerabilities could weigh on growth.
Vietnam’s economy grows steadily despite global headwinds. |
A gradual return of new orders and consumer spending revived manufacturing growth in late 2023, with the momentum likely to strengthen in 2024. Lower interest rates, supportive fiscal measures to boost growth, and recent improvements in the legal framework related to land will support construction. However, slowing global growth and still elevated global policy rates could weigh on export-oriented manufacturing growth.
Low domestic interest rates, supportive fiscal policy measures, and wage increases will boost consumer services in 2024. Retail sales in Q1 2024 were 8.2% higher year-on-year. The recovery in economic activity, albeit modest, will support logistics services, while a more open visa policy will boost tourism.
Monetary policy will pursue the twin goals of price stability and growth, even as policy space is limited. The expected recession in the global economy in 2024 may restrain global oil prices, easing inflationary pressures. Headline inflation moderated to 3.8% in the first quarter of 2024 from a 4.2% peak in the same period last year.
The US Federal Reserve is expected to cut interest rates in 2024, and external inflation will continue to moderate, albeit more slowly than anticipated. The Fed’s rate cuts in 2024 will help reduce pressure on the dong. However, elevated risks of non-performing loans—peaking at an estimated 4.6% of total outstanding credit by end-2023, compared with 2.0% in 2022—will dampen prospects for further monetary easing. The amended Law on Credit Institutions, effective July 1, 2024, will also strengthen oversight of lending practices.
ADB Country Director for Vietnam Shantanu Chakraborty said: “Vietnam’s economy is expected to grow at a solid pace this year and next, despite the challenging global environment.
“However, global geopolitical uncertainties and domestic structural constraints could affect this outlook. Therefore, policy responses in 2024 will need to combine near-term support for growth to bolster domestic demand with longer-term structural reforms to promote sustainable growth,” said Mr. Chakraborty.
The ADB official noted that weakening global demand due to a slower-than-anticipated recovery and delayed normalization of interest rates in the United States and other advanced economies, along with ongoing geopolitical tensions, could hamper the full recovery of Vietnam’s export-led growth in 2024. To boost growth, stronger efforts are needed to address domestic structural weaknesses such as the heavy reliance by the manufacturing sector on FDI-foreign companies, weak linkages between the manufacturing sector and the rest of the economy, an immature capital market, excessive reliance on bank credit, and complex regulatory barriers to doing business.
ADB Principal Economist Nguyen Ba Hung noted that policy space for monetary easing through further interest rate cuts is limited. Amid limited monetary policy space, fiscal spending and investment will be key to growth in 2024. The issue of low credit growth is not only due to interest rates, but because credit demand and absorption capacity are still limited and demand for consumption and investment is not yet strong. Credit will increase when demand for consumption and investment increases, but it is necessary to channel funds into real production activities. Therefore, rather than monetary policy, the ADB economists recommended additional fiscal stimulus, such as fiscal policy.

ADB Principal Economist Nguyen Ba Hung- Photo: VGP/HT
|
Accelerating Public Investment Disbursement Overcoming the Challenges
ADB Principal Economist Nguyen Ba Hung said that public investments remain a strong driver for Vietnam’s economic growth, and efficient implementation of public investments is critical for stimulating growth.
The ADB economist appreciated the government’s efforts to boost growth, including setting an ambitious 95% disbursement target this year. This is the right approach as public investment is a key engine for economic growth, not only stimulating activities related to the project but also having spillover effects and making economic activities more vibrant after the project completion.
However, the ADB official said the challenge is to make this engine work. Despite numerous measures by the government to accelerate public investment and improve implementation efficiency, there is a need for more systematic measures to improve legal and regulatory processes that reduce bottlenecks for efficient project implementation.
According to the Ministry of Planning and Investment, a 1% increase in public investment disbursement is associated with a 0.058% increase in GDP. In addition, every dong of public investment disbursed would stimulate 1.61 dong of investment from the non-state sector. However, the implementation rate against the plan remains low at around 80% over the years. Despite government efforts to address this issue, the progress has been insufficient. First, approved projects with allocated budgets are sometimes not ready for implementation, causing long delays. A systemic approach to improving project readiness could significantly increase implementation efficiency. Many projects require essential preparatory activities such as feasibility studies, land clearance arrangements, and procurement tender preparation to be conducted in parallel with project approval procedures. Projects with a high degree of readiness allow faster implementation and minimize cost overruns.
Second, projects sometimes require design or budget changes even after approval and budget allocation. This can cause long delays before project activities can commence. A major impediment to timely and quality project preparation is the complexity of regulations, especially in land use planning, land acquisition, and site clearance. This rigidity presents a significant challenge in a dynamic market environment.
Price increases due to shortages of raw materials and inputs for construction—caused by regulatory bottlenecks—result in higher costs, requiring contract renegotiation or additional funding and supplementary approvals; regulations need to be revised to allow for flexibility based on principles and fit-for-purpose adjustment as part of improving project cycle procedures. This will facilitate efficient project approval and management, adaptable to diverse situations without repeating the approval process. Enhancing the capacity of staff in charge of public investment at the provincial and local levels is also important for improving project preparation quality.
Third, weak coordination between public investment and the budget process results in delayed and insufficient budget allocation. In recent years, reports show that central agencies receive higher budget allocations than their proposals, while provinces receive less than their requirements. The pressing challenge posed by the gap between allocated budgets and assigned investment tasks often leads to funding shortages and implementation delays. The budget may not be optimally allocated to identified priority areas, resulting in suboptimal use of resources. This constrains project progress and the effectiveness of capital utilization.
The government has introduced measures to strengthen transparency, efficiency, and accountability in budget allocation and disbursement. These promote better coordination between central and local governments, prioritize projects based on impact and readiness, and implement stringent monitoring mechanisms to ensure capital is used efficiently with high performance.
However, the effectiveness of these measures seems to have been limited. The disparity in implementation capacity across government levels highlights the need to strengthen the capital allocation process and build capacity in local governments. The ongoing decentralization of public investment tasks and fiscal responsibilities has revealed weaknesses in addressing interprovincial or interregional challenges. The budget process should be adjusted to allow for flexibility, which can be more effectively managed centrally or provincially.
In 2024, public investment will continue to play a critical role in supporting the economy. Following the National Assembly’s budget approval, the Prime Minister has approved an allocation plan of VND688.5 trillion to continue building infrastructure and driving economic development. The government has introduced various policy measures to accelerate public investment disbursement and improve implementation efficiency. These include a series of resolutions and directives focusing on different aspects of public investment disbursement.